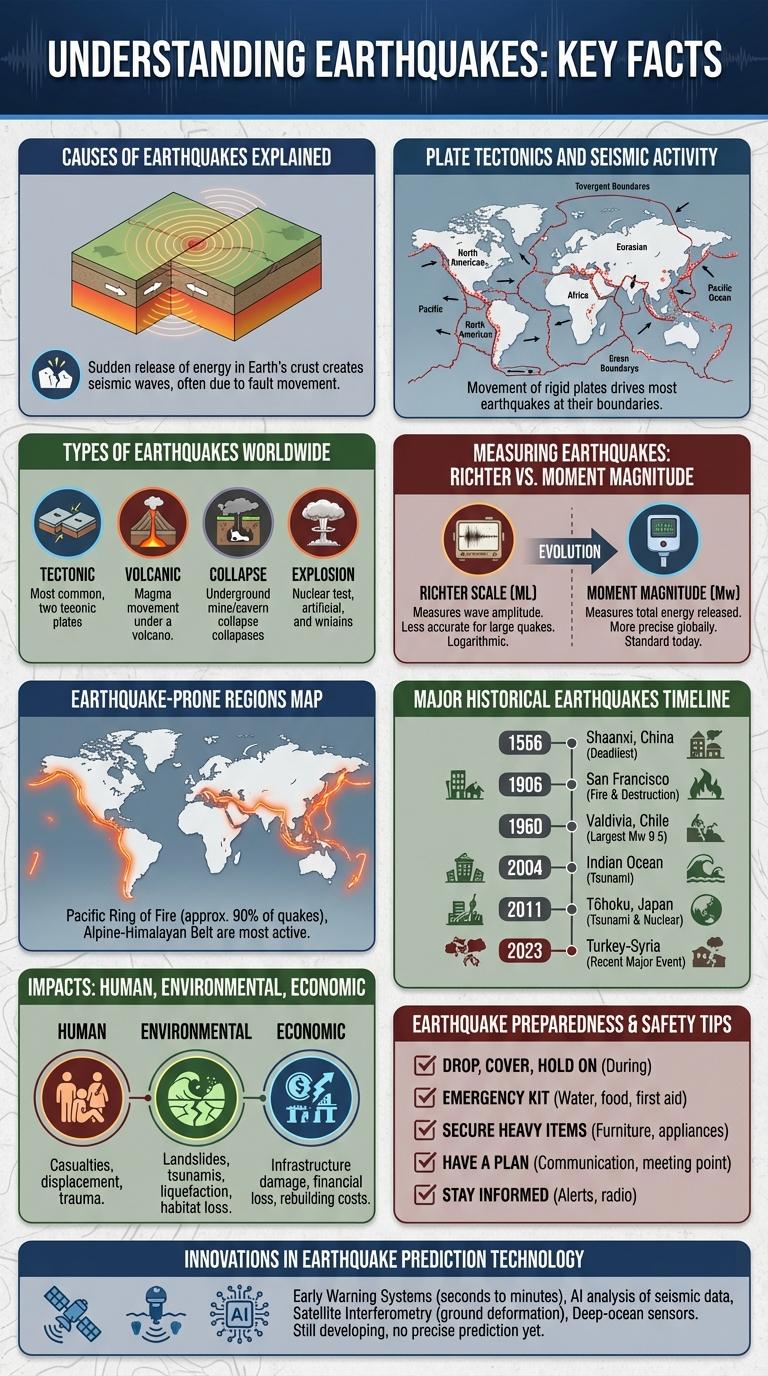
An earthquake PowerPoint infographic presents crucial data in a visually engaging format, simplifying complex seismic information. It highlights key aspects such as causes, effects, and safety measures to enhance audience understanding. Using clear icons and concise text ensures effective communication for educational or professional presentations.
Understanding Earthquakes: Key Facts
Earthquakes are natural phenomena caused by the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, resulting in seismic waves. Understanding the key facts about earthquakes helps in disaster preparedness and risk reduction.
- Causes of Earthquakes - Earthquakes mainly occur due to the movement of tectonic plates along fault lines.
- Seismic Magnitude - The Richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake based on the energy released.
- Impact on Structures - Strong earthquakes can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure, posing safety hazards.
