Infographics about emotions visually break down complex feelings into easily understandable segments, allowing for quick comprehension and emotional awareness. They use colors, icons, and concise text to represent various emotions, helping viewers identify and relate to their own experiences. Such visual tools enhance emotional intelligence by simplifying how people recognize and manage their feelings.
Understanding Core Human Emotions
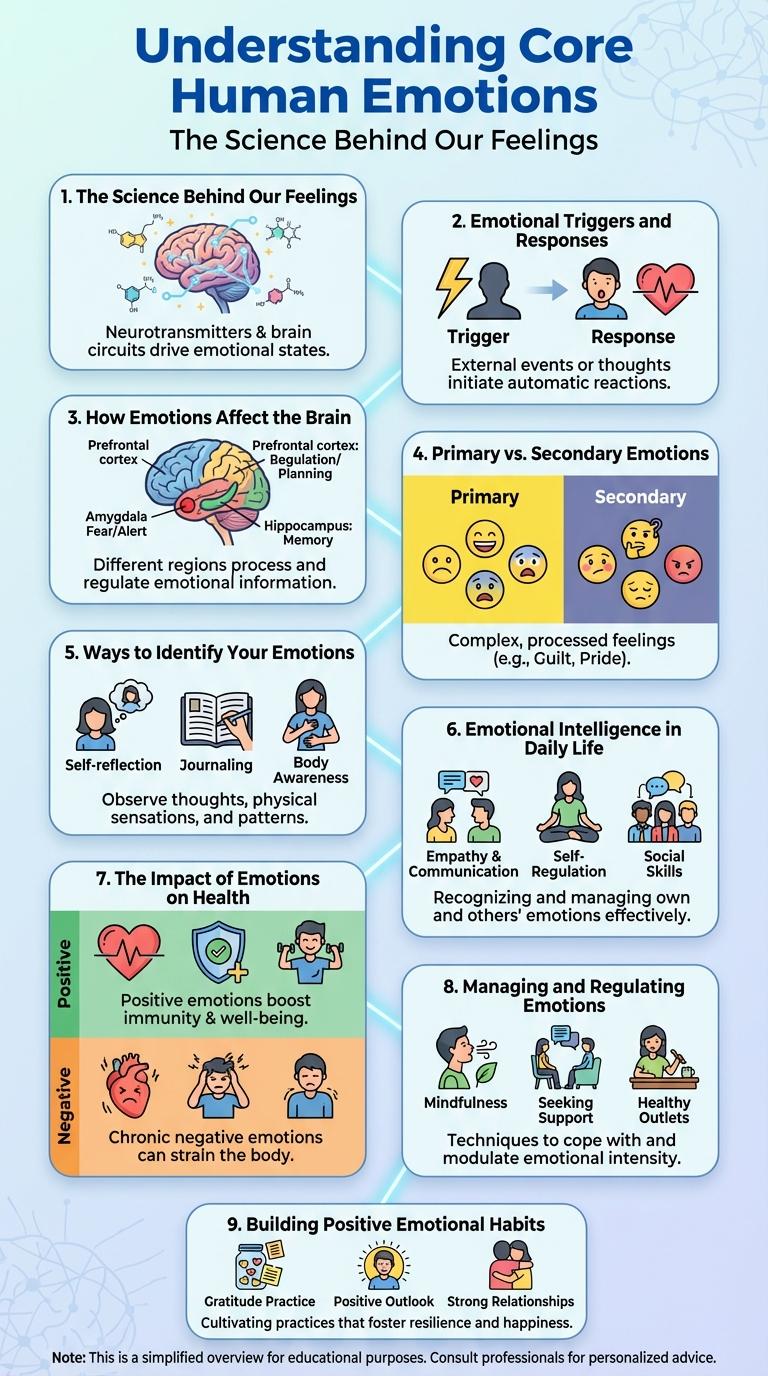
Core human emotions form the foundation of our psychological experience, influencing thoughts, behaviors, and social interactions. Recognizing these emotions helps individuals improve emotional intelligence and empathy.
Psychologists often classify core emotions into categories such as happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, and disgust. Each emotion triggers distinct physiological and cognitive responses vital for survival and communication.
