Air and water are essential elements that sustain life on Earth, vital for health, environment, and biodiversity. Understanding their quality and the factors that affect them helps in promoting sustainable practices and mitigating pollution. This infographic highlights key data and insights on air and water conditions worldwide, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
The Essential Elements: Air & Water
Air and water are fundamental elements that sustain all life on Earth. Their quality directly impacts health, ecosystems, and climate stability.
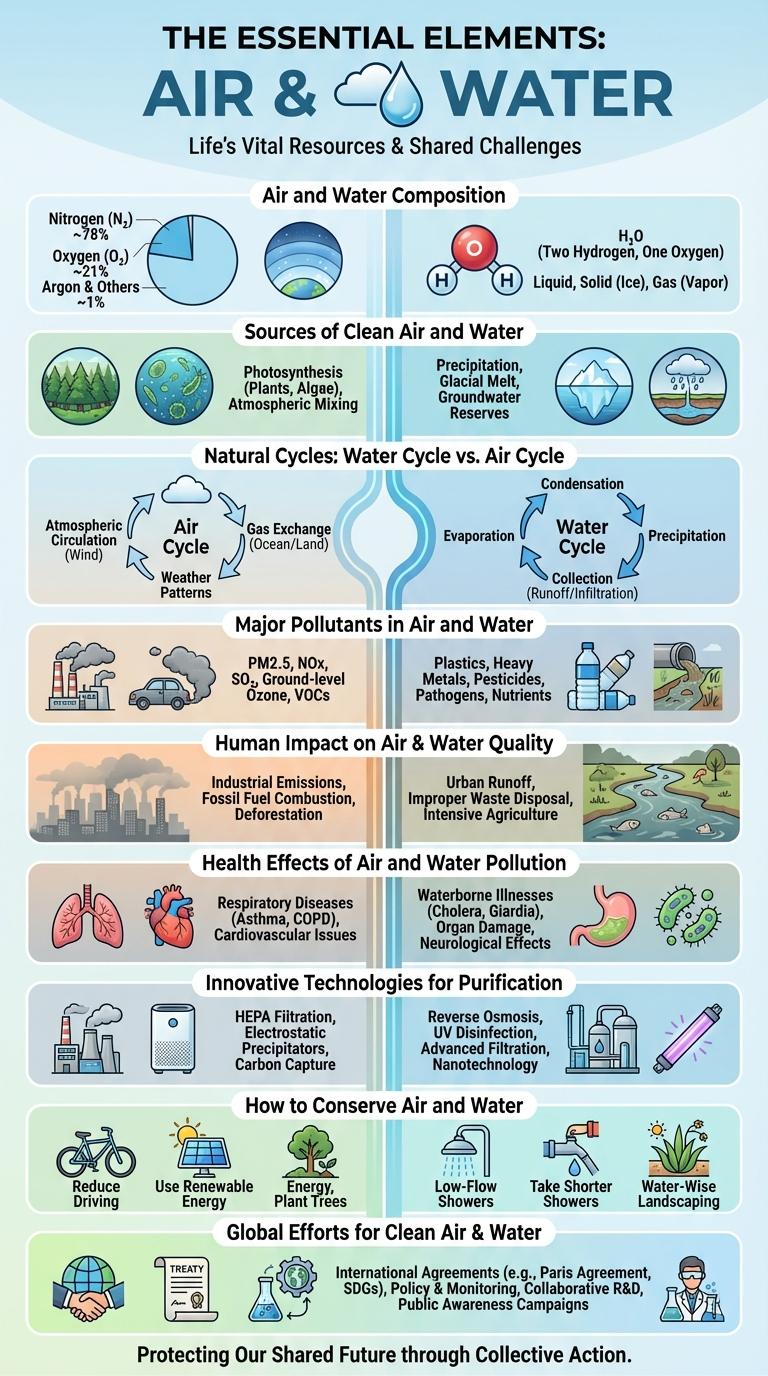
- Air Composition - Earth's atmosphere primarily consists of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), vital for respiration and combustion.
