Dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating mood, motivation, and reward. This infographic breaks down how dopamine influences brain function and behavior, highlighting its impact on pleasure, learning, and movement. Understanding dopamine's pathways offers insight into mental health conditions such as depression and Parkinson's disease.
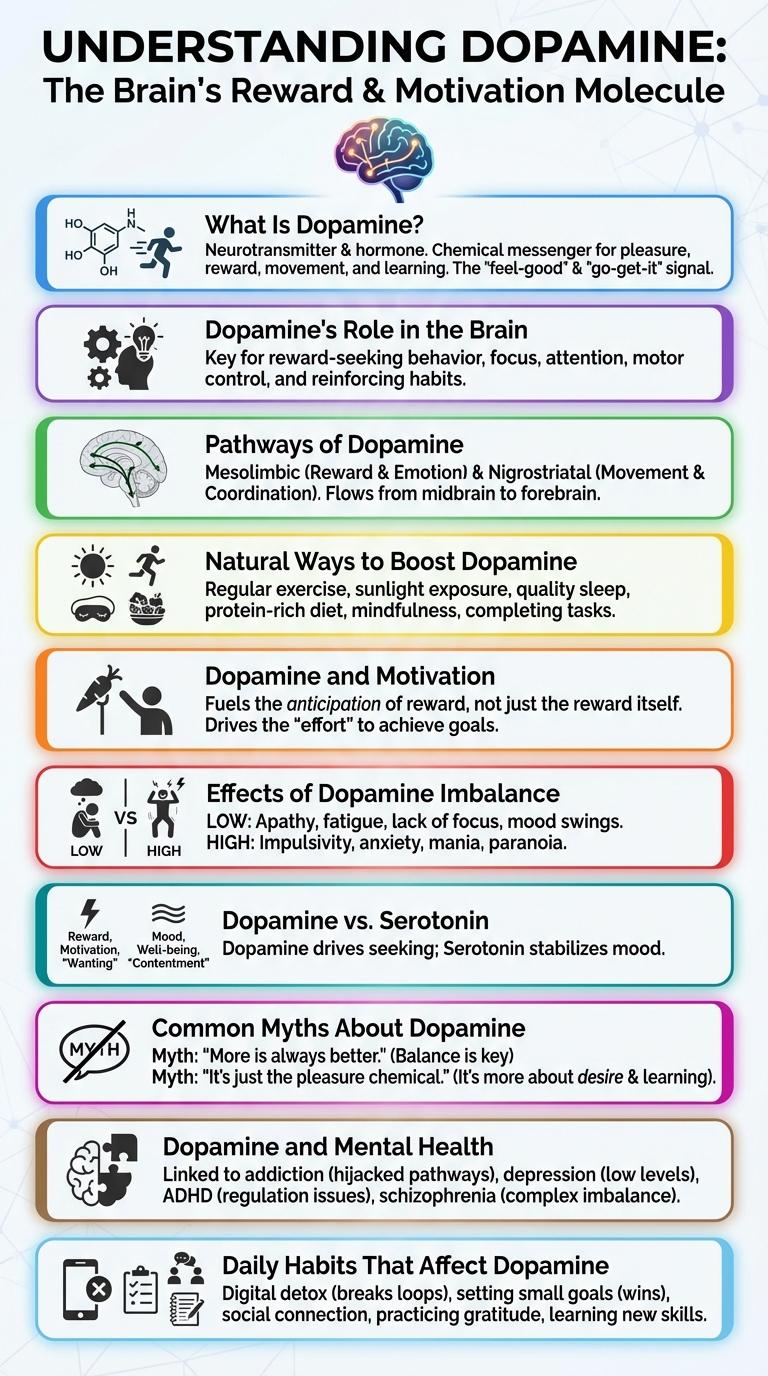
What Is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter crucial for transmitting signals in the brain and other areas of the body. It plays a vital role in reward, motivation, and motor control functions.
