Metabolism refers to the complex biochemical processes that convert food into energy necessary for bodily functions. This infographic visualizes key components and stages of metabolic pathways, highlighting how nutrients are transformed and utilized. Understanding metabolism helps in managing weight, improving energy levels, and enhancing overall health.
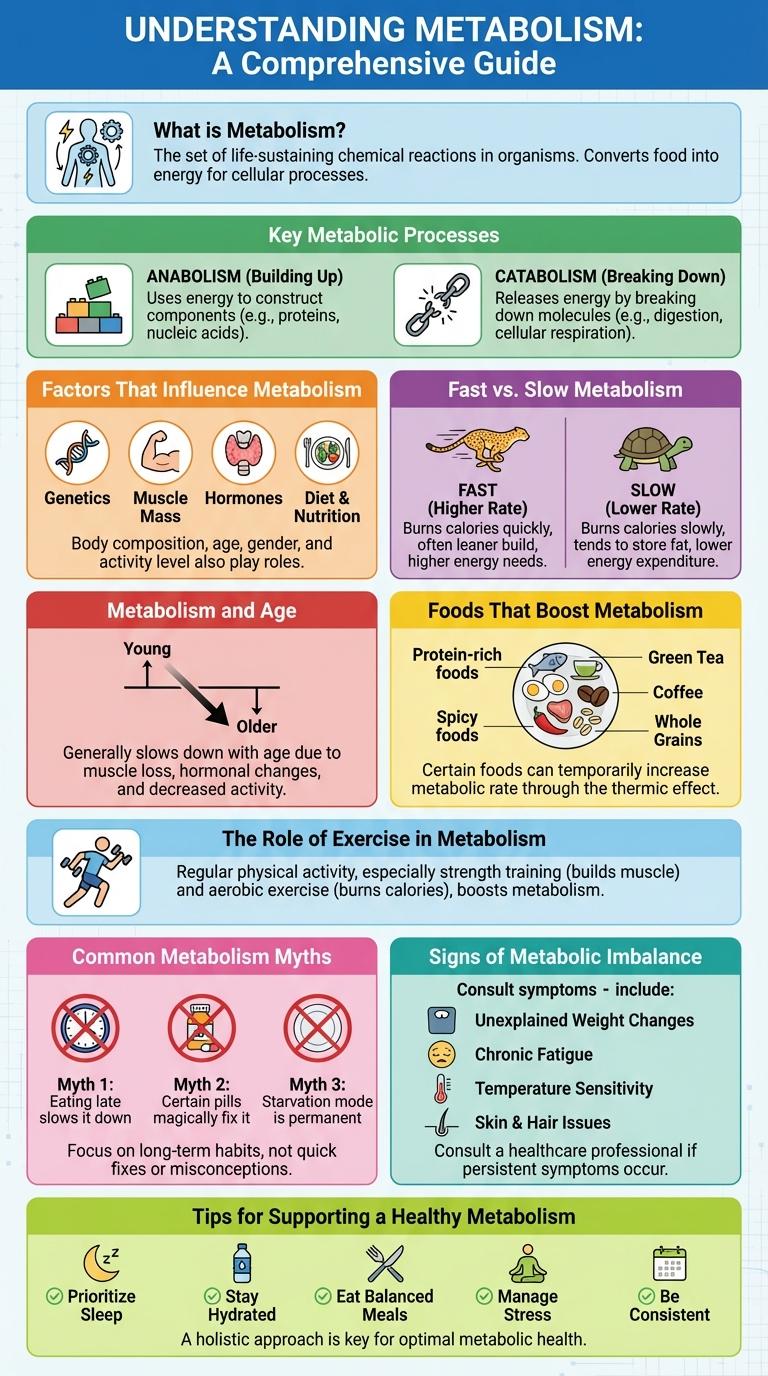
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that occur within living organisms to maintain life. It converts food into energy and building blocks for growth and repair.
