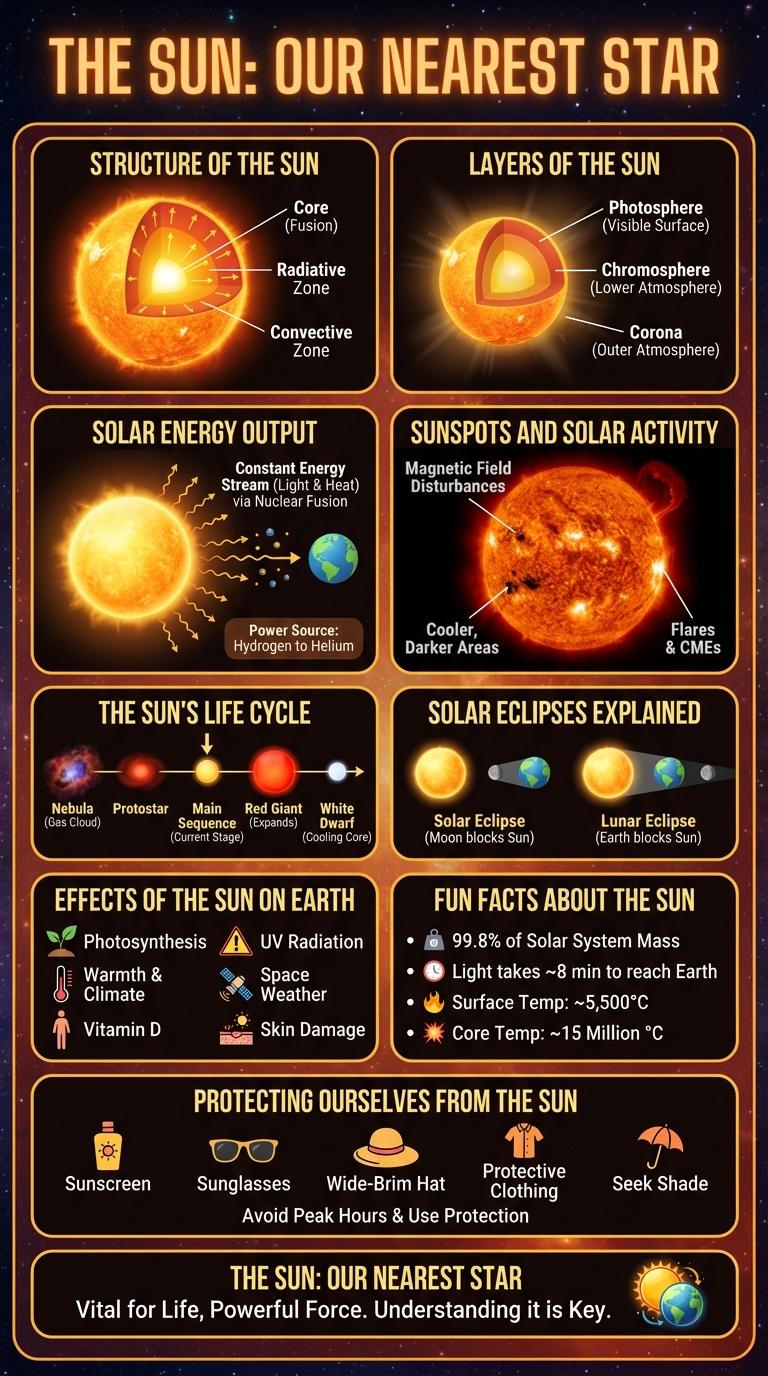
The infographic reveals key facts about the sun's structure, including its core, radiative zone, and corona. It highlights the sun's role as the primary source of energy for Earth, driving weather patterns and sustaining life. Sunspots and solar flares displayed in the infographic emphasize the sun's dynamic and ever-changing nature.
The Sun: Our Nearest Star
The Sun is a massive ball of hot, glowing plasma at the center of our solar system. It is the closest star to Earth, located about 93 million miles away. The Sun's energy supports life by providing light and heat essential for climate and ecosystems.
