Exploring the vastness of space reveals astonishing facts about stars, planets, and galaxies. This infographic breaks down complex astronomical concepts into clear visuals, highlighting key data on cosmic phenomena. Discover the scale, composition, and mysteries of the universe through engaging images and concise information.
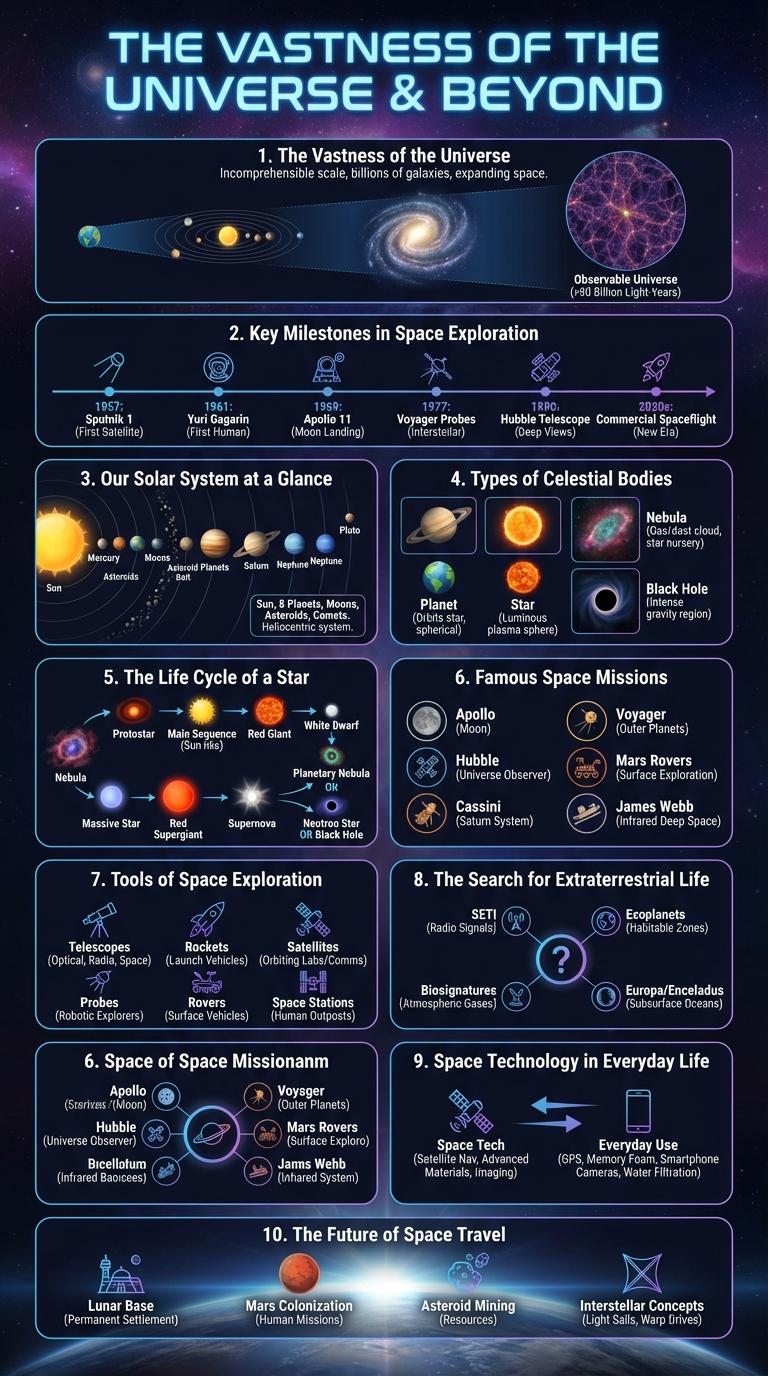
The Vastness of the Universe
How vast is the universe beyond our planet Earth?
The observable universe spans approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter. It contains over 2 trillion galaxies, each with billions of stars and countless planets.
