Exploring the vast universe through stunning visuals enhances understanding of complex astronomical concepts. Infographics about astronomy distill data on planets, stars, and cosmic phenomena into clear, engaging formats. These visual tools make celestial knowledge accessible and captivating for all audiences.
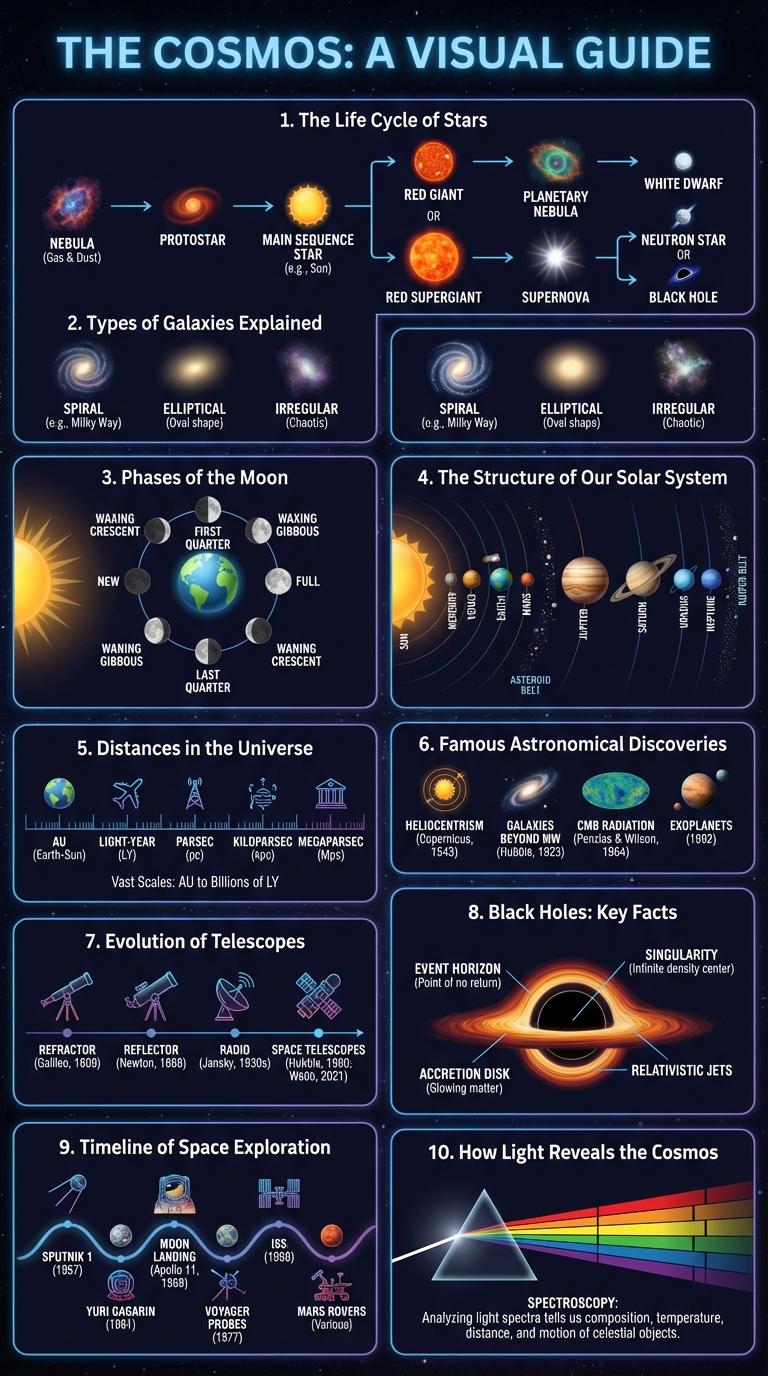
The Life Cycle of Stars
The life cycle of stars begins with a nebula, a vast cloud of gas and dust where gravity triggers the formation of a protostar. As the protostar gains mass, nuclear fusion ignites, marking its main sequence phase where it spends most of its life converting hydrogen into helium. The star's fate varies by mass, evolving into red giants or supergiants, and ultimately ending as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes.
