The urinary system plays a vital role in filtering waste and maintaining fluid balance in the body. Comprising the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, it efficiently removes toxins and excess fluids through urine. Understanding this complex network can help promote better health and early detection of urinary conditions.
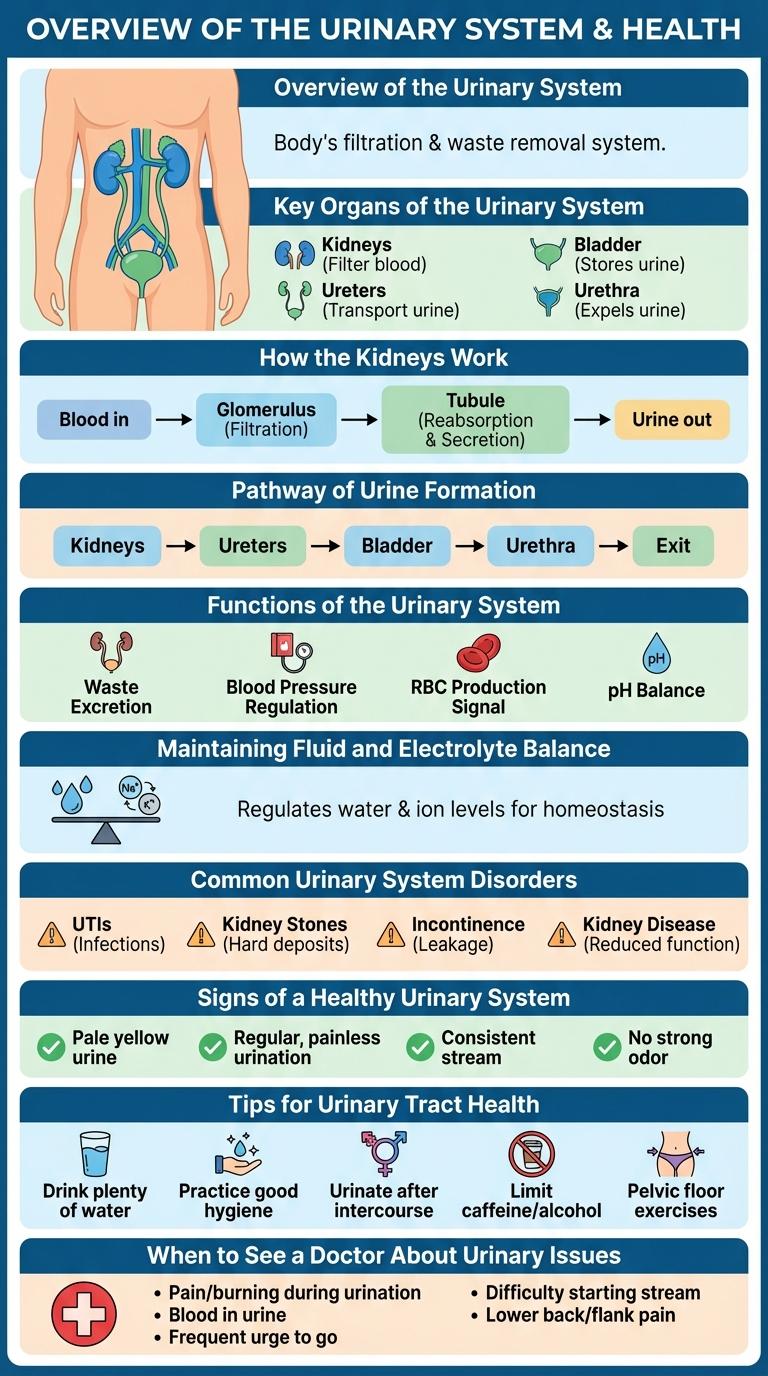
Overview of the Urinary System
The urinary system is responsible for removing waste and excess fluids from the bloodstream to maintain the body's fluid and electrolyte balance. Key organs involved include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Kidneys - These bean-shaped organs filter blood to produce urine and regulate vital substances like electrolytes and blood pressure.
