Agriculture shapes the foundation of food security and global economies, driving innovation and sustainability efforts. Visualizing key data through infographics highlights trends in crop production, resource management, and technological advancements. This approach simplifies complex information, making it accessible for farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike.
The Future of Smart Farming
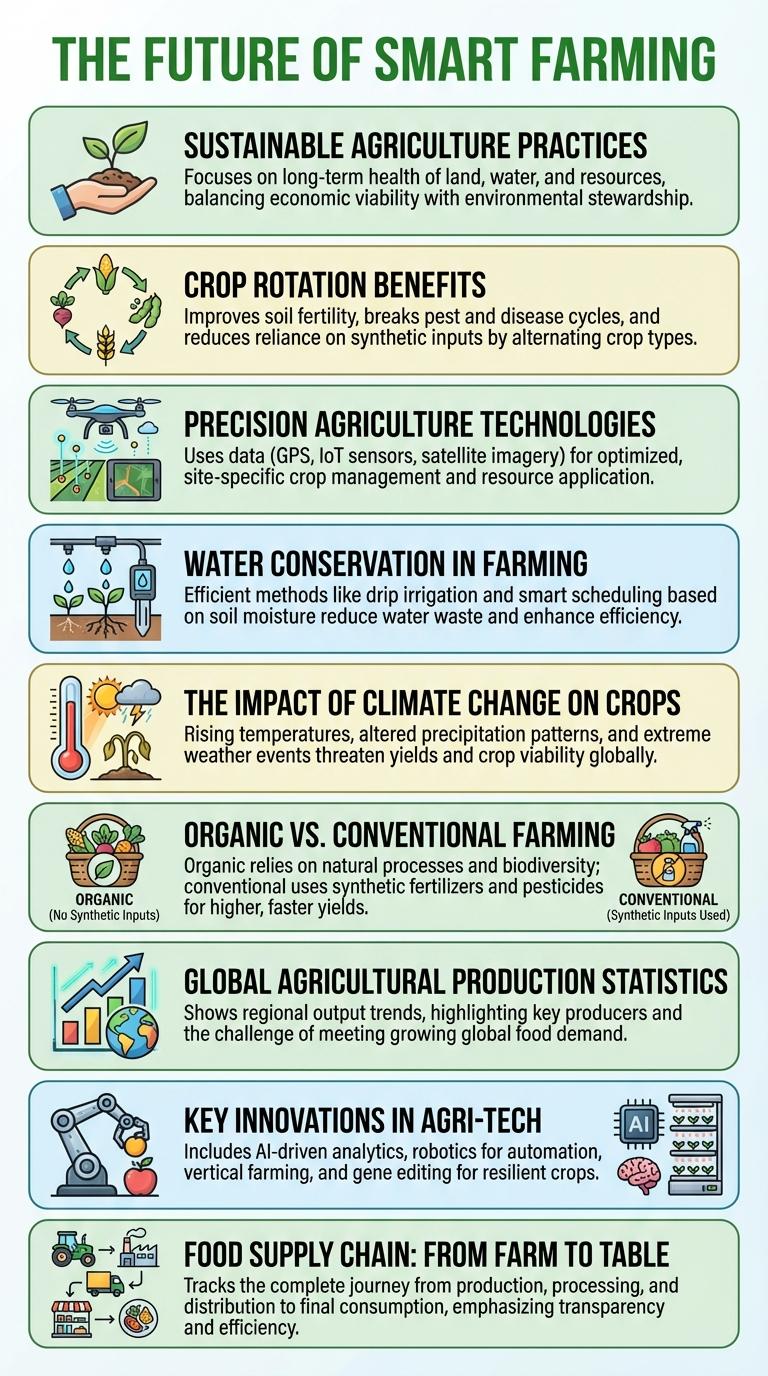
Smart farming integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and drones to optimize agricultural productivity and resource management. This innovation enhances crop monitoring, soil health analysis, and automated irrigation, leading to increased yields and sustainability. The future of agriculture hinges on data-driven decisions that promote environmental conservation and food security worldwide.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
What are sustainable agriculture practices? Sustainable agriculture practices aim to meet current food needs without compromising future generations' ability to produce food. These methods enhance environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity in farming.