Key Milestones in Space Exploration
Space exploration has revolutionized our understanding of the universe through groundbreaking missions and technological advancements. Key milestones mark humanity's journey beyond Earth, showcasing achievements in satellite launches, human spaceflight, and planetary exploration.
In 1957, Sputnik 1 became the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth, initiating the space age. The Apollo 11 mission in 1969 achieved the first manned moon landing, a pivotal moment in space history.
The 1970s featured the launch of the Voyager probes, which provided unprecedented data about the outer planets and continue to send signals from interstellar space. Mars rovers, including Spirit, Opportunity, and Perseverance, have transformed our knowledge of the Red Planet's geology and potential for life.
International cooperation led to the International Space Station (ISS), orbiting Earth since 1998 as a hub for scientific research and human presence in space. Recent milestones include private company advancements in reusable rocket technology and missions targeting asteroids and distant moons.
Our Solar System at a Glance
Our Solar System consists of the Sun and all celestial bodies gravitationally bound to it, including eight planets, their moons, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. The eight planets, ordered from the Sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. This dynamic system spans over 4.5 billion years of formation, occupying a vast region in our Milky Way galaxy.
Types of Celestial Bodies
Space contains various types of celestial bodies, each with unique characteristics and compositions. Stars, such as the Sun, are massive spheres of plasma generating energy through nuclear fusion. Planets orbit stars and can be rocky like Earth or gaseous like Jupiter, while moons are natural satellites orbiting planets.
The Life Cycle of a Star
Stars are born from vast clouds of gas and dust in space, known as nebulae. Over millions of years, gravitational forces cause these clouds to collapse, forming a protostar.
A protostar continues to gather mass until nuclear fusion ignites in its core, marking the birth of a main sequence star. This phase can last billions of years depending on the star's mass. Eventually, the star exhausts its fuel, leading to its transformation into a red giant or supergiant.
Famous Space Missions
Famous space missions have dramatically expanded our understanding of the cosmos. These missions mark significant milestones in exploration, technology, and human achievement.
The Apollo 11 mission in 1969 was the first to land humans on the Moon, with astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin setting foot on the lunar surface. The Mars Rover missions, including Spirit, Opportunity, and Perseverance, have provided extensive data about Mars' geology and potential for life.
Tools of Space Exploration
Space exploration relies on advanced tools to study the cosmos and gather data beyond Earth's atmosphere. These tools enable scientists to understand celestial bodies, cosmic phenomena, and the universe's origins.
- Telescope - Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope capture detailed images and spectra of distant stars and galaxies.
- Rover - Robotic vehicles such as Mars rovers explore planetary surfaces and collect soil and rock samples.
- Spectrometer - Devices analyze light from stars and planets to determine their composition and physical properties.
The Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The search for extraterrestrial life explores whether life exists beyond Earth in the universe. Scientific efforts focus on detecting microbial life forms and intelligent beings on distant planets and moons.
Researchers use advanced technology to analyze atmospheric conditions and signals from outer space to uncover signs of life.
- Exoplanet Discovery - Thousands of planets outside our solar system have been detected, some located in habitable zones where liquid water could exist.
- Astrobiology Research - Studies examine extreme environments on Earth to understand how life might survive in harsh conditions elsewhere.
- SETI Programs - Scientists scan radio waves and signals from space to identify patterns indicating intelligent extraterrestrial communication.
Space Technology in Everyday Life
Space technology has significantly influenced modern daily life by enhancing communication and navigation systems. Its applications extend beyond exploration, benefiting various industries globally.
- GPS Navigation - Satellites provide precise location data enabling accurate directions for transportation and logistics.
- Satellite Communication - Space-based networks support global internet, television, and emergency communication services.
- Weather Forecasting - Spaceborne sensors monitor atmospheric conditions improving weather predictions and disaster preparedness.
Innovations derived from space technology continue to drive improvements in safety, connectivity, and environmental monitoring worldwide.
