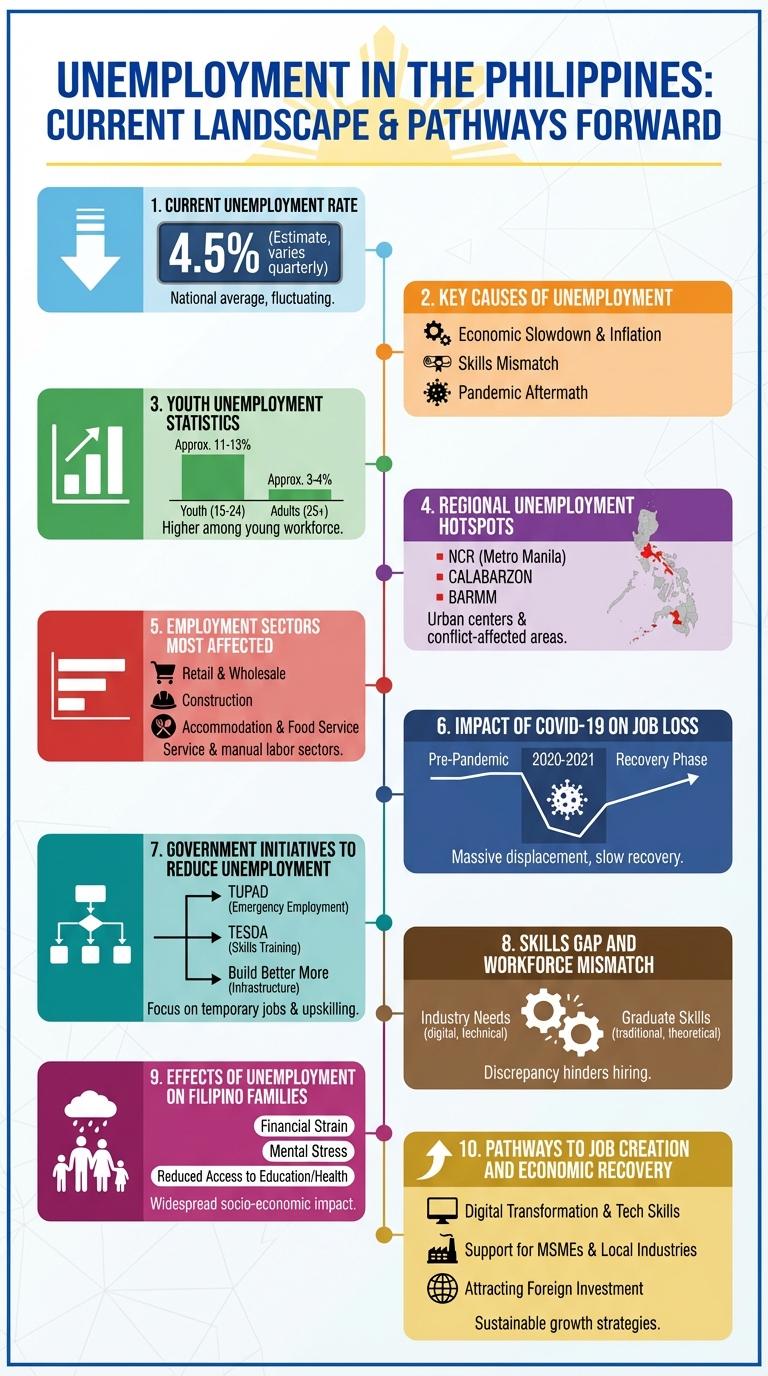
Unemployment in the Philippines highlights significant economic challenges faced by the workforce, with key factors such as youth underemployment and regional disparities shaping the labor market. The infographic presents data on unemployment rates, sector-specific impacts, and government initiatives aimed at job creation. These insights reveal the complexity of addressing employment issues amid evolving economic conditions.
Current Unemployment Rate in the Philippines
The current unemployment rate in the Philippines reflects ongoing challenges in the labor market amid economic recovery efforts. Tracking this rate is crucial for understanding workforce dynamics and policy effectiveness.
As of the latest data, the unemployment rate stands at approximately 5.4%, indicating a gradual improvement compared to previous years.
- Philippines Unemployment Rate - The rate is around 5.4% based on recent labor force surveys.
- Youth Unemployment Impact - Young workers face a higher unemployment rate, often exceeding 15%, highlighting challenges in entry-level job opportunities.
- Sectoral Influence - Services and manufacturing sectors significantly affect overall unemployment due to their large employment base.
