Adaptation is crucial for survival, enabling organisms and systems to adjust to changing environments effectively. This infographic highlights key examples of biological, technological, and cultural adaptations that demonstrate resilience and innovation. Understanding these processes helps illustrate the dynamic relationship between organisms and their habitats.
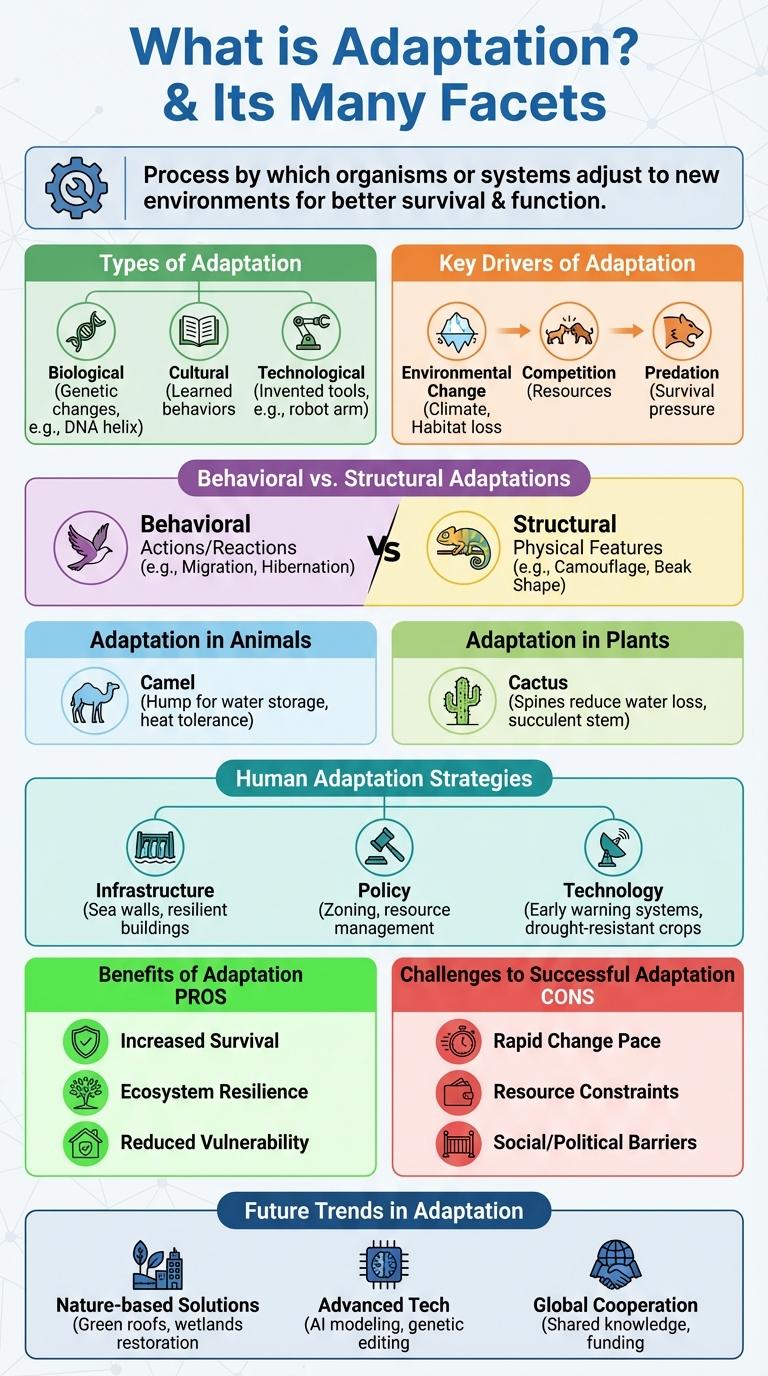
What is Adaptation?
