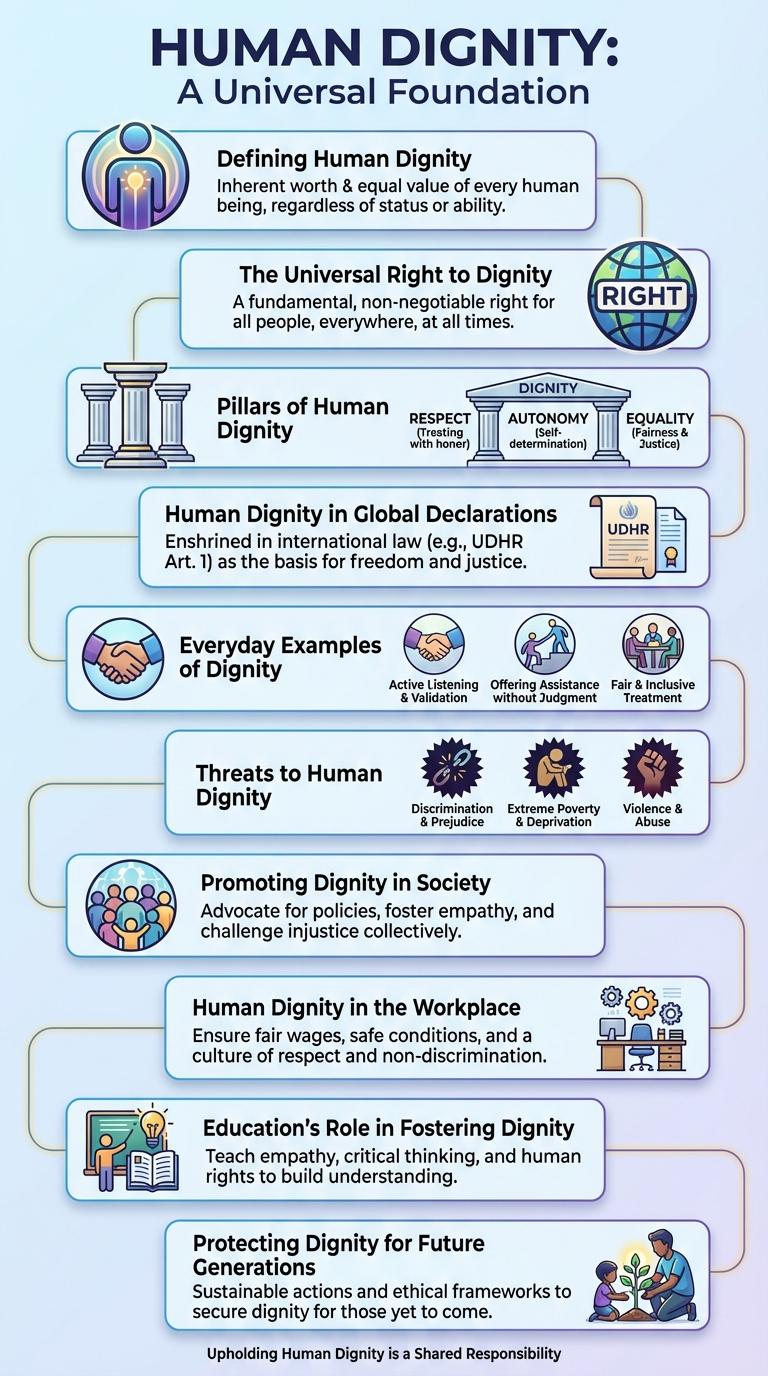
Human dignity represents the intrinsic worth and respect every individual deserves regardless of background or status. This infographic visually highlights key principles and universal rights that uphold human dignity in society. Understanding these elements fosters empathy and promotes equitable treatment for all people.
