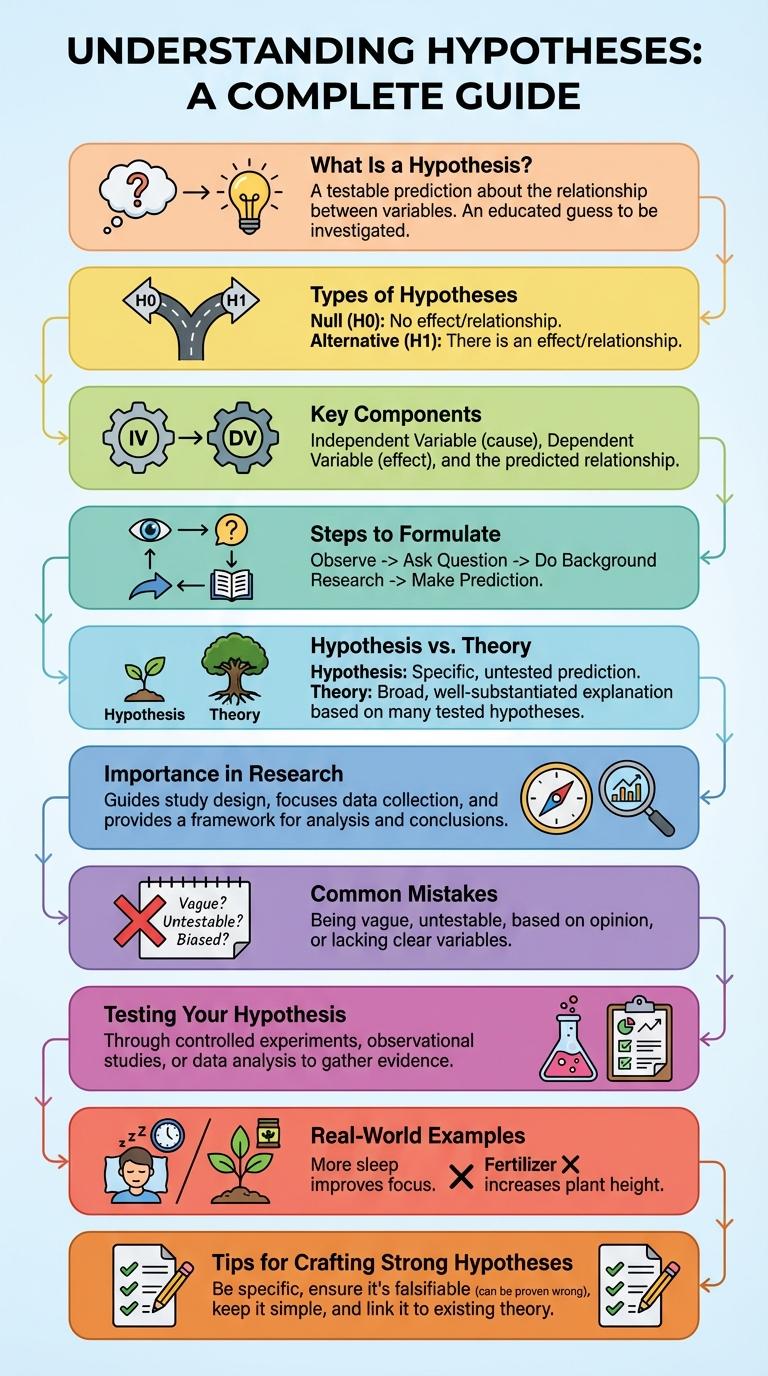
A hypothesis serves as a foundational element in scientific research, guiding experiments and investigations. It represents a testable prediction that helps researchers explore relationships between variables. Visualizing hypotheses through infographics can simplify complex concepts, making them accessible and easier to understand.
What Is a Hypothesis?
What is a hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a clear, testable statement predicting the outcome of an experiment or study. It serves as the foundation for scientific investigation by guiding research design and data analysis.
Types of Hypotheses
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon that can be tested through research and experimentation. Different types of hypotheses serve various purposes in scientific studies and data analysis. Understanding these types helps researchers design effective experiments and interpret results accurately.
| Type of Hypothesis | Description |
|---|---|
| Null Hypothesis (H0) | States there is no effect or relationship between variables; serves as the default assumption to be tested and possibly rejected. |
| Alternative Hypothesis (Ha) | Proposes a specific effect or relationship different from the null hypothesis; what researchers aim to support. |
| Directional Hypothesis | Predicts the direction of the expected relationship or effect between variables. |
| Non-directional Hypothesis | States that a relationship exists but does not specify its direction. |
| Complex Hypothesis | Involves multiple variables and predicts relationships among them. |
Key Components of a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a testable statement predicting the relationship between variables. It serves as the foundation for scientific experimentation and research.
Key components include the independent variable, which is manipulated or changed. The dependent variable is the observed outcome or effect. A clear, concise, and measurable prediction completes the hypothesis structure.
Steps to Formulate a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a testable prediction that explains a phenomenon or answers a research question. Formulating a clear hypothesis is essential for guiding scientific investigations.
Start by identifying the research problem and conducting preliminary observations. Next, generate a specific, measurable, and testable statement predicting the relationship between variables.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is an initial, testable explanation for a specific phenomenon. A theory is a well-substantiated, comprehensive explanation based on extensive evidence.
- Hypothesis - A proposed prediction that can be tested through experiments or observations.
- Theory - A broad framework that explains multiple hypotheses and is supported by substantial data.
- Development - A hypothesis evolves into a theory after repeated validation and consensus.
Understanding the distinction between hypothesis and theory clarifies the scientific process and knowledge validation.
Importance of Hypotheses in Research
Hypotheses play a crucial role in guiding research by providing clear, testable predictions. They help structure investigations and enable researchers to validate theories through empirical evidence.
Formulating a strong hypothesis directs the focus of a study, making data collection and analysis more efficient. Hypotheses also facilitate replication and comparison across different studies, enhancing scientific credibility.
- Guides Research Design - Hypotheses define what variables to observe and how to measure them in a study.
- Enables Empirical Testing - Clear hypotheses allow researchers to confirm or refute assumptions based on data.
- Improves Scientific Communication - Hypotheses provide a concise explanation of expected outcomes to share with the academic community.
Common Mistakes in Hypothesis Writing
Crafting a clear and testable hypothesis is crucial for effective scientific research. Avoiding common mistakes ensures that your hypothesis is both meaningful and researchable.
- Vagueness - A hypothesis should be specific and clearly define the variables and expected relationship.
- Lack of Testability - The hypothesis must be framed so it can be supported or refuted through empirical data.
- Overly Complex Wording - Simple and concise language improves clarity and comprehension of the hypothesis.
Testing Your Hypothesis
Testing your hypothesis involves designing experiments that effectively measure the predicted outcomes. Collecting and analyzing data reveals whether the hypothesis holds true or needs revision. Accurate testing ensures scientific validity and drives research forward.
Real-World Hypothesis Examples
| Hypothesis | Real-World Example |
|---|---|
| Scientific Hypothesis | Increasing sunlight exposure leads to faster plant growth. |
| Business Hypothesis | Offering free shipping increases online sales by 20%. |
| Medical Hypothesis | Daily vitamin D supplements reduce the risk of flu infections. |
| Educational Hypothesis | Using interactive technology improves student engagement. |
| Psychological Hypothesis | Listening to music decreases stress levels in adults. |
