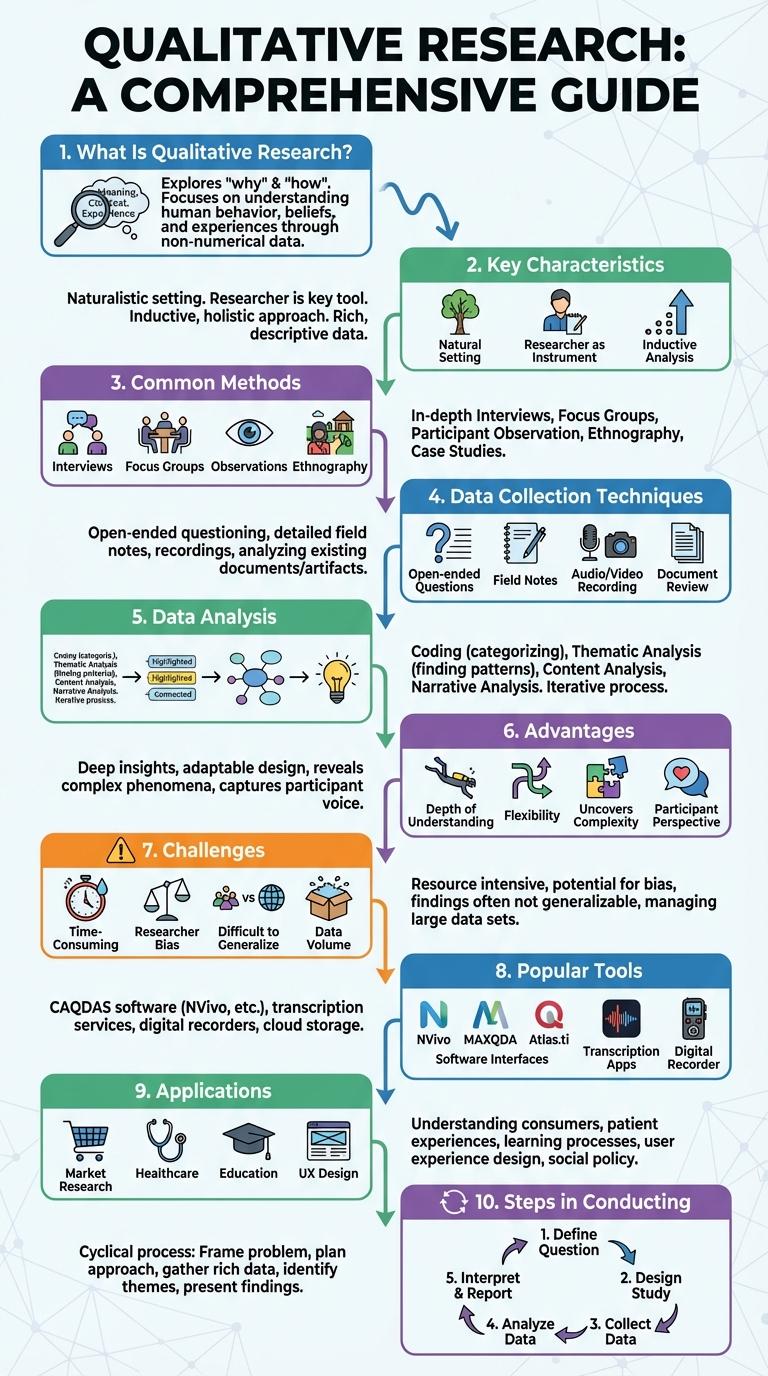
Qualitative research explores human experiences and behaviors through detailed, non-numerical data collection methods such as interviews and observations. Infographics visually represent this complex information, highlighting key themes, patterns, and insights in an accessible format. They enhance understanding by breaking down qualitative data into clear, engaging visuals that facilitate deeper analysis and communication.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research explores complex phenomena through detailed, non-numerical data. It provides insights into participants' experiences, motivations, and social contexts.
- Nature of Data - Focuses on words, images, and observations rather than statistics or numbers.
- Purpose - Aims to understand how and why people behave in certain ways within their natural settings.
- Methods - Uses interviews, focus groups, and participant observation to gather rich, in-depth information.
Key Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research explores human experiences through detailed, non-numerical data like interviews and observations. It emphasizes depth over breadth, focusing on participants' perspectives and meanings. Key characteristics include open-ended data collection, thematic analysis, and contextual understanding.
Common Methods in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research explores human experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena through in-depth and subjective analysis. It aims to understand meanings, patterns, and motivations behind actions.
Common methods in qualitative research include interviews, focus groups, and participant observation. These techniques provide rich, detailed data that quantitative methods often overlook.
Data Collection Techniques
What are the primary data collection techniques used in qualitative research?
Qualitative research employs various data collection techniques to gain in-depth understanding of participants' perspectives. These techniques include interviews, focus groups, observations, and document analysis.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Interviews | One-on-one conversations designed to explore participants' experiences and viewpoints in detail. |
| Focus Groups | Group discussions that gather diverse opinions and stimulate dialogue among participants. |
| Observations | Systematic recording of behaviors and interactions within natural settings to capture real-life contexts. |
| Document Analysis | Reviewing textual or visual materials to extract meaningful insights related to the research topic. |
Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify patterns, themes, and meanings within textual or visual data collected from interviews, observations, or documents. |
| Common Methods | Thematic Analysis, Content Analysis, Narrative Analysis, Grounded Theory, Discourse Analysis. |
| Process Steps | Data Preparation, Coding, Theme Development, Interpretation, Reporting. |
| Tools | NVivo, ATLAS.ti, MAXQDA, manual coding techniques. |
| Outcome | Rich, detailed insights that explain participants' perspectives, experiences, and social contexts. |
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research provides deep insights into human behavior, motivations, and experiences through detailed data collection methods like interviews and focus groups. This approach captures the complexity of social phenomena, offering rich and nuanced understanding beyond quantitative measures.
It allows researchers to explore new areas where little prior knowledge exists, fostering flexibility in study design and data interpretation. The method supports the discovery of patterns and themes that inform theory development and practical applications in real-world contexts.
Challenges in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research faces challenges such as participant bias, which can affect the authenticity of collected data. Data analysis demands meticulous attention, as interpreting non-numeric information requires deep contextual understanding. Maintaining researcher objectivity remains critical to ensure credible and valid study outcomes.
Popular Qualitative Research Tools
Qualitative research explores human behavior and the reasons behind it through detailed, non-numerical data. It relies heavily on tools that capture rich, contextual insights from participants.
Popular qualitative research tools include interviews, focus groups, and observation. Interviews allow deep, one-on-one exploration of thoughts and experiences. Focus groups enable group dynamics analysis, capturing diverse perspectives within a controlled setting.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research explores human behavior, motivations, and social contexts through detailed, non-numerical data. It provides deep insights that quantitative methods may not capture.
- Market Research - Helps businesses understand consumer attitudes, preferences, and decision-making processes.
- Healthcare - Investigates patient experiences and the impact of treatments on quality of life.
- Education - Explores teaching methods, student engagement, and learning environments.
- Social Sciences - Examines cultural practices, social interactions, and community dynamics.
- Product Development - Guides design and improvement based on user feedback and behavior observations.
Qualitative research applications span multiple fields, offering nuanced understanding that supports effective strategies and innovations.