Structure of the Sun
The Sun is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma at the center of our solar system. It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, undergoing nuclear fusion to produce energy.
The Sun's structure includes several layers: the core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. Each layer plays a vital role in energy transfer and solar phenomena such as sunspots and solar flares.
Layers of the Sun
The Sun consists of several distinct layers, each playing a crucial role in its structure and function. The innermost layer is the core, where nuclear fusion generates immense energy. Surrounding the core are the radiative zone, the convective zone, the photosphere, and the outer atmospheric layers called the chromosphere and corona.
Solar Energy Output
The sun generates an immense amount of solar energy, producing approximately 384.6 yottawatts (YW) of power every second. This energy output surpasses global human energy consumption by thousands of times, highlighting its vast potential as a renewable resource.
Solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface averages about 1,368 watts per square meter at the top of the atmosphere. Only a fraction of this energy is harnessed through photovoltaic cells and solar thermal systems. Advances in solar technology are increasing efficiency, making solar power a key component of sustainable energy strategies worldwide.
Sunspots and Solar Activity
The Sun exhibits dynamic solar activity that influences space weather and Earth's climate. Sunspots are visible dark areas on the Sun's surface associated with intense magnetic activity.
- Sunspots - Cooler, darker regions on the Sun caused by concentrated magnetic fields blocking convection.
- Solar Cycle - An approximately 11-year cycle during which sunspot numbers wax and wane, affecting solar radiation.
- Solar Flares - Sudden releases of magnetic energy near sunspots that emit intense radiation and charged particles.
Solar activity, including sunspots and flares, drives phenomena such as auroras and can impact satellite communications and power grids on Earth.
The Sun's Life Cycle
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Protostar | Cloud of gas and dust contracts under gravity, heating up before nuclear fusion begins. |
| Main Sequence | Sun fuses hydrogen into helium, producing light and heat over approximately 10 billion years. |
| Red Giant | Hydrogen fuel depletes; Sun expands and cools while fusing helium in its core. |
| Planetary Nebula | Outer layers are ejected into space, forming a glowing shell of gas around the core. |
| White Dwarf | Remaining core cools and shrinks, emitting residual heat over billions of years. |
Solar Eclipses Explained
Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, temporarily blocking the Sun's light. These events create dramatic changes in daylight and are visible only from specific locations on Earth.
- Total Solar Eclipse - The Moon completely covers the Sun, resulting in a brief period of darkness during daytime.
- Partial Solar Eclipse - Only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon, causing a partial dimming of sunlight.
- Annular Solar Eclipse - The Moon covers the Sun's center, leaving a bright ring or "annulus" of the Sun visible around the edges.
Effects of the Sun on Earth
How does the Sun affect Earth's climate and environment? The Sun is the primary source of energy for our planet, driving weather patterns and ocean currents. Solar radiation influences temperature, enabling life to thrive on Earth.
What role does the Sun play in photosynthesis? Sunlight provides energy for plants to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process forms the base of the food chain and sustains ecosystems worldwide.
How does the Sun impact Earth's magnetic field? Solar wind interacts with Earth's magnetosphere, causing phenomena like the aurora borealis and australis. These interactions protect the planet from harmful cosmic radiation.
Can solar activity affect human technology? Solar flares and coronal mass ejections can disrupt satellite communications, GPS systems, and power grids. Monitoring solar activity is crucial for mitigating potential damage.
In what ways does the Sun influence Earth's water cycle? Solar energy drives evaporation, leading to cloud formation and precipitation. This cycle maintains freshwater availability and supports diverse habitats.
Fun Facts About the Sun
The Sun is a massive ball of hot plasma at the center of our solar system, providing essential energy for all life on Earth. It consists mainly of hydrogen and helium, undergoing nuclear fusion to produce light and heat.
The Sun's surface temperature reaches approximately 5,500 degrees Celsius, while its core can soar up to 15 million degrees Celsius. Solar flares and sunspots frequently occur, influencing space weather and Earth's magnetic environment.
