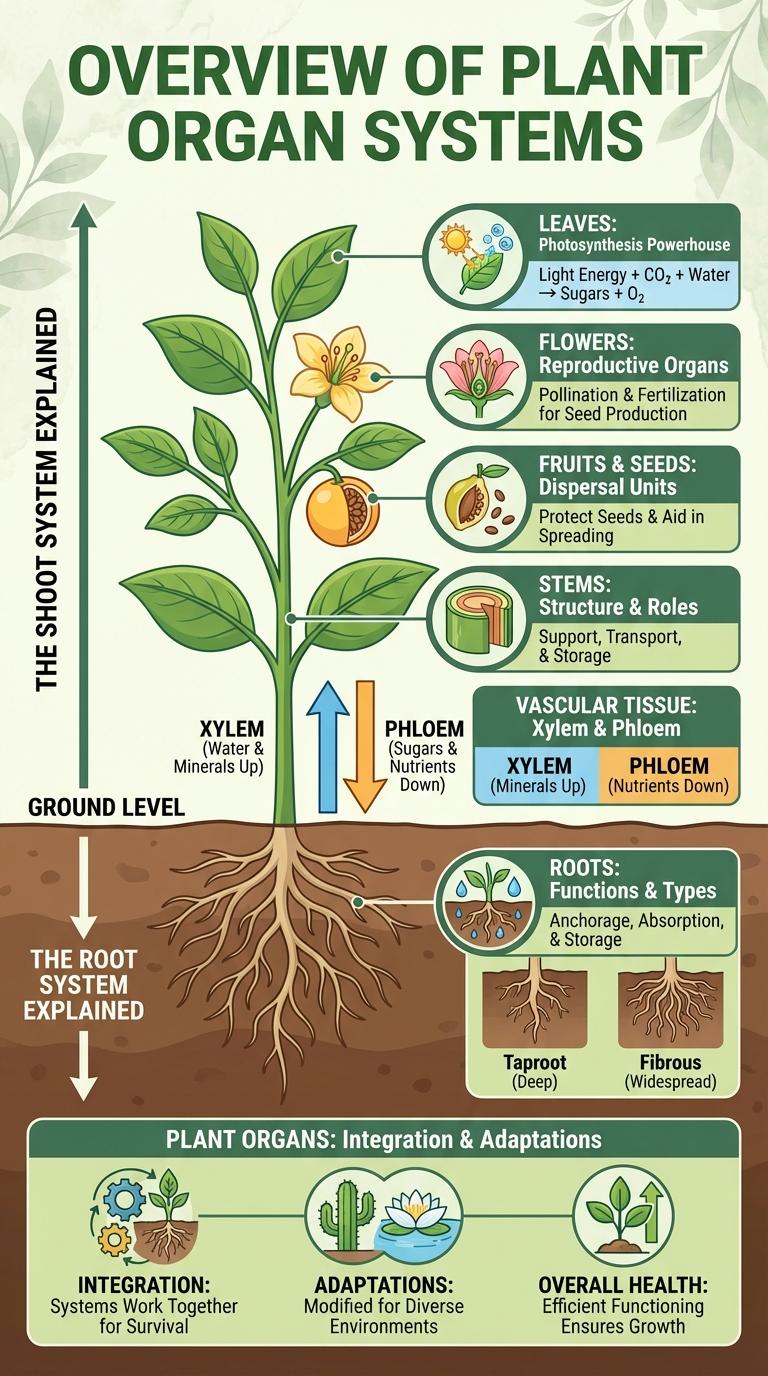
Plant organ systems consist of the root system and the shoot system, each performing vital functions for growth and survival. Roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil, while the shoot system, which includes stems, leaves, and flowers, supports photosynthesis, reproduction, and transport of nutrients. Understanding these interconnected systems provides insight into how plants thrive and adapt in various environments.