- Ureters - Tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the bladder for temporary storage.
- Bladder - A muscular sac that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body.
Key Organs of the Urinary System
The urinary system is vital for filtering blood and producing urine to eliminate waste. Key organs include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Each organ plays a specific role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Kidneys | Filter blood to produce urine and regulate electrolytes |
| Ureters | Transport urine from kidneys to bladder |
| Bladder | Stores urine until it is expelled |
| Urethra | Conducts urine out of the body |
How the Kidneys Work
The kidneys filter blood to remove waste products and excess fluids, forming urine. Each kidney contains around one million nephrons, the microscopic filtering units that regulate water and electrolyte balance.
Blood enters the kidneys through the renal arteries and passes through the nephrons, where filtration, reabsorption, and secretion occur. Processed fluid then moves to the ureters, transporting urine to the bladder for storage before elimination.
Pathway of Urine Formation
The urinary system plays a vital role in filtering blood and forming urine to remove waste from the body. Urine formation occurs primarily in the kidneys through a complex, multi-step process.
Filtration starts in the glomerulus, where blood plasma is filtered into Bowman's capsule. Reabsorption then takes place in the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule, returning essential substances to the bloodstream. Finally, secretion in the distal tubule adds additional wastes to the urine before it flows into the collecting duct and onward to the bladder.
Functions of the Urinary System
The urinary system is responsible for filtering waste products and excess substances from the blood, forming urine. It helps maintain the body's fluid and electrolyte balance by regulating the volume and composition of blood. The system also plays a key role in controlling blood pressure and red blood cell production through hormone secretion.
Maintaining Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
The urinary system plays a vital role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. It filters blood, removes waste, and regulates essential minerals to support homeostasis.
- Filtration of Blood - The kidneys filter excess fluids and electrolytes, removing toxins and maintaining stable blood composition.
- Reabsorption Processes - Selective reabsorption in the nephrons ensures necessary electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and calcium are returned to the bloodstream.
- Hormonal Regulation - Hormones such as aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone adjust urine concentration to control fluid and electrolyte levels.
Proper kidney function ensures balanced hydration and electrolyte levels essential for nerve and muscle function.
Common Urinary System Disorders
The urinary system plays a crucial role in filtering waste and maintaining fluid balance. Understanding common urinary system disorders helps promote early detection and treatment.
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) - Caused by bacteria, UTIs result in painful urination and frequent urge to urinate.
- Kidney Stones - Hard deposits formed in kidneys that cause severe pain and possible urinary blockage.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) - Progressive loss of kidney function leading to waste accumulation in the body.
Signs of a Healthy Urinary System
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear, Light-Colored Urine | Indicates proper hydration and normal kidney function. |
| Regular Urination Frequency | Typically 4-8 times per day, showing normal bladder activity. |
| Absence of Pain During Urination | Signals no infections or inflammation in the urinary tract. |
| Normal Urine Output | Averaging 1-2 liters daily, reflecting balanced fluid intake and kidney health. |
| No Blood in Urine | Indicates the urinary tract is free from injury or infection. |
Tips for Urinary Tract Health
How can you maintain a healthy urinary tract? Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria and toxins, reducing the risk of infections. Regular urination and good hygiene practices also support urinary tract health.
What foods promote urinary tract health? Consuming cranberries and blueberries provides antioxidants that may prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls. Avoiding excessive caffeine and spicy foods can reduce irritation and inflammation.
Why is urine color important for urinary health? Clear or light yellow urine generally indicates proper hydration and good kidney function. Dark urine may signal dehydration or possible infection requiring medical attention.
How do lifestyle habits affect urinary tract health? Regular exercise helps maintain overall bodily function including the urinary system. Avoiding smoking and managing chronic conditions like diabetes improves urinary tract resilience.
When should you see a doctor for urinary symptoms? Persistent pain, burning sensation during urination, or frequent urges can indicate urinary tract infections or other issues needing prompt medical care. Early diagnosis prevents complications and promotes faster recovery.
