Organic compounds consist primarily of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements, forming the basis of all known life. They exhibit diverse structures ranging from simple molecules like methane to complex macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Understanding the classification, properties, and functions of organic compounds is essential for fields like chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Introduction to Organic Compounds
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Organic compounds are chemical compounds primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms, often including oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and other elements. |
| Carbon Importance | Carbon's ability to form four covalent bonds allows it to create complex and diverse molecular structures essential for life. |
| Types of Organic Compounds | Include hydrocarbons, alcohols, acids, ethers, esters, and polymers. |
| Role in Biology | Organic compounds form the basis of biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. |
| Applications | Used in pharmaceuticals, plastics, fuels, and food additives, driving industrial and medical advances. |
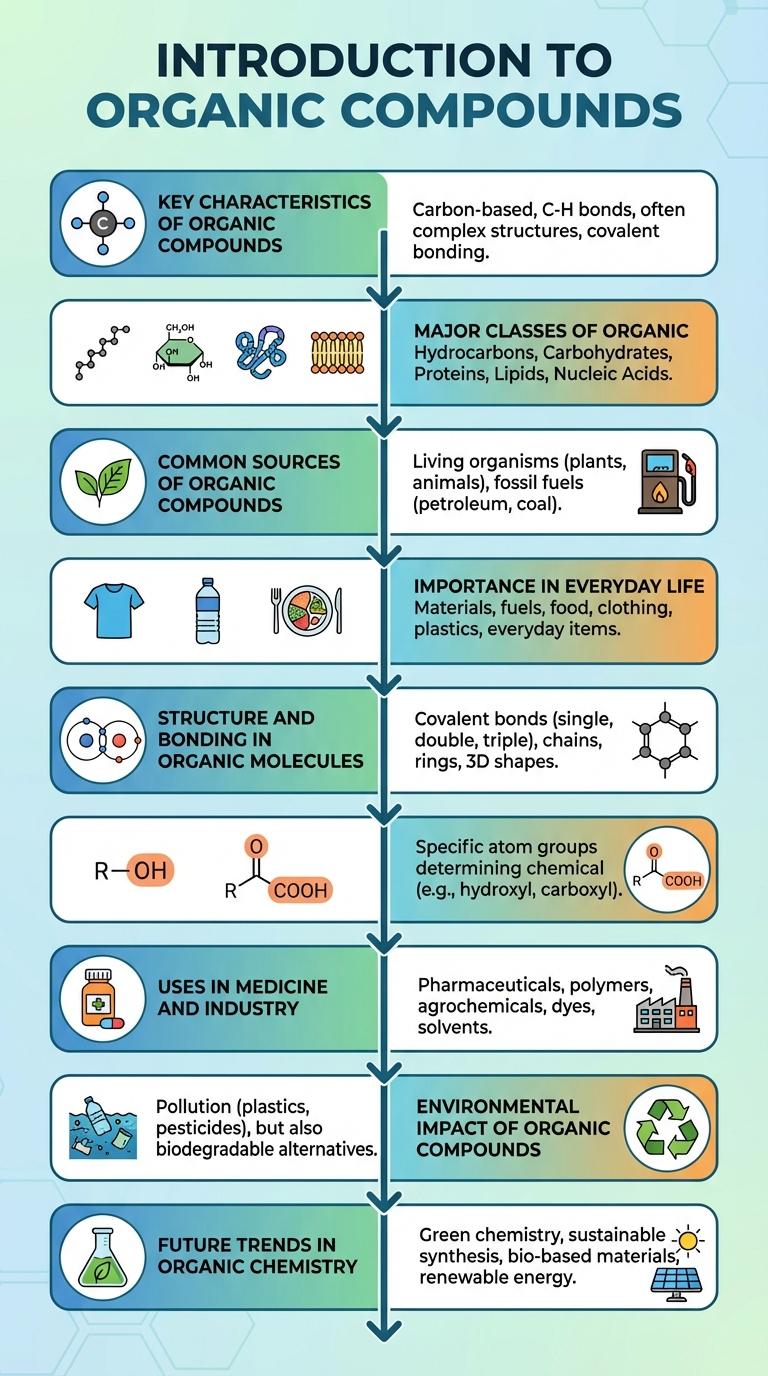
Key Characteristics of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds primarily consist of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements. These molecules form the basis of all known life and are crucial in biochemistry and industrial applications.
They exhibit diverse structures such as chains, rings, and branches, allowing for immense chemical variety. Key chemical properties include covalent bonding, flammability, and the ability to undergo reactions like substitution and addition.
Major Classes of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are primarily composed of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements. The major classes of organic compounds include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, each playing crucial roles in biological systems. These compounds serve as energy sources, structural components, and information carriers within living organisms.
Common Sources of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are primarily found in living organisms and their byproducts. Common sources include plants, animals, fossil fuels, and synthetic materials. These compounds form the basis of life and are widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and plastics.
Importance in Everyday Life
Organic compounds are fundamental to many aspects of daily life, forming the basis of all living organisms. They include essential substances such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
These compounds are also crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and food production. Their versatility supports the development of medicines, fertilizers, and biodegradable materials.
Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules
Organic compounds consist primarily of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements. The unique bonding properties of carbon allow the formation of diverse and complex molecular structures essential to life.
Carbon atoms form four covalent bonds, enabling the creation of chains, rings, and branching frameworks. These bonds include single, double, and triple covalent bonds, influencing the molecule's shape and reactivity. The specific arrangement of atoms and type of bonding determine an organic compound's chemical properties and biological functions.
Functional Groups Explained
Organic compounds are primarily defined by their functional groups, which determine their chemical reactivity and properties. Understanding these groups is essential for studying biological molecules and synthetic materials.
- Hydroxyl Group - Consists of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, often found in alcohols and contributing to polarity.
- Carbonyl Group - Contains a carbon double-bonded to oxygen, present in aldehydes and ketones, influencing reactivity.
- Carboxyl Group - Combines a carbonyl and hydroxyl group, forming acids that ionize in aqueous solutions.
Uses in Medicine and Industry
Organic compounds play a crucial role in medicine and industrial applications due to their diverse chemical properties. These compounds form the basis of many pharmaceuticals and synthetic materials essential to modern technology.
- Pharmaceuticals - Organic compounds serve as active ingredients in drugs that treat a wide range of diseases and conditions.
- Antibiotics - Many antibiotics are organic molecules that inhibit bacterial growth and fight infections.
- Polymers - Organic compounds are fundamental in producing polymers used in plastics, textiles, and packaging materials.
- Solvents - Organic solvents like ethanol and acetone are integral to chemical manufacturing and laboratory processes.
- Agrochemicals - Organic compounds are key components in pesticides and herbicides, enhancing crop protection and yield.
Environmental Impact of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds play a crucial role in ecosystems but can also contribute to environmental pollution. Their impact varies based on their chemical structure and source.
- Persistence in Environment - Some organic compounds, like PCBs and pesticides, resist degradation and accumulate in soil and water.
- Bioaccumulation - Toxic organic compounds can build up in the tissues of living organisms, affecting food chains and biodiversity.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions - Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and climate change.
Understanding the environmental impact of organic compounds helps in developing sustainable chemical management strategies.