Overview of Plant Organ Systems
| Plant Organ System | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Root System | Anchors plant, absorbs water and nutrients, stores food |
| Shoot System | Supports leaves and flowers, conducts photosynthesis, reproduction |
The plant organ systems consist of two main parts: the root system and the shoot system. The root system includes all the roots below ground. Roots anchor the plant in soil, absorb water and minerals, and store carbohydrates. The shoot system exists above ground and includes stems, leaves, and reproductive organs such as flowers. Stems support leaves and transport nutrients. Leaves perform photosynthesis converting sunlight into energy. Flowers facilitate reproduction through pollination and seed production.
Roots: Functions and Types
Roots are vital components of the plant organ system responsible for anchoring and nutrient absorption. They exhibit various types adapted to different environmental conditions.
- Anchorage - Roots secure the plant firmly in the soil, providing stability.
- Absorption - Root hairs increase surface area to efficiently absorb water and minerals.
- Types of Roots - Taproots penetrate deep into the soil, while fibrous roots form dense mats near the surface.
Root systems play a crucial role in plant growth, nutrient uptake, and overall health.
Stems: Structure and Roles
Stems are vital components of the plant organ system responsible for support and transport. They connect roots to leaves, facilitating nutrient and water movement.
Stems consist of vascular tissues, nodes, and internodes, each contributing to growth and structural integrity.
- Support - Stems provide mechanical support, holding leaves and flowers upright.
- Transport - Xylem and phloem within stems transport water, minerals, and food throughout the plant.
- Storage - Some stems store nutrients and water, aiding plant survival in adverse conditions.
Leaves: Photosynthesis Powerhouse
Leaves are the primary sites of photosynthesis in plants, converting sunlight into chemical energy. They contain chloroplasts filled with chlorophyll, which absorb light for this process.
The leaf structure includes the epidermis, mesophyll, and veins, each playing a crucial role in photosynthesis. Stomata on the leaf surface regulate gas exchange, allowing carbon dioxide in and oxygen out. This organ system efficiently transforms light energy into glucose, fueling plant growth and oxygen production.
Flowers: Reproductive Organs
Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms, responsible for sexual reproduction. They contain specialized structures that facilitate pollination and fertilization.
The main parts include the stamen (male organ) and the pistil (female organ). Stamens produce pollen, while pistils house the ovary, where seeds develop after fertilization.
Fruits and Seeds: Dispersal Units
Fruits and seeds serve as vital dispersal units in the plant organ system, ensuring species propagation across diverse environments. Fruits protect seeds and aid in their distribution through mechanisms like wind, water, and animal interaction. Seed dispersal enhances genetic diversity and colonization potential for plants in new habitats.
Vascular Tissue: Xylem and Phloem
What are the main functions of vascular tissue in plants? Vascular tissue consists of xylem and phloem, which transport water, minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem moves water and dissolved minerals from roots to leaves, while phloem distributes sugars produced by photosynthesis.
| Vascular Tissue | Function |
|---|---|
| Xylem | Transports water and minerals upward from roots to leaves |
| Phloem | Distributes sugars and organic nutrients from leaves to all parts of the plant |
The Shoot System Explained
The shoot system of a plant consists of stems, leaves, and flowers, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis, support, and reproduction. Stems provide structural support and transport nutrients and water between roots and leaves through vascular tissues. Leaves capture sunlight to produce energy, while flowers are responsible for reproduction by facilitating pollination and seed formation.
The Root System Explained
The root system is a vital part of a plant, responsible for anchoring and nutrient absorption. It supports plant growth by accessing water and essential minerals from the soil.
Understanding the root system helps in improving plant health and optimizing agricultural practices.
- Primary Root - The main root that grows downward, providing structural support and absorption.
- Secondary Roots - Branch from the primary root to increase surface area for water and nutrient uptake.
- Root Hairs - Tiny extensions that enhance the root's ability to absorb water and minerals efficiently.