How does crop rotation contribute to sustainability? Crop rotation improves soil fertility and reduces pest and disease cycles. This practice minimizes the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting a healthier ecosystem.
Why is water conservation critical in agriculture? Efficient water use prevents resource depletion and reduces environmental impact. Techniques like drip irrigation optimize water delivery directly to plant roots, decreasing water waste.
What role do cover crops play in sustainable farming? Cover crops protect soil from erosion, enhance organic matter, and suppress weeds. They support soil biodiversity and improve long-term productivity.
How does integrated pest management (IPM) support sustainability? IPM combines biological, cultural, and chemical methods to control pests with minimal environmental harm. This balanced approach reduces chemical pesticide use and promotes ecosystem balance.
Crop Rotation Benefits
Crop rotation is a sustainable agricultural practice involving the sequential planting of different crops on the same land. It helps maintain soil health, reduce pest and disease buildup, and improve crop yields.
Rotating crops enhances nutrient balance by varying the demand on soil nutrients, preventing depletion of key elements like nitrogen and phosphorus. This method also minimizes the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting eco-friendly farming.
Precision Agriculture Technologies
Precision agriculture technologies enhance farming efficiency by using GPS, sensors, and drones to monitor crop health and soil conditions. These tools enable farmers to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides precisely where needed, reducing waste and environmental impact. Data-driven decisions improve crop yields and promote sustainable agricultural practices worldwide.
Water Conservation in Farming
Water conservation is a critical aspect of sustainable agriculture, ensuring efficient use of water resources to enhance crop yields while preserving the environment. Innovative irrigation techniques and soil moisture management play key roles in reducing water waste.
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Crop rotation and cover cropping improve soil health, enhancing its ability to retain moisture. Farmers adopting rainwater harvesting systems capture and store rainfall, reducing dependency on external water sources.
The Impact of Climate Change on Crops
Climate change significantly affects agricultural productivity worldwide, altering crop growth patterns and yields. Shifts in temperature and precipitation directly influence crop health and food security.
- Rising Temperatures - Increased heat stress reduces photosynthesis efficiency, leading to lower crop yields.
- Altered Rainfall Patterns - Changes in rainfall cause droughts or floods, disrupting soil moisture crucial for crops.
- Increased CO2 Levels - Elevated carbon dioxide can enhance plant growth but often reduces nutritional quality.
Adapting agricultural practices is essential to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on global food production.
Organic vs. Conventional Farming
| Aspect | Organic Farming |
|---|---|
| Use of Chemicals | No synthetic pesticides or fertilizers |
| Soil Health | Enhances soil biodiversity and structure through natural compost and crop rotation |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces chemical runoff and promotes ecosystem balance |
| Yield | Typically lower yields compared to conventional methods |
| Certification | Requires official organic certification and adherence to strict standards |
| Aspect | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|
| Use of Chemicals | Relies on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides |
| Soil Health | May degrade soil quality due to chemical overuse and monoculture |
| Environmental Impact | Higher risk of pollution and biodiversity loss |
| Yield | Generally produce higher yields with intensive techniques |
| Certification | No specific certification required for standard practices |
Global Agricultural Production Statistics
Global agricultural production supports billions worldwide, influencing food security and economies. Key crops and livestock vary significantly by region, reflecting diverse climates and cultures.
- Top Crop Yields - Wheat, rice, and maize dominate global production, accounting for over 50% of total cereal output.
- Leading Countries - China, India, and the United States are the largest agricultural producers by volume and value.
- Livestock Production - Poultry and cattle farming contribute major shares to global meat supply, with poultry leading in growth rate.
Key Innovations in Agri-Tech
Key innovations in agri-tech are transforming the agriculture industry by enhancing productivity and sustainability. Precision farming techniques use data analytics and IoT devices to optimize crop yields and resource management.
Vertical farming and hydroponics enable year-round crop production in controlled environments, reducing land and water usage. Advanced drones and satellite imaging provide real-time field monitoring, improving pest control and soil health management.