These biochemical processes are divided into catabolism, which breaks down molecules to release energy, and anabolism, which uses energy to synthesize essential compounds. Metabolism regulates how efficiently the body uses fuel and manages energy balance. A healthy metabolism is crucial for maintaining overall vitality and proper bodily functions.
Key Metabolic Processes
Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions that sustain life within cells. It converts food into energy and building blocks for growth and repair.
- Catabolism - Breaks down molecules to release energy used by the body.
- Anabolism - Builds complex molecules from simpler ones, supporting cell growth and repair.
- ATP Production - Generates adenosine triphosphate as the main energy currency for cellular activities.
Factors That Influence Metabolism
Metabolism is the process by which the body converts food into energy, impacting overall health and weight management. Factors influencing metabolism include age, muscle mass, genetics, and hormone levels, each altering how efficiently the body burns calories. Lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and sleep also play crucial roles in regulating metabolic rate.
Fast vs. Slow Metabolism
Metabolism is the process by which your body converts food into energy. Fast and slow metabolism rates influence how quickly calories are burned.
- Fast Metabolism - Burns calories quickly, aiding in weight management and higher energy levels.
- Slow Metabolism - Processes calories at a slower rate, often leading to weight gain if calorie intake is not adjusted.
- Factors Affecting Metabolism - Age, genetics, muscle mass, and physical activity significantly impact metabolic speed.
Understanding your metabolism type helps tailor diet and exercise plans for optimal health results.
Metabolism and Age
| Age Group | Average Metabolic Rate Impact |
|---|---|
| Teens (13-19 years) | Highest metabolic rate due to growth and development |
| Young Adults (20-39 years) | Stable metabolic rate, supporting daily energy needs |
| Middle Age (40-59 years) | Metabolic rate declines approximately 5-10% per decade |
| Senior Adults (60+ years) | Significant metabolic slowdown contributing to weight gain |
| Factors Accelerating Decline | Muscle loss, hormonal changes, decreased physical activity |
Foods That Boost Metabolism
Metabolism is the process through which your body converts food into energy. Certain foods can help increase metabolic rate and support weight management.
- Green Tea - Contains antioxidants and caffeine that enhance fat oxidation and boost metabolic rate.
- Protein-Rich Foods - Require more energy to digest, increasing the thermic effect and stimulating metabolism.
- Chili Peppers - Contain capsaicin, which can raise metabolic rate by promoting calorie burning.
The Role of Exercise in Metabolism
How does exercise influence metabolism? Exercise significantly boosts metabolic rate by increasing energy expenditure both during and after physical activity. Regular physical activity enhances muscle mass, which in turn elevates resting metabolic rate.
What types of exercise are best for metabolism? High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and strength training are most effective in stimulating metabolism. These exercises promote fat loss and muscle growth, sustaining a higher metabolic rate over time.
How long does exercise impact metabolism? Metabolic rate can remain elevated for several hours post-exercise, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). The duration of EPOC depends on exercise intensity and duration.
Can exercise overcome a slow metabolism? While genetics influence metabolism, consistent exercise can significantly improve metabolic efficiency. Combining aerobic and resistance training yields the best results in optimizing metabolic function.
What role does muscle mass play in metabolism? Muscle tissue requires more energy to maintain than fat, increasing resting metabolic rate. Building and preserving muscle through resistance training is crucial for long-term metabolic health.
Common Metabolism Myths
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that occur within a living organism to maintain life. It encompasses all the biochemical reactions involved in converting food into energy.
Many myths surround metabolism, often leading to misconceptions about weight management and health. Understanding these myths helps in adopting realistic lifestyle choices for better wellness.
Signs of Metabolic Imbalance
Metabolic imbalance occurs when the body's ability to convert food into energy is disrupted. This imbalance can affect various bodily functions and overall health.
Common signs of metabolic imbalance include unexplained weight changes and persistent fatigue. Other indicators are frequent headaches and difficulty concentrating.