- Water Coverage - Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by water, crucial for hydration and habitat for countless species.
- Interdependence - Air and water cycles interact constantly, regulating climate and supporting biodiversity worldwide.
Air and Water Composition
Air and water are essential components of Earth's ecosystem, each with distinct compositions that support life. Understanding their makeup helps in analyzing environmental and health impacts.
- Air Composition - Air is primarily composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases including argon and carbon dioxide.
- Water Composition - Water consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom, forming H2O molecules that cover about 71% of Earth's surface.
- Trace Elements - Both air and water contain trace elements such as pollutants or minerals that affect quality and usability.
Both air and water compositions are critical for sustaining life and maintaining ecological balance.
Sources of Clean Air and Water
Clean air primarily originates from natural sources such as forests, wetlands, and oceans, which filter pollutants and produce oxygen. Urban areas rely on air quality management strategies like emission controls and green spaces to maintain breathable air. Clean water sources include rivers, lakes, underground aquifers, and protected watersheds, which supply safe drinking water after natural or engineered purification.
Natural Cycles: Water Cycle vs. Air Cycle
The water cycle and air cycle are essential natural processes that sustain life on Earth. These cycles describe the continuous movement and transformation of water and air through various environmental stages.
The water cycle involves evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection, continuously recycling Earth's water resources. The air cycle includes the movement of air masses, absorption of gases, and temperature changes that influence weather patterns. Together, these natural cycles regulate climate, support ecosystems, and maintain atmospheric balance.
Major Pollutants in Air and Water
Air and water pollution pose significant threats to environmental and human health. Understanding the major pollutants helps in developing effective prevention and control strategies.
Common air pollutants include particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3). Key water pollutants consist of heavy metals, pathogens, nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, chemical contaminants, and plastic debris.
Human Impact on Air & Water Quality
Human activities significantly alter air and water quality, impacting ecosystems and public health. Emissions from factories, vehicles, and agriculture release pollutants that degrade the natural environment.
Water contamination results from industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and improper waste disposal. These pollutants harm aquatic life and reduce the availability of clean water for communities.
Health Effects of Air and Water Pollution
Air and water pollution significantly impact human health worldwide, contributing to a range of acute and chronic diseases. Understanding the health effects helps prioritize pollution control and public health interventions.
Exposure to polluted air and water leads to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and impaired immune function in affected populations.
- Respiratory Diseases - Inhalation of airborne pollutants like PM2.5 and ozone causes asthma, bronchitis, and other chronic respiratory conditions.
- Waterborne Illnesses - Contaminated water sources transmit pathogens causing diarrhea, cholera, and typhoid fever.
- Cardiovascular Effects - Long-term exposure to air pollutants increases risks of heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension.
- Neurological Disorders - Toxic chemicals in polluted air and water can lead to cognitive impairments and developmental delays in children.
- Cancer Risk - Persistent exposure to carcinogens in the environment raises the incidence of lung, bladder, and skin cancers.
Innovative Technologies for Purification
| Technology | Application |
|---|---|
| Photocatalytic Oxidation | Decomposes airborne pollutants using UV light and titanium dioxide, improving indoor air quality. |
| Membrane Filtration | Removes bacteria, viruses, and chemicals from water through nanoscale membranes, ensuring safe drinking water. |
| Electrochemical Water Treatment | Utilizes electric current to degrade organic contaminants in water, effective in industrial waste management. |
| Activated Carbon Air Filters | Adsorbs volatile organic compounds and odors, enhancing air purification in residential and commercial spaces. |
| Ultrafiltration | Employs pressure-driven membrane technology to eliminate suspended solids and microorganisms from water. |
How to Conserve Air and Water
How can individuals effectively conserve air and water in daily life? Reducing vehicle emissions by using public transportation or carpooling helps improve air quality. Fixing leaks and using water-efficient appliances significantly minimize water waste.