Adaptation is a biological process where organisms adjust to their environment to increase survival chances. It enables species to thrive in changing conditions by developing beneficial traits.
- Definition - Adaptation involves genetic changes or behavioral shifts that improve an organism's ability to survive and reproduce.
- Types - Adaptations can be structural, behavioral, or physiological, each enhancing survival in different ways.
- Importance - Adaptation drives evolution and biodiversity by allowing species to cope with environmental challenges.
Types of Adaptation
Adaptation refers to the biological process where organisms adjust to their environment to enhance survival. Various types of adaptation enable species to thrive under different conditions.
- Structural Adaptation - Physical features of an organism, like fur or beaks, that improve survival in specific habitats.
- Behavioral Adaptation - Actions or behaviors that organisms develop, such as migration or hibernation, to cope with environmental changes.
- Physiological Adaptation - Internal body processes, like toxin production or temperature regulation, that support an organism's survival.
Understanding these adaptation types illuminates how life evolves in response to environmental challenges.
Key Drivers of Adaptation
Adaptation involves adjusting to new environmental conditions to reduce vulnerability and enhance resilience. Key drivers of adaptation include climate change impacts, socio-economic factors, and technological advancements.
Climate change impacts such as rising temperatures and extreme weather events force communities and ecosystems to adapt. Socio-economic factors like population growth, urbanization, and economic development shape adaptation needs and capacities. Technological advancements offer innovative solutions, improving the effectiveness of adaptation strategies across various sectors.
Behavioral vs. Structural Adaptations
Adaptations enable organisms to survive and thrive in their environments. Behavioral adaptations involve actions or habits that improve an organism's survival chances.
Structural adaptations refer to physical features that enhance an organism's ability to live in its habitat. Examples include thicker fur or specialized beaks.
Adaptation in Animals
Adaptation in animals refers to the physical and behavioral changes that enable survival in specific environments. These changes improve their ability to find food, reproduce, and avoid predators.
Animal adaptations can be structural, physiological, or behavioral, each playing a vital role in evolutionary success.
- Camouflage - Animals develop colors or patterns that blend with their surroundings to avoid predators.
- Mimicry - Certain species imitate the appearance or behavior of other species to deter predators or lure prey.
- Hibernation - Some animals enter a dormant state during unfavorable conditions to conserve energy and survive winter.
Adaptation in Plants
Adaptation in plants refers to the structural and functional changes that enable them to survive in diverse environments. These adaptations help plants conserve water, obtain nutrients, and reproduce successfully under varying conditions.
Examples include thick waxy cuticles in desert plants to reduce water loss, and broad leaves in rainforest plants to capture sunlight efficiently. Root systems also adapt, with deep roots accessing groundwater in dry areas and shallow roots absorbing nutrients from the surface in nutrient-poor soils.
Human Adaptation Strategies
Human adaptation strategies involve behavioral, physiological, and technological changes that enhance survival in diverse environments. These strategies include cultural practices, genetic adaptations, and innovations such as clothing and shelter design. Understanding these mechanisms helps explain how humans thrive in extreme conditions worldwide.
Benefits of Adaptation
| Benefit of Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Resilience | Enhances ability to withstand environmental and societal changes, reducing vulnerability. |
| Economic Stability | Minimizes financial losses through proactive measures in infrastructure and resource management. |
| Improved Public Health | Reduces risks related to heat waves, disease outbreaks, and extreme weather by adjusting community planning. |
| Preservation of Ecosystems | Supports biodiversity and natural habitats by adapting conservation strategies to changing conditions. |
| Enhanced Food Security | Promotes sustainable agricultural practices to maintain stable food supplies amid climate shifts. |
Challenges to Successful Adaptation
Adaptation faces significant challenges including environmental unpredictability, resource limitations, and social resistance. These obstacles hinder the implementation of effective strategies necessary for coping with changing conditions. Overcoming such barriers requires innovative approaches and collaborative efforts across sectors.
