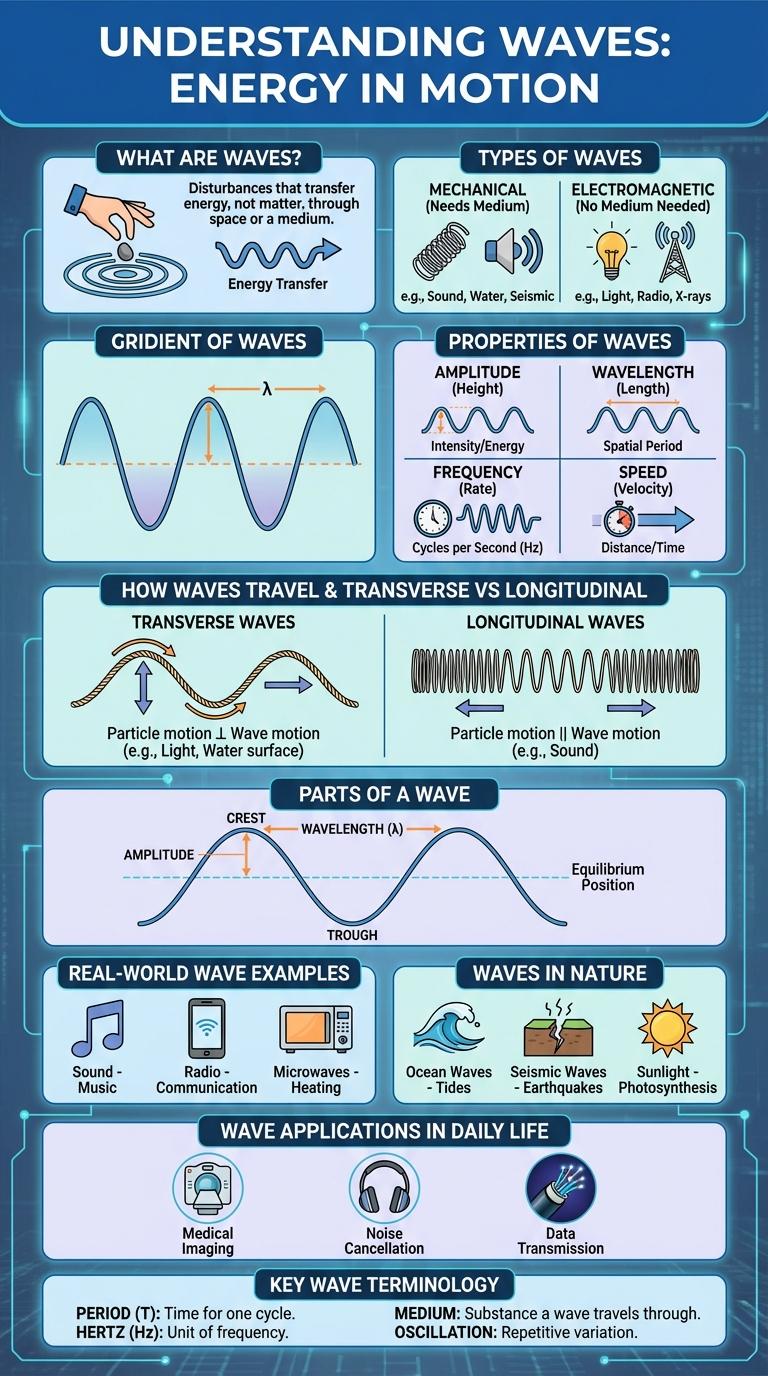
Waves are powerful natural phenomena that transfer energy through water, air, or other mediums in rhythmic patterns. Understanding the types, causes, and effects of waves offers insight into both environmental processes and everyday ocean experiences. This infographic visually breaks down the science and significance of waves, highlighting key concepts and fascinating facts.
What Are Waves?
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one point to another without the physical transport of matter. They occur in various forms including sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
- Mechanical Waves - Require a medium like air, water, or solids to travel through.
- Electromagnetic Waves - Do not need a medium and can travel through the vacuum of space.
- Wave Properties - Characterized by wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed.
Types of Waves
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through different mediums without transporting matter. Understanding the types of waves helps in various fields, from physics to communication technology.
There are two primary types of waves: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through, while electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum.
Properties of Waves
Waves transfer energy through a medium without transferring matter. Key properties of waves include wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed. These characteristics determine how waves behave and interact with their environment.
How Waves Travel
Waves transfer energy through a medium without the permanent displacement of particles. Understanding how waves travel helps explain phenomena in physics, oceanography, and communication technology.
- Mechanical waves require a medium - Mechanical waves travel through solids, liquids, or gases by causing particles to vibrate and pass energy along.
- Electromagnetic waves do not need a medium - These waves can travel through a vacuum, allowing light and radio waves to propagate through space.
- Waves move in different modes - Transverse waves move perpendicular to the wave direction, while longitudinal waves move parallel to it.
Transverse vs Longitudinal Waves
Waves transfer energy through different mediums by causing particles to oscillate in specific directions. Understanding transverse and longitudinal waves highlights their unique particle motion and wave propagation methods.
- Transverse Waves - Particles move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, creating crests and troughs.
- Longitudinal Waves - Particles oscillate parallel to the wave direction, forming compressions and rarefactions.
- Examples - Transverse waves include light and water waves, while sound waves exemplify longitudinal waves.
Both wave types are fundamental in physics, impacting fields such as acoustics, optics, and seismology.
Wave Applications in Daily Life
| Wave Type | Daily Life Application |
|---|---|
| Sound Waves | Communication through speech, music, and alarms |
| Light Waves | Vision, photography, and illumination |
| Radio Waves | Wireless communication such as radio, TV, and mobile phones |
| Microwaves | Cooking food, satellite communication, and radar technology |
| Water Waves | Recreational activities, coastal energy generation |
Parts of a Wave
Waves consist of several key parts including the crest, trough, wavelength, amplitude, and frequency. The crest is the highest point of the wave, while the trough is the lowest. Wavelength measures the distance between two crests, amplitude indicates wave height, and frequency refers to how often waves pass a point.
Real-World Wave Examples
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through various mediums, observable in both natural and man-made settings. Real-world wave examples demonstrate how energy moves in different forms, such as water, sound, and light waves.
Ocean waves exemplify mechanical waves, where wind energy causes water particles to oscillate and transfer energy across vast distances. Sound waves travel through air by compressing and rarefying particles, enabling communication and music. Electromagnetic waves, including visible light and radio waves, propagate through space, carrying energy without requiring a medium.
Waves in Nature
What are waves in nature and how do they form?
Waves in nature are disturbances that transfer energy through different mediums such as air, water, or earth. They occur due to various forces like wind, gravitational pull, or seismic activities.
How do ocean waves differ from sound waves?
Ocean waves are mechanical waves that travel through water, characterized by their crests and troughs. Sound waves are longitudinal waves that propagate through air or other gases by compressions and rarefactions.
What role do waves play in Earth's ecosystems?
Waves contribute to coastal erosion, sediment transport, and nutrient mixing in marine habitats. They influence the distribution and health of aquatic plants and animals.
How do seismic waves help scientists study natural disasters?
Seismic waves generated by earthquakes reveal information about Earth's interior structure. Monitoring these waves helps predict earthquakes and assess their impact.
What types of waves are commonly observed in nature?
| Wave Type | Description |
| Ocean Waves | Surface waves caused by wind energy on water |
| Sound Waves | Pressure waves traveling through air or solids |
| Seismic Waves | Energy waves from earthquakes traveling through Earth |
| Light Waves | Electromagnetic waves visible to the human eye |