Causes of Earthquakes Explained
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Tectonic Plate Movements | Earthquakes occur when stress builds up due to the movement of Earth's tectonic plates, causing sudden energy release along faults. |
| Volcanic Activity | Magma movement beneath the surface can create pressure and cracks, resulting in volcanic earthquakes near active volcanoes. |
| Human Activities | Activities like mining, reservoir-induced seismicity from large dams, and underground nuclear tests can trigger earthquakes. |
| Stress Accumulation | Accumulated stress over time in the earth's crust causes fractures, leading to faults slipping and generating seismic waves. |
| Isostatic Rebound | Earth's crust adjusts after being weighed down by ice sheets or sediment, causing earthquakes during the rebound process. |
Plate Tectonics and Seismic Activity
Plate tectonics describes the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath. These plate interactions, including convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries, generate significant seismic activity. Earthquakes primarily occur along these boundaries due to the buildup and release of stress caused by plate movements.
Types of Earthquakes Worldwide
Earthquakes occur due to sudden releases of energy in the Earth's crust, resulting in seismic waves. Different types of earthquakes are classified based on their origin and movement along fault lines.
Common types of earthquakes include tectonic, volcanic, and collapse earthquakes. Tectonic earthquakes are the most prevalent, caused by the movement of tectonic plates worldwide.
Measuring Earthquakes: Richter vs. Moment Magnitude
Earthquake measurement is crucial for understanding seismic activity and preparing for potential hazards. Two primary scales used are the Richter and Moment Magnitude scales, each with distinct methods for quantifying earthquake size.
The Richter scale quantifies earthquake magnitude based on recorded seismic waves, mainly effective for small to medium earthquakes near the epicenter. The Moment Magnitude scale measures the total energy released, providing a more accurate estimate for large, distant earthquakes.
- Richter Scale - Measures earthquake magnitude using amplitude of seismic waves recorded by seismographs.
- Moment Magnitude Scale - Calculates magnitude based on seismic moment, reflecting fault area and slip.
- Applicability - Richter is suitable for local, moderate earthquakes, while Moment Magnitude is reliable globally and for large events.
Earthquake-Prone Regions Map
An earthquake-prone regions map highlights areas with frequent seismic activity worldwide. These maps use color codes to represent varying levels of earthquake risk, aiding in disaster preparedness and mitigation. Key regions include the Pacific Ring of Fire, parts of Asia, and the Mediterranean belt.
Major Historical Earthquakes Timeline
An infographic about earthquake PPT highlights the Major Historical Earthquakes Timeline. It visually represents significant seismic events that shaped geological understanding.
The timeline includes key earthquakes such as the 1906 San Francisco quake, the 1960 Valdivia earthquake in Chile, and the 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan. These events are marked by their magnitude, impact, and contribution to advancing earthquake science.
Impacts: Human, Environmental, Economic
Earthquakes cause profound impacts on human populations, the environment, and economies worldwide. Understanding these effects is crucial for disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Human Impact - Earthquakes result in loss of life, injuries, and displacement of communities, severely affecting social structures.
- Environmental Impact - Seismic activity triggers landslides, soil liquefaction, and changes in landforms, disrupting ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Economic Impact - Infrastructure damage and business interruptions lead to significant economic losses and long-term recovery costs.
Effective earthquake response plans mitigate these impacts and enhance community resilience.
Earthquake Preparedness & Safety Tips
What are the essential steps to prepare for an earthquake? Preparing for an earthquake involves creating an emergency plan and assembling a safety kit with supplies like water, food, and first-aid materials. Knowing safe spots indoors and practicing drop, cover, and hold techniques can significantly reduce injury during a quake.
How can you ensure your home is safe during an earthquake? Securing heavy furniture, appliances, and gas lines helps prevent damage and injury. Reinforcing walls and fixing structural weaknesses also improve home safety in seismic events.
Why is it important to stay calm and informed during an earthquake? Staying calm helps you make quicker decisions and avoid panic. Listening to emergency broadcasts provides crucial updates and instructions for safety measures.
What should you include in an earthquake emergency kit? A comprehensive kit contains water, non-perishable food, flashlight, batteries, a first aid kit, and important documents. Having these ready ensures basic needs are met during power outages or displacement.
How can communities enhance earthquake preparedness collectively? Community drills, educational workshops, and clear communication channels increase overall readiness. Collaborating on risk assessment helps implement local safety improvements effectively.
