Food processing transforms raw ingredients into consumable products, enhancing flavor, safety, and shelf life. This infographic highlights key techniques such as pasteurization, fermentation, and freezing, illustrating their roles in maintaining nutritional value and preventing spoilage. Understanding these methods reveals how everyday foods are prepared and preserved for consumers.
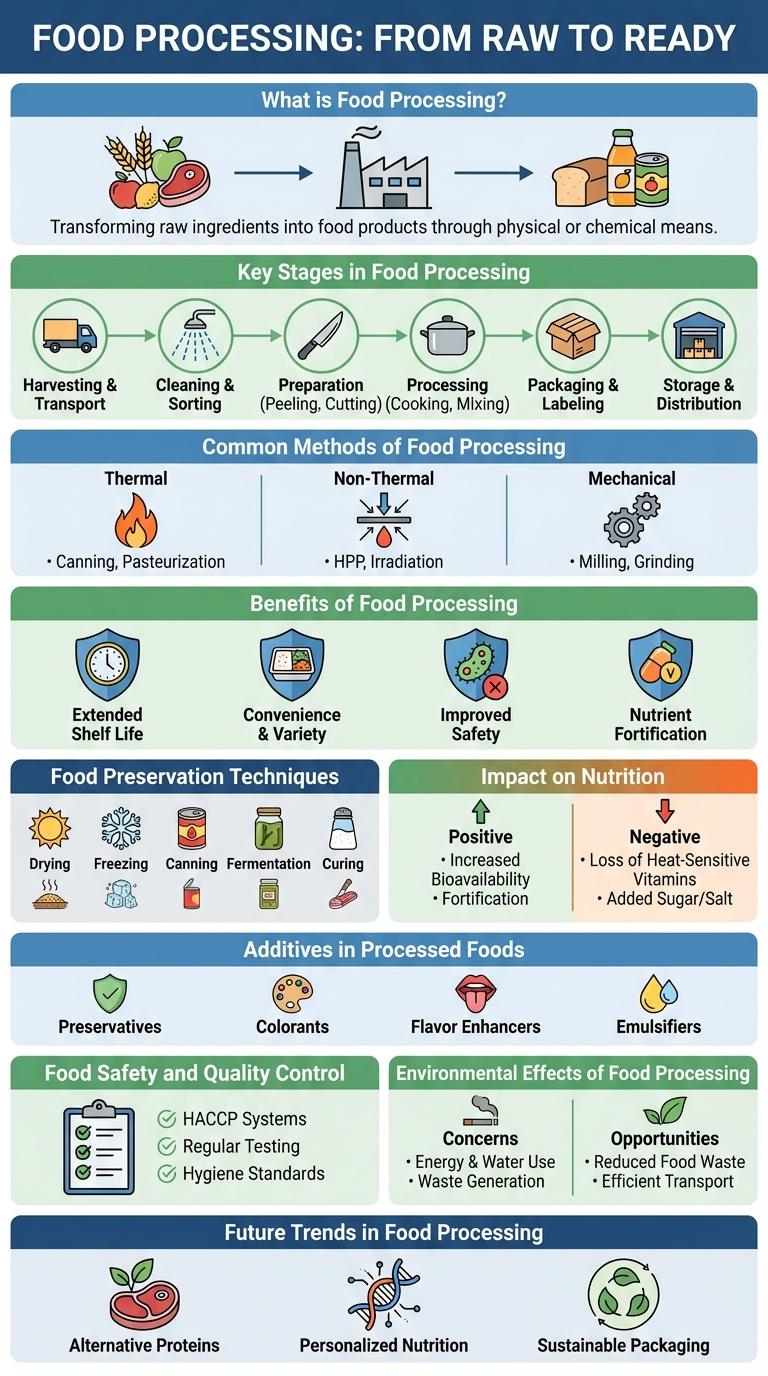
What is Food Processing?
Food processing involves the transformation of raw ingredients into consumable food products. It includes various methods such as cleaning, cooking, preserving, and packaging to enhance food safety and shelf life.
This process plays a crucial role in ensuring food quality, extending freshness, and preventing spoilage. Techniques like pasteurization, freezing, and drying are commonly used in food processing industries. Food processing also enables the creation of convenience foods and supports global food distribution.
Key Stages in Food Processing
| Key Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | Removal of dirt, debris, and contaminants from raw food materials using physical and chemical methods. |
| Sorting and Grading | Classification of food based on size, quality, and ripeness to ensure uniformity and quality control. |
| Cutting and Slicing | Shaping food into desired sizes and forms for further processing or packaging. |
| Cooking and Heat Treatment | Application of heat to enhance flavor, texture, and safety by eliminating pathogens and enzymes. |
| Packaging | Enclosing processed food in appropriate materials to protect against contamination and extend shelf life. |
Common Methods of Food Processing
Food processing involves various techniques to transform raw ingredients into safe, edible products. These methods enhance shelf life, flavor, and nutritional value while ensuring food safety.
- Heating - Applies heat through boiling, baking, or pasteurization to kill pathogens and preserve food.
- Freezing - Rapidly lowers temperature to slow microbial growth and maintain freshness.
- Drying - Removes moisture from food to inhibit bacterial growth and extend shelf life.
- Fermentation - Uses microorganisms to convert sugars into acids or alcohol, adding flavor and preservation.
- Packaging - Protects food from contamination and physical damage using materials like vacuum sealing or cans.
Benefits of Food Processing
Food processing enhances food safety by eliminating harmful bacteria and pathogens. It extends shelf life, reducing food waste and ensuring availability year-round. Processing also improves nutritional value and convenience, making food easier to store, prepare, and consume.
Food Preservation Techniques
What are the main food preservation techniques used in food processing? Food preservation techniques include methods such as refrigeration, freezing, drying, canning, and fermentation. These techniques help extend shelf life, maintain nutritional value, and prevent spoilage caused by microorganisms.
Impact on Nutrition
Food processing significantly alters the nutritional content of food, affecting vitamins, minerals, and fiber levels. Some methods, like freezing and drying, help preserve nutrients, while others, such as canning and frying, may lead to nutrient loss or the addition of unhealthy fats and sodium. Understanding these impacts guides healthier food choices and promotes balanced diets.
Additives in Processed Foods
Food processing often involves the use of additives to enhance flavor, texture, and shelf life. These substances can include preservatives, colorants, emulsifiers, and flavor enhancers.
Common additives such as sodium benzoate prevent microbial growth while artificial colors improve visual appeal. Understanding these ingredients helps consumers make informed dietary choices.
Food Safety and Quality Control
Food processing involves transforming raw ingredients into final products through various mechanical and chemical methods. Ensuring food safety and quality control is crucial to protect consumer health and maintain product standards.
Food safety protocols include hazard analysis, critical control points, and contamination prevention techniques. Quality control measures involve sensory evaluation, microbial testing, and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
Environmental Effects of Food Processing
Food processing significantly impacts the environment through resource consumption and pollution. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing sustainable food systems.
- Energy Consumption - Food processing industries use large amounts of electricity and fuel, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Water Usage - High water demand in processing leads to depletion of freshwater resources and affects local ecosystems.
- Waste Generation - Processing produces organic and plastic waste, increasing landfill burden and environmental contamination.
