UV rays from the sun emit invisible radiation that can cause significant damage to skin and eyes. Understanding the different types of UV radiation--UVA, UVB, and UVC--is essential for effective sun protection. This infographic breaks down how UV rays affect health and provides tips on minimizing exposure to reduce risks.
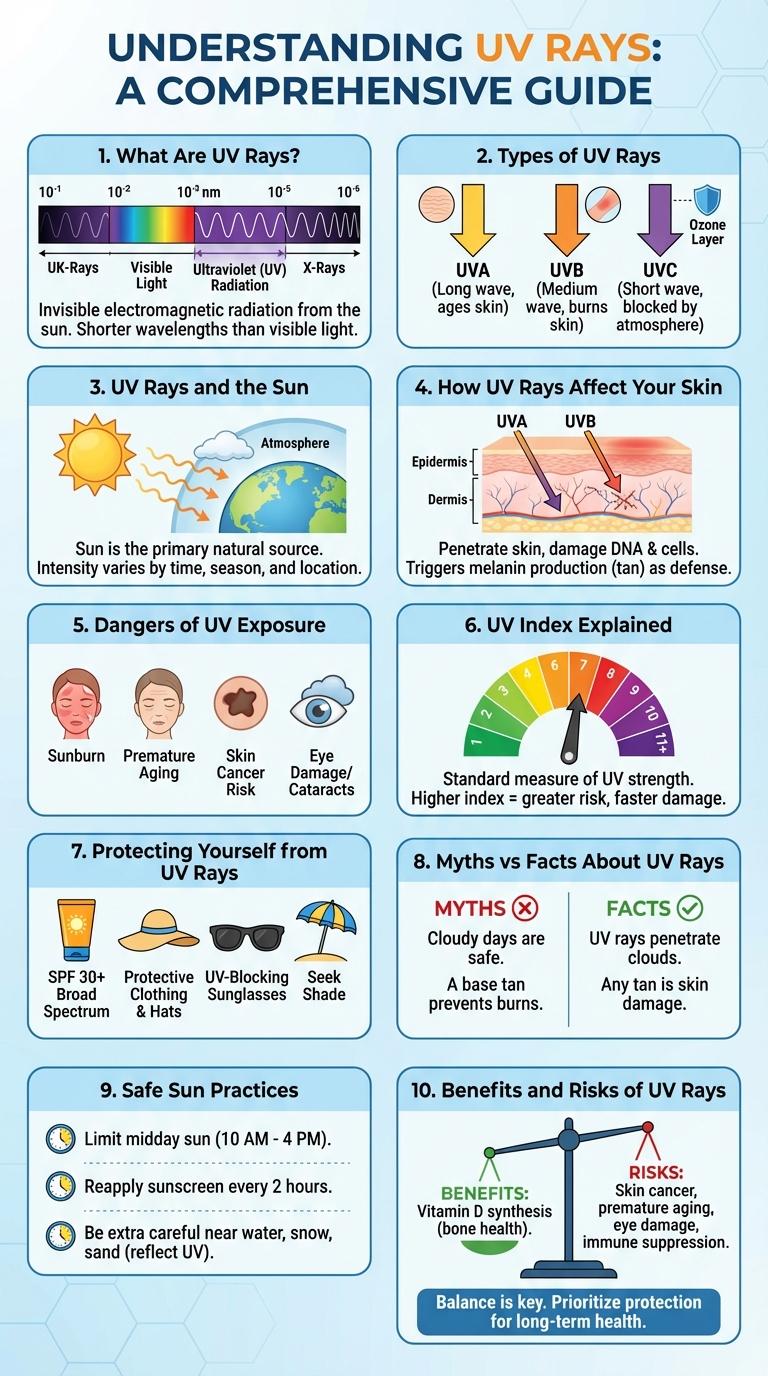
What Are UV Rays?
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. These rays are invisible to the human eye and are categorized into UVA, UVB, and UVC based on their wavelength. UV rays have both beneficial effects, like vitamin D production, and harmful impacts, such as skin damage and increased cancer risk.
Types of UV Rays
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. These rays are categorized into three main types based on their wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
UVA rays have the longest wavelength and penetrate deep into the skin, contributing to aging and long-term damage. UVB rays have a medium wavelength and primarily affect the surface of the skin, causing sunburn and playing a key role in skin cancer development.
UV Rays and the Sun
UV rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun, crucial for producing vitamin D but harmful in excess. These rays are classified into UVA, UVB, and UVC, with UVA and UVB reaching the Earth's surface.
The sun emits UV rays that vary in intensity depending on the time of day, season, and geographic location. Prolonged exposure to UV rays can lead to skin damage, eye problems, and increased risk of skin cancer.
How UV Rays Affect Your Skin
| UV Ray Type | Impact on Skin |
|---|---|
| UVA Rays | Penetrate deep into the skin, causing premature aging, wrinkles, and long-term skin damage. |
| UVB Rays | Cause sunburn by damaging the skin's outer layers; significant contributor to skin cancers. |
| Effects of Overexposure | Leads to DNA damage, immune suppression, increased risk of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers. |
| Skin Protection | Regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen blocks UVA and UVB rays, preventing skin damage. |
| Signs of UV Damage | Freckles, sunspots, redness, dryness, and leathery skin texture. |
Dangers of UV Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun pose significant health risks. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can cause severe skin and eye damage.
- Skin Cancer Risk - UV rays damage DNA in skin cells, increasing the chance of melanoma and other skin cancers.
- Premature Aging - Exposure to UV radiation accelerates skin aging, leading to wrinkles and loss of elasticity.
- Eye Damage - UV rays contribute to cataracts and photokeratitis, harming the cornea and lens of the eye.
UV Index Explained
What is the UV Index and why does it matter? The UV Index measures the strength of ultraviolet radiation from the sun at a specific place and time. This scale helps people understand the risk of skin damage from sun exposure.
How is the UV Index calculated? It is based on factors like the angle of the sun, cloud cover, ozone levels, and altitude. Higher values indicate greater potential harm to skin and eyes.
What do different UV Index values mean? A UV Index of 0 to 2 signals low exposure risk, while values above 8 indicate very high risk. Protecting skin with sunscreen and shade is essential at high UV levels.
| UV Index | Exposure Risk |
|---|---|
| 0-2 | Low |
| 3-5 | Moderate |
| 6-7 | High |
| 8-10 | Very High |
| 11+ | Extreme |
Protecting Yourself from UV Rays
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can cause skin damage, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer. Protect yourself by wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and wearing protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses. Regularly checking your skin for any unusual changes can help detect early signs of UV-related damage.
Myths vs Facts About UV Rays
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can cause skin damage, eye problems, and increase skin cancer risk. Myths about UV rays often lead to inadequate protection and health risks.
Understanding the facts helps you protect your skin effectively and reduce harmful UV exposure.
- Myth: Tanning is safe and healthy - UV exposure from tanning damages skin cells and increases skin cancer risk, making tanning unsafe.
- Myth: Sunscreen is only necessary on sunny days - UV rays penetrate clouds and cause skin damage even on overcast days.
- Myth: Dark skin doesn't need sun protection - All skin tones are susceptible to UV damage and need adequate sun protection.
- Fact: UV rays cause premature aging - Exposure to UVA rays accelerates skin aging, causing wrinkles and loss of elasticity.
- Fact: Sunglasses protect eyes from UV damage - Proper UV-blocking sunglasses reduce the risk of cataracts and eye damage.
Safe Sun Practices
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun pose risks such as skin cancer and premature aging. Protecting your skin is essential for long-term health.
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily, even on cloudy days. Wear protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Seek shade during peak sun hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