- Neurochemical Messenger - Dopamine acts as a chemical messenger between neurons, influencing communication and brain activity.
- Reward System - It regulates pleasure and reward pathways that reinforce behaviors essential for survival and enjoyment.
- Movement Regulation - Dopamine controls motor function, with deficiencies linked to disorders such as Parkinson's disease.
Dopamine's Role in the Brain
What is dopamine's role in the brain? Dopamine acts as a neurotransmitter essential for transmitting signals between nerve cells. It influences motivation, reward, and motor control.
How does dopamine affect behavior? This neurotransmitter regulates pleasure and reinforcement, driving goal-directed behavior. Imbalances can lead to mood disorders or neurological diseases.
Where is dopamine produced in the brain? Dopamine is primarily produced in areas like the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area. These regions are critical for movement, cognition, and emotional responses.
Why is dopamine important for learning? Dopamine signals reward prediction, enhancing learning and memory formation. It helps the brain adapt based on experience and outcomes.
What disorders are linked to dopamine dysfunction? Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia are associated with dopamine imbalances. Proper dopamine regulation is vital for mental and physical health.
Pathways of Dopamine
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter involved in reward, motivation, and motor control. It operates through several distinct pathways in the brain.
The four primary pathways of dopamine include the mesolimbic, mesocortical, nigrostriatal, and tuberoinfundibular pathways. The mesolimbic pathway plays a crucial role in reward and pleasure. The nigrostriatal pathway is vital for movement regulation, while the mesocortical pathway affects cognition and executive function. The tuberoinfundibular pathway regulates hormone secretion from the pituitary gland.
Natural Ways to Boost Dopamine
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter that influences motivation, pleasure, and reward in the brain. Natural methods can enhance dopamine levels to improve mood and cognitive function.
- Exercise Regularly - Physical activity stimulates dopamine production and supports overall brain health.
- Consume Tyrosine-rich Foods - Foods like almonds, bananas, and eggs provide tyrosine, a precursor to dopamine synthesis.
- Practice Meditation - Mindfulness and meditation increase dopamine release, reducing stress and enhancing focus.
Dopamine and Motivation
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter crucial for motivation by reinforcing rewarding behaviors and encouraging goal-directed actions. It activates the brain's reward system, creating feelings of pleasure that drive individuals to pursue desired outcomes. Low dopamine levels can lead to reduced motivation and difficulty in initiating tasks, impacting overall productivity.
Effects of Dopamine Imbalance
Dopamine is a critical neurotransmitter that influences mood, motivation, and motor control. Imbalances in dopamine levels can significantly impact mental and physical health.
- Depression - Low dopamine levels are linked to feelings of sadness, lack of motivation, and impaired concentration.
- Parkinson's Disease - Dopamine deficiency causes motor symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and slowed movement.
- Schizophrenia - Excess dopamine activity may contribute to hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Maintaining balanced dopamine levels is essential for emotional stability and overall well-being.
Dopamine vs. Serotonin
Dopamine and serotonin are two key neurotransmitters that play distinct roles in brain function and mood regulation. Dopamine is primarily associated with reward, motivation, and pleasure.
Serotonin regulates mood, social behavior, and overall sense of well-being. Both chemicals influence mental health but through different neural pathways.
Common Myths About Dopamine
Dopamine is often misunderstood as simply a "pleasure chemical," but it plays a crucial role in motivation, reward, and motor control. Misconceptions about dopamine can lead to oversimplified views of brain function and behavior.
One common myth is that dopamine only causes pleasure, while it actually helps regulate attention, learning, and emotional responses. Another false belief is that increasing dopamine always improves mood, but imbalances can contribute to disorders like Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia.
Dopamine and Mental Health
Dopamine plays a crucial role in regulating mood, motivation, and emotional responses, significantly impacting mental health. Imbalances in dopamine levels are linked to disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. Understanding dopamine's function helps in developing targeted treatments for these mental health conditions.