Defining Human Dignity
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Human dignity refers to the intrinsic worth of every individual, regardless of race, gender, status, or abilities. |
| Philosophical Roots | Rooted in ethical and moral philosophy emphasizing respect, autonomy, and equality. |
| Legal Recognition | Found in international documents such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. |
| Core Principles | Respect, equality, freedom, and non-discrimination constitute the foundation of human dignity. |
| Importance | Ensures protection of rights and fosters social justice and peace within communities. |
The Universal Right to Dignity
Human dignity is a fundamental human right recognized universally across cultures and legal systems. It guarantees every individual respect, equality, and protection from degrading treatment. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights explicitly affirms the inherent dignity and equal rights of all members of the human family.
Pillars of Human Dignity
Human dignity is the intrinsic worth that every person holds, deserving of respect and ethical treatment. Recognizing the pillars of human dignity helps uphold fundamental human rights and justice.
- Respect for Autonomy - Each individual has the right to make decisions about their own life and body.
- Equality - All humans possess equal value regardless of race, gender, or status.
- Recognition - Acknowledging identity, culture, and personal beliefs fosters dignity.
Protecting these pillars ensures a just and humane society where dignity is preserved for all.
Human Dignity in Global Declarations
What is the role of Human Dignity in global declarations?
Human dignity is a foundational principle in international human rights law. It emphasizes the inherent worth of every person, guiding the protection and promotion of fundamental rights worldwide.
Which global declarations explicitly reference Human Dignity?
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) prominently highlights human dignity as central to rights and freedoms. The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966) and the Charter of the United Nations also affirm this principle.
How does the Universal Declaration of Human Rights emphasize Human Dignity?
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration states that "all human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights." This establishes a universal standard that underpins respect for individual value and equality.
Why is Human Dignity important in the Charter of the United Nations?
The UN Charter recognizes human dignity as essential for maintaining peace and security. It fosters cooperation among nations on the basis of mutual respect for fundamental human rights.
| Declaration | Focus on Human Dignity |
|---|---|
| Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) | Recognizes dignity as the foundation of freedom, justice, and peace. |
| International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966) | Affirms protection of personal dignity through civil and political rights. |
| Charter of the United Nations (1945) | Emphasizes dignity as core to peaceful international relations. |
| International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (1966) | Links dignity to social and economic rights for all individuals. |
| Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989) | Highlights respect for dignity in the protection of children's rights. |
Everyday Examples of Dignity
Human dignity is reflected in everyday actions that show respect and kindness toward others. Simple gestures like listening attentively and valuing someone's opinion reinforce their sense of worth.
Respecting personal space and privacy in public or work settings preserves individual dignity. Offering help without judgment and acknowledging others' efforts fosters a supportive environment.
Threats to Human Dignity
Human dignity is the inherent worth and respect every individual deserves. Threats to human dignity arise when this fundamental respect is violated.
Common threats to human dignity include discrimination, exploitation, and violence. These actions undermine self-respect and societal equality.
Promoting Dignity in Society
Human dignity is the inherent worth of every individual, deserving respect and ethical treatment. Promoting dignity in society fosters inclusion, equality, and mutual respect among all members.
- Equal Rights - Ensuring equal access to education, healthcare, and employment upholds human dignity.
- Anti-Discrimination - Combating prejudice based on race, gender, or background protects individual dignity.
- Empowerment - Supporting personal growth and community participation strengthens societal respect for dignity.
Human Dignity in the Workplace
Human dignity in the workplace ensures respect, fairness, and equality for all employees, fostering a positive work environment. Recognizing each individual's inherent worth promotes collaboration, motivation, and productivity. Upholding human dignity reduces discrimination, harassment, and workplace conflicts, leading to long-term organizational success.
Education's Role in Fostering Dignity
Human dignity is a fundamental human right that emphasizes respect, worth, and equality for every individual. Education plays a vital role in fostering this dignity by promoting understanding and empathy.
Effective education systems teach values such as respect, fairness, and human rights, empowering students to appreciate themselves and others. Inclusive curricula that celebrate diversity reduce discrimination and encourage social harmony. Developing critical thinking skills helps learners challenge stereotypes and advocate for justice, enhancing a culture of dignity.