Types of Galaxies Explained
| Type of Galaxy | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Spiral Galaxies | Flat, rotating disks with spiral arms, composed of stars, gas, and dust. Example: Milky Way. |
| Elliptical Galaxies | Elliptical or oval-shaped, containing older stars and less gas. Range from nearly spherical to elongated shapes. |
| Irregular Galaxies | Lack a defined shape, often chaotic, rich in gas and dust, sites of active star formation. Example: Large Magellanic Cloud. |
| Lenticular Galaxies | Disk-like structures without spiral arms, acting as a transition between spiral and elliptical galaxies. |
| Ring Galaxies | Ring-shaped structures formed due to gravitational interactions or collisions with other galaxies. |
Phases of the Moon
The Phases of the Moon illustrate the changing appearances of the Moon as observed from Earth over a lunar month. These phases result from the Moon's orbit around Earth and the varying angles of sunlight reflecting off its surface.
- New Moon - The Moon is positioned between Earth and the Sun, making it invisible from Earth's perspective.
- First Quarter - Half of the Moon's surface facing Earth is illuminated, appearing as a half-circle.
- Full Moon - The entire face of the Moon visible from Earth is fully lit by the Sun.
- Last Quarter - The Moon's illuminated half appears on the opposite side compared to the First Quarter phase.
- Waxing and Waning - Waxing phases show increasing illumination, while waning phases display decreasing illumination of the Moon.
Each lunar cycle takes approximately 29.5 days to complete all Moon phases, influencing tides and nocturnal illumination on Earth.
The Structure of Our Solar System
The structure of our solar system consists of the Sun at its center, surrounded by eight planets orbiting in elliptical paths. Inner planets, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, are rocky and smaller, while the outer planets--Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune--are gas giants with extensive moon systems. Beyond Neptune lies the Kuiper Belt, home to dwarf planets like Pluto, and the distant Oort Cloud, a spherical shell of icy bodies.
Distances in the Universe
The vastness of the universe is measured using various distance units that help astronomers understand the scale of cosmic objects. Distances range from kilometers within our solar system to billions of light-years for distant galaxies.
Accurate distance measurement is crucial for mapping the universe and studying celestial phenomena.
- Light-Year - The distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers, used to express distances to stars and galaxies.
- Parsec - Equal to about 3.26 light-years, this unit is derived from the parallax angle and is commonly used in astronomy for measuring stellar distances.
- Astronomical Unit (AU) - The average distance between Earth and the Sun, about 150 million kilometers, ideal for distances within our solar system.
Famous Astronomical Discoveries
Famous astronomical discoveries have shaped our understanding of the universe. Key breakthroughs include the identification of planets, the laws of planetary motion, and the expansion of the universe.
Galileo's telescopic observations revealed moons orbiting Jupiter, challenging geocentric models. Edwin Hubble's discovery of galaxy redshift provided evidence for the universe's expansion.
Evolution of Telescopes
The evolution of telescopes has revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Early refracting telescopes used lenses to magnify distant objects, enabling astronomers like Galileo to make groundbreaking discoveries.
Reflecting telescopes, introduced in the 17th century, use mirrors to gather light, allowing for larger apertures and clearer images. Modern telescopes, including space-based observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope, capture detailed data beyond Earth's atmosphere.
Black Holes: Key Facts
Black holes are regions in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. They form from the remnants of massive stars after supernova explosions.
Black holes can be classified by size: stellar, intermediate, and supermassive. The event horizon marks the boundary beyond which no information can return. Scientists study black holes through their interaction with nearby matter and gravitational waves.
Timeline of Space Exploration
When did human space exploration begin? The timeline of space exploration marks significant milestones starting in the mid-20th century. Key events highlight humanity's progress from launching the first satellite to landing on the moon and exploring distant planets.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1957 | Launch of Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite by the Soviet Union |
| 1961 | Yuri Gagarin becomes the first human in space |
| 1969 | Apollo 11 moon landing, first humans walk on the Moon |
| 1998 | Start of construction of the International Space Station (ISS) |
| 2020 | Perseverance rover lands on Mars to search for signs of past life |
