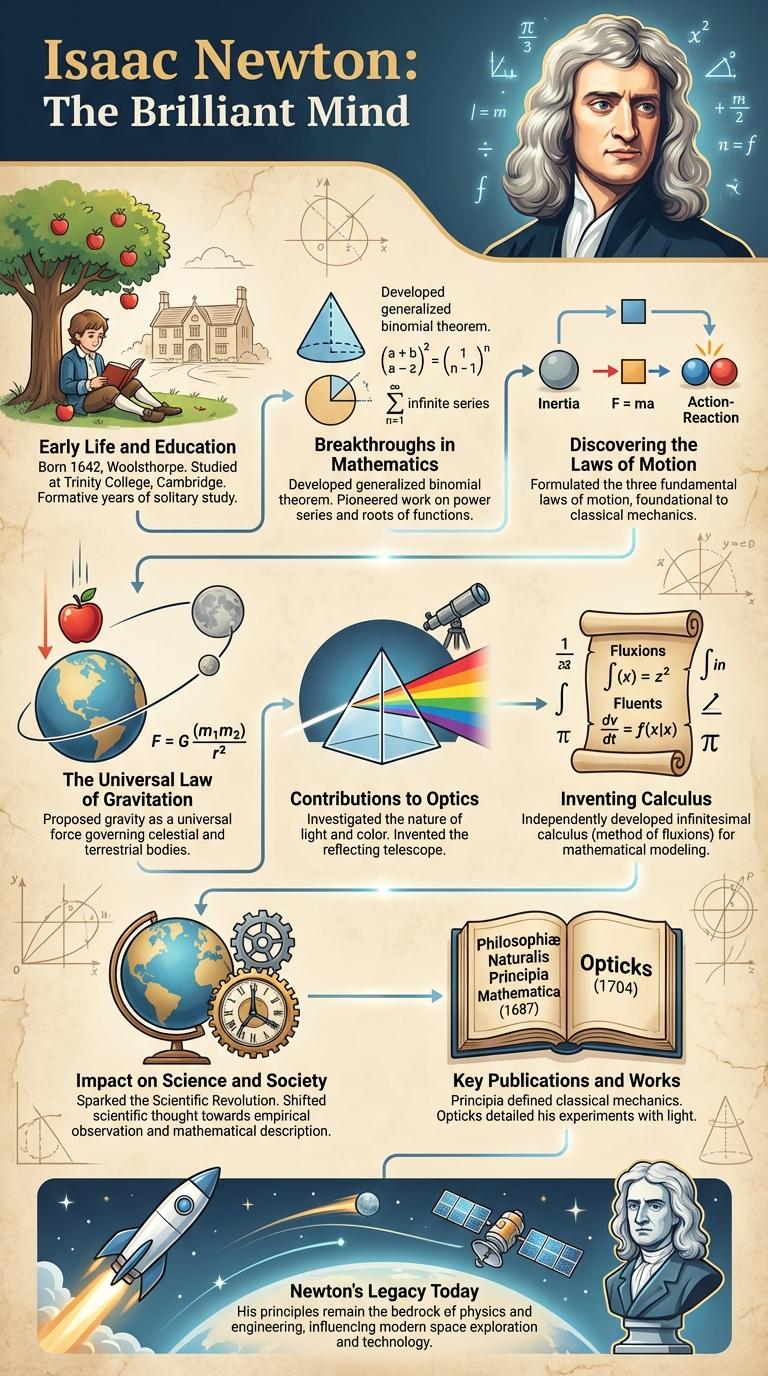
Isaac Newton revolutionized science with his groundbreaking discoveries in physics and mathematics. His laws of motion and universal gravitation laid the foundation for classical mechanics, influencing countless scientific advancements. This infographic highlights key moments and contributions that defined Newton's enduring legacy.
Isaac Newton: The Brilliant Mind
Isaac Newton was a pioneering physicist and mathematician whose work laid the foundation for classical mechanics. His laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized the scientific understanding of the natural world.
Newton's contributions extended beyond physics to mathematics, where he developed calculus independently. His genius transformed multiple scientific disciplines, earning him a place as one of history's most influential thinkers.
Early Life and Education
Sir Isaac Newton was born on January 4, 1643, in Woolsthorpe, England. His early education laid the foundation for groundbreaking discoveries in physics and mathematics.
- Birth and Family Background - Newton was born prematurely and raised by his grandmother after his father's death.
- Schooling - He attended the King's School in Grantham where he showed an early interest in mechanics and mathematics.
- University Education - Newton enrolled at Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1661, where he studied classical philosophy, mathematics, and physics.
Breakthroughs in Mathematics
Isaac Newton revolutionized mathematics with his development of calculus, enabling precise calculations of change and motion. His work laid the groundwork for modern mathematical analysis and scientific computation.
Newton formulated the binomial theorem for non-integer exponents, expanding algebraic understanding. He introduced methods to solve complex equations and developed infinite series expansions. His mathematical innovations remain foundational in physics, engineering, and economics today.
Discovering the Laws of Motion
Isaac Newton formulated the three fundamental Laws of Motion, which describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it. His First Law states that an object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. The Second Law quantifies force as the product of mass and acceleration, while the Third Law asserts that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
The Universal Law of Gravitation
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Isaac Newton |
| The Universal Law of Gravitation | Every particle attracts every other particle with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. |
| Formula | F = G * (m1 * m2) / r2 |
| Gravitational Constant (G) | 6.674 x 10-11 N*m2/kg2 |
| Significance | Explains planetary motion, tides, and objects falling towards Earth, foundational to classical physics and astronomy. |
Contributions to Optics
Isaac Newton made groundbreaking contributions to the field of optics that transformed scientific understanding of light and color. His work laid the foundation for modern optical physics and techniques.
- Discovery of the Spectrum - Newton demonstrated that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors by dispersing sunlight through a prism.
- Reflecting Telescope Invention - He designed the first practical reflecting telescope, improving image quality by reducing chromatic aberration.
- Particle Theory of Light - Newton proposed that light consists of particles called corpuscles, challenging the wave theory of his time.
Newton's optics experiments and theories remain fundamental in both physics and engineering disciplines.
Inventing Calculus
How did Isaac Newton revolutionize mathematics with his invention of calculus?
Isaac Newton developed calculus in the late 1660s to solve problems related to motion and change. His work laid the foundation for modern physics and engineering by providing tools to analyze varying quantities continuously.
Impact on Science and Society
Isaac Newton revolutionized science by formulating the laws of motion and universal gravitation, forming the foundation of classical mechanics. His work enabled precise predictions of planetary movements, advancing the field of astronomy significantly.
Newton's scientific breakthroughs influenced technology, engineering, and mathematics, shaping modern scientific thought. His impact extends beyond science, inspiring Enlightenment philosophy and transforming society's understanding of the natural world.
Key Publications and Works
Isaac Newton published "Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica" in 1687, outlining the laws of motion and universal gravitation. His work "Opticks" explored the properties of light and color, significantly advancing the study of optics. Newton's contributions laid the foundation for classical mechanics and profoundly influenced the scientific revolution.