Key Causes of Unemployment
Unemployment in the Philippines remains a significant socio-economic challenge. Various factors contribute to this persistent issue, impacting millions of Filipinos seeking jobs.
Key causes of unemployment include a mismatch between skills and job market demands, high population growth leading to labor surplus, and inadequate access to quality education and vocational training. Structural changes in the economy, such as shifts from agriculture to services, also affect employment opportunities. Additionally, slow economic growth and limited investment hinder job creation.
Youth Unemployment Statistics
Youth unemployment remains a significant challenge in the Philippines, affecting the country's economic growth and social stability. Addressing this issue requires targeted policies and programs to enhance youth employability and skills development.
- Youth Unemployment Rate - The youth unemployment rate in the Philippines was approximately 14.2% in 2023, higher than the national average of 5.5%.
- Age Group Affected - The most affected age group is 15 to 24 years old, facing difficulties entering the labor market.
- Education Impact - Graduates with only a high school diploma experience higher unemployment rates compared to those with college degrees.
Government and private sector initiatives focus on vocational training and entrepreneurship programs to reduce youth unemployment in the country.
Regional Unemployment Hotspots
The Philippines faces significant unemployment challenges, with certain regions emerging as critical hotspots. Key areas such as the National Capital Region, CALABARZON, and Central Luzon exhibit higher unemployment rates compared to the national average. Understanding these regional disparities aids policymakers in targeting economic growth and job creation efforts effectively.
Employment Sectors Most Affected
The unemployment rate in the Philippines has significantly impacted various employment sectors, with the Services sector experiencing the highest job losses due to reduced consumer demand and restrictions on face-to-face interactions. The Agriculture sector follows closely, affected by supply chain disruptions and limited access to markets. The Industry sector, including manufacturing and construction, has also seen a decline in employment because of halted projects and decreased production activities.
Impact of COVID-19 on Job Loss
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly increased unemployment rates in the Philippines, disrupting various sectors such as tourism, manufacturing, and retail. Lockdowns and reduced economic activities led to millions of job losses, especially among informal workers.
Government reports indicated a peak unemployment rate of 17.7% in 2020, the highest in decades. Recovery efforts continue, but full employment levels have yet to return to pre-pandemic figures as many businesses adjust to new operational models.
Government Initiatives to Reduce Unemployment
What measures has the Philippine government implemented to combat unemployment? The government has launched several initiatives aimed at boosting job creation and skills development. These programs focus on enhancing employability and providing livelihood opportunities across various sectors.
| Initiative | Description |
| TESDA Skills Training | Provides technical and vocational education to improve workforce skills aligned with market demand. |
| Public Employment Service Office (PESO) | Facilitates job matching services and employment facilitation at the local government level. |
| JobStart Philippines | Offers youth employment programs including job coaching, internships, and job placement. |
| Livelihood Assistance Program | Supports small entrepreneurs with capital and training to promote self-employment. |
| Infrastructure Development Projects | Generates large-scale employment opportunities through government-funded infrastructure initiatives. |
Skills Gap and Workforce Mismatch
Unemployment in the Philippines is significantly influenced by the skills gap and workforce mismatch, limiting economic growth and job opportunities. Addressing these challenges requires targeted education and training programs aligned with industry needs.
The skills gap refers to the difference between the skills workers have and the skills employers require, impacting employment rates. Workforce mismatch occurs when job seekers' qualifications do not align with available job vacancies, causing inefficiencies in the labor market.
- High Skill Deficiency - Many Filipino workers lack proficiency in technical and digital skills demanded by modern industries.
- Industry Demand Shift - Rapid changes in sectors such as IT and manufacturing increase the demand for specialized skill sets not widely available in the workforce.
- Educational Mismatch - Graduates often pursue degrees unrelated to current market needs, resulting in underemployment or unemployment.
- Training Program Gaps - Existing vocational and technical training programs are insufficient to bridge the skills gap effectively.
- Geographic Workforce Imbalance - Job opportunities concentrate in urban areas while skilled talent in rural regions remains underutilized.
Effects of Unemployment on Filipino Families
| Effect on Filipino Families | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Instability | Loss of steady income leads to difficulties in meeting basic needs, increasing poverty risks within households. |
| Emotional Stress | Unemployment causes anxiety and depression among family members, creating tension and strained relationships. |
| Reduced Educational Opportunities | Families may struggle to afford schooling fees, resulting in interrupted or discontinued education for children. |
| Health and Nutrition Challenges | Limited income reduces access to nutritious food and medical care, raising the risk of malnutrition and illness. |
| Social Isolation | Unemployment can cause families to withdraw from community activities due to shame or lack of resources. |
