Limited access to quality education significantly hinders personal and societal growth, perpetuating cycles of poverty and inequality. Lack of education restricts job opportunities, reduces income potential, and limits social mobility. This infographic highlights key statistics and consequences of educational disparities worldwide.
The Global Education Gap
The global education gap remains a critical challenge, affecting millions of children worldwide. Access to quality education varies significantly between regions, income levels, and genders.
- Unequal Access - Over 258 million children and youth are out of school globally, highlighting significant disparities.
- Regional Disparities - Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia have the highest rates of children lacking basic education opportunities.
- Gender Inequality - Girls are disproportionately affected, with nearly 130 million girls worldwide not attending school.
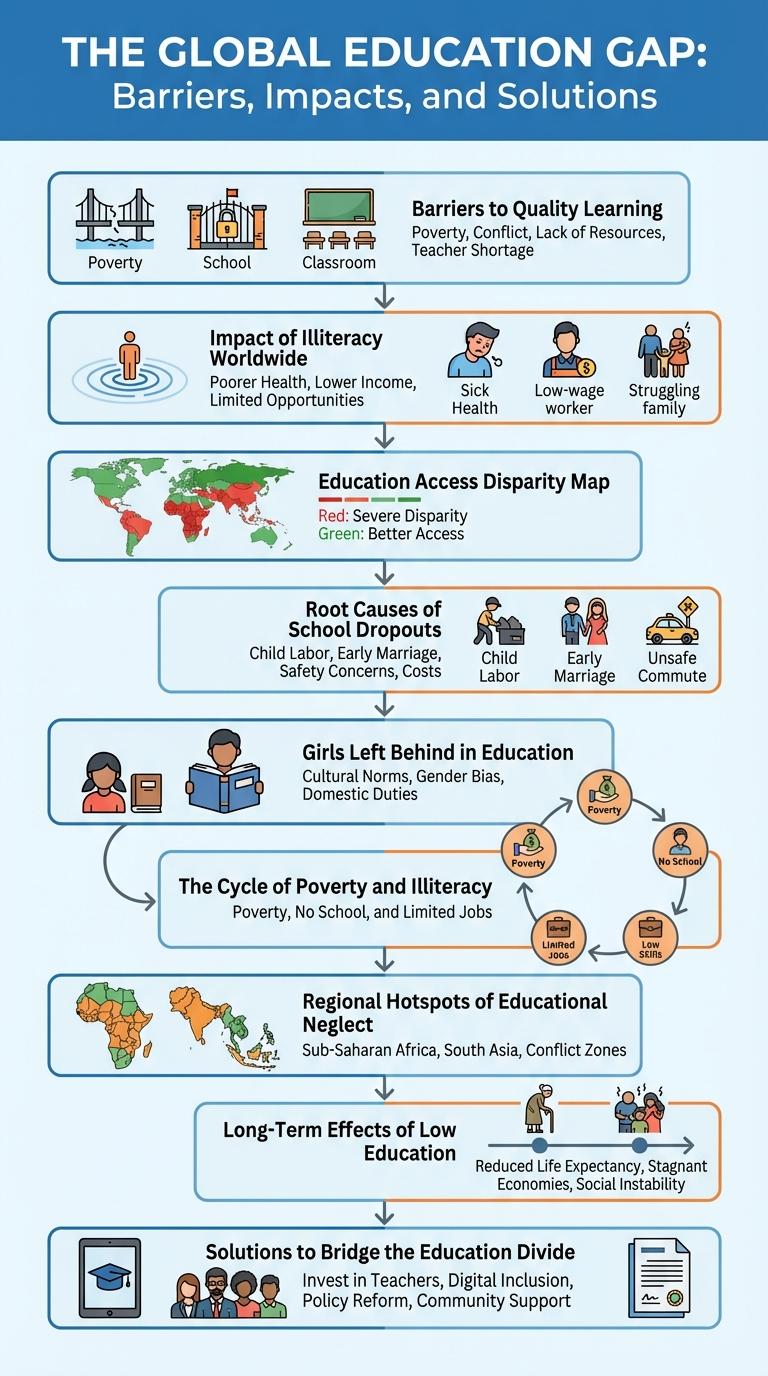
Barriers to Quality Learning
Lack of education remains a critical issue worldwide, with millions of children unable to access quality learning opportunities. Barriers such as poverty, inadequate infrastructure, and social inequality hinder educational progress.
Limited resources and poorly trained teachers further exacerbate the problem, impacting student achievement. Cultural norms and gender discrimination restrict access for marginalized groups, deepening the education gap.
Impact of Illiteracy Worldwide
Illiteracy affects over 750 million adults worldwide, hindering their ability to access employment and healthcare opportunities. Countries with high illiteracy rates often experience increased poverty and lower economic growth. Lack of education perpetuates social inequality, limiting personal development and community progress.
Education Access Disparity Map
| Region | Percentage Without Access to Education |
|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 40% |
| South Asia | 30% |
| Middle East & North Africa | 20% |
| Latin America & Caribbean | 12% |
| East Asia & Pacific | 10% |
The Education Access Disparity Map highlights significant global inequalities in education availability. Regions like Sub-Saharan Africa face the most severe lack of access, with nearly 40% of children out of school. South Asia also shows critical gaps, impacting 30% of youth. Disparities result from factors such as poverty, infrastructure deficits, and socio-political instability. Closing this gap is essential for improving literacy rates, economic development, and social equity worldwide.
Root Causes of School Dropouts
What are the main root causes of school dropouts? Poverty is a significant factor, limiting access to educational resources and stable living conditions. Family issues, including lack of support and domestic responsibilities, also contribute heavily to students leaving school early.
Girls Left Behind in Education
Millions of girls worldwide are denied access to quality education due to poverty, cultural norms, and early marriage. This educational gap limits their opportunities and perpetuates cycles of inequality.
In developing countries, girls are 1.5 times more likely to be out of school compared to boys. Lack of education reduces future income potential and increases vulnerability to exploitation and health risks. Investing in girls' education boosts economic growth and community well-being.
The Cycle of Poverty and Illiteracy
The cycle of poverty and illiteracy creates deeply rooted challenges that hinder social and economic development. Limited access to education leads to low literacy rates, reducing job opportunities and perpetuating poverty within communities. Breaking this cycle requires targeted educational programs and community support to empower individuals through learning.
Regional Hotspots of Educational Neglect
Educational neglect remains a critical issue in various global regions, impacting millions of children. Certain areas consistently show higher rates of school absenteeism and dropout due to economic, social, and infrastructural challenges.
Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia are identified as major hotspots of educational neglect. These regions face obstacles such as poverty, gender inequality, and insufficient educational resources, contributing to widespread lack of schooling.
Long-Term Effects of Low Education
Low levels of education significantly influence an individual's quality of life and societal progress. The long-term effects of educational deficiencies span economic, health, and social dimensions.
- Economic Hardship - Limited education reduces job opportunities and lifetime earnings, increasing poverty risk.
- Health Challenges - Lower educational attainment correlates with poorer health outcomes and reduced access to healthcare.
- Social Inequality - Educational gaps perpetuate social disparities and limit civic participation.
Addressing educational deficits is crucial to improving individual well-being and fostering equitable societal development.