The Science Behind Our Feelings
What happens in our brain when we experience emotions? Emotions are complex reactions involving multiple brain regions that interpret stimuli and generate feelings. The amygdala plays a crucial role in processing emotional responses, especially fear and pleasure.
How do hormones influence our emotions? Hormones like cortisol, adrenaline, and oxytocin impact mood and emotional regulation by altering brain function and body chemistry. These biochemical changes help the body respond to stress, bonding, and reward.
Can emotions affect our physical health? Yes, prolonged emotional stress can increase the risk of heart disease, weaken the immune system, and cause chronic inflammation. Understanding this connection highlights the importance of managing emotional well-being.
What role does the autonomic nervous system play in emotions? It controls physiological reactions such as heart rate, respiration, and sweating that accompany emotions. This system helps prepare the body for fight-or-flight or relaxation depending on emotional stimuli.
How do different brain regions cooperate during emotional experiences?
| Brain Region | Role in Emotions |
|---|---|
| Amygdala | Processes fear and pleasure signals |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Regulates emotion and decision-making |
| Hippocampus | Links emotions to memories |
| Hypothalamus | Controls hormonal responses |
| Insula | Processes bodily awareness and empathy |
Emotional Triggers and Responses
Emotional triggers are specific events or stimuli that provoke strong emotional reactions in individuals. Common triggers include stress, memories, and social interactions, which can lead to responses such as anxiety, joy, or anger. Understanding these triggers helps manage emotions effectively and improve mental well-being.
How Emotions Affect the Brain
Emotions play a crucial role in shaping brain function and overall mental health. Understanding how emotions impact neural activity helps in managing stress and improving cognitive performance.
- Emotions Activate the Amygdala - The amygdala processes emotional responses, especially fear and pleasure, influencing memory formation and decision-making.
- Prefrontal Cortex Regulates Emotions - This brain region controls emotional responses by assessing risk and reward, contributing to self-control and social behavior.
- Emotional Stress Affects Neuroplasticity - Chronic stress from negative emotions can reduce the brain's ability to adapt and form new connections, impacting learning.
Primary vs. Secondary Emotions
Emotions can be categorized into primary and secondary types based on their origin and complexity. Understanding the distinction helps in recognizing how feelings influence behavior and decision-making.
Primary emotions are instinctive and universal, while secondary emotions develop from social and personal experiences.
- Primary Emotions - These are basic, innate emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust.
- Secondary Emotions - These emotions are complex and often arise from a combination of primary emotions influenced by individual experiences and social context.
- Emotional Development - Secondary emotions typically emerge later in life, shaped by culture and personal understanding of social interactions.
Ways to Identify Your Emotions
Understanding your emotions begins with paying close attention to physical sensations, such as tension or warmth, that signal specific feelings. Observing your thoughts and reactions during different situations helps pinpoint emotional triggers. Journaling regularly provides insight into patterns and deepens emotional awareness over time.
Emotional Intelligence in Daily Life
Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to identify, understand, and manage emotions in oneself and others. It plays a crucial role in enhancing communication and relationships in daily life.
High emotional intelligence helps individuals navigate social complexities and resolve conflicts effectively. It improves decision-making by incorporating emotional data with rational thought. Developing EI leads to greater empathy, self-awareness, and stress management, promoting overall well-being.
The Impact of Emotions on Health
| Emotion | Impact on Health |
|---|---|
| Stress | Increases risk of heart disease, weakens immune system, elevates blood pressure |
| Happiness | Boosts immune function, lowers pain perception, improves cardiovascular health |
| Anger | Triggers inflammation, raises cortisol levels, associated with higher risk of stroke |
| Sadness | Linked to fatigue, decreased immune response, potential for chronic illness |
| Fear | Activates fight-or-flight response, increases heart rate, may cause digestive issues |
Managing and Regulating Emotions
Managing and regulating emotions is essential for maintaining mental well-being and fostering healthy relationships. Effective emotional regulation helps individuals respond to situations thoughtfully rather than react impulsively.
Techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive reappraisal, and deep breathing enhance emotional control. These methods reduce stress and improve decision-making by promoting awareness and adaptive responses.
