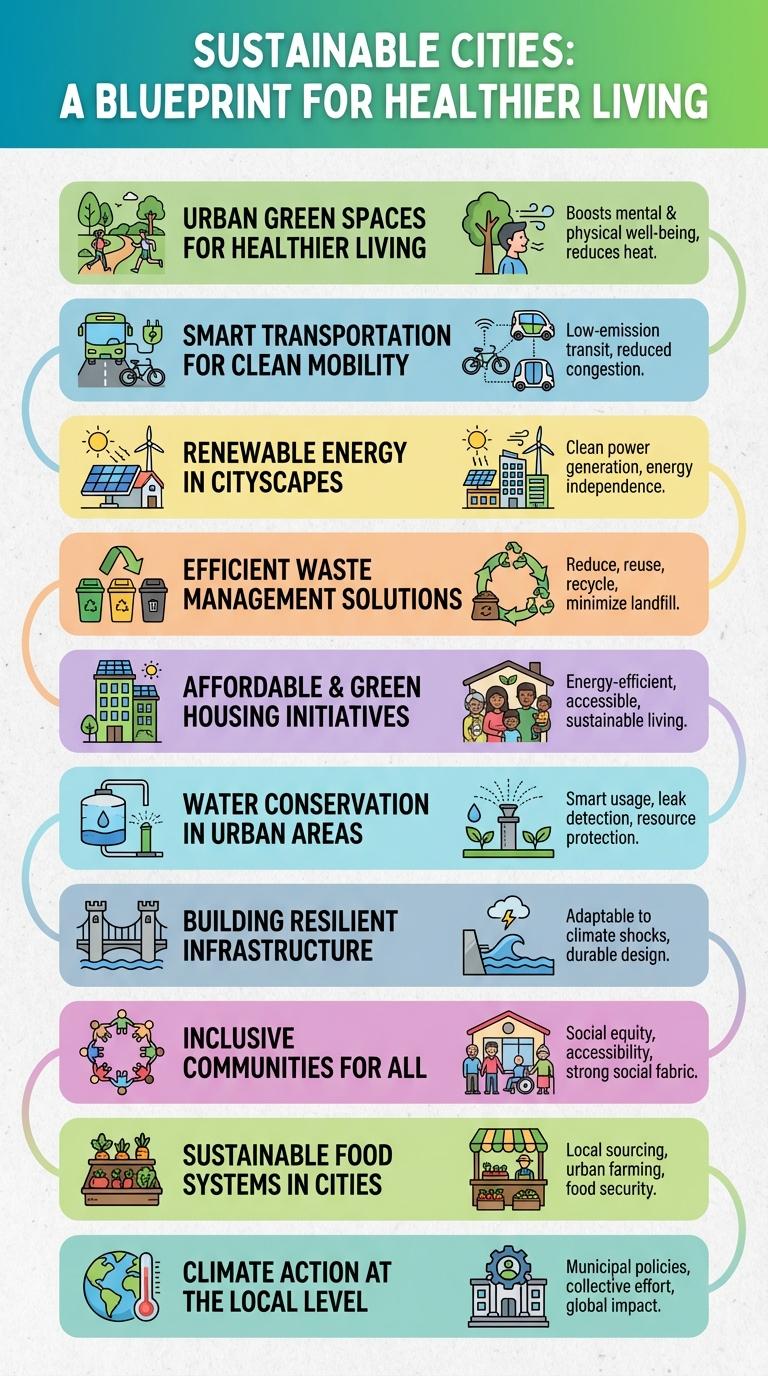
Sustainable cities and communities focus on creating urban environments that balance economic growth, social well-being, and environmental protection. Key elements include efficient resource management, green infrastructure, and inclusive urban planning. These strategies help reduce carbon footprints, promote resilience, and improve the quality of life for all residents.
Urban Green Spaces for Healthier Living
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Urban green spaces include parks, gardens, green roofs, street trees, and natural reserves within city boundaries. |
| Health Benefits | Improved air quality, reduced stress, increased physical activity, and enhanced mental well-being. |
| Climate Impact | Urban green areas reduce urban heat island effect by cooling cities, improving microclimates, and managing stormwater. |
| Social Benefits | Promote social cohesion, support community engagement, and provide inclusive public spaces for diverse populations. |
| Examples | Singapore's Gardens by the Bay, New York's Central Park, and Copenhagen's green bike lanes illustrate successful green urban planning. |
Smart Transportation for Clean Mobility
Smart transportation systems play a critical role in developing sustainable cities and communities by reducing traffic congestion and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Integrating electric vehicles, bike-sharing programs, and efficient public transit encourages clean mobility options for urban dwellers. Advanced technologies like IoT sensors and AI optimize traffic flow, improving air quality and promoting healthier living environments.
Renewable Energy in Cityscapes
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in transforming cityscapes into sustainable urban environments. Integrating solar panels, wind turbines, and other green technologies reduces carbon footprints and enhances energy efficiency in cities.
Urban areas are increasingly adopting renewable energy sources to meet the growing demand for clean power. Solar rooftops, urban wind farms, and geothermal systems contribute to smarter, eco-friendly infrastructure. These sustainable solutions support healthier communities by lowering pollution and promoting energy independence.
Efficient Waste Management Solutions
Efficient waste management solutions play a crucial role in building sustainable cities and communities by reducing environmental impact and conserving resources. Implementing advanced recycling systems and promoting waste segregation at the source significantly minimizes landfill use.
Smart waste collection technologies, such as sensor-equipped bins and optimized routing, enhance operational efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. Community engagement and public education further drive behavioral change toward waste reduction and sustainable living.
Affordable & Green Housing Initiatives
Sustainable cities prioritize affordable and green housing initiatives to enhance community living and reduce environmental impact. Integrating energy-efficient designs and accessible housing options fosters inclusive urban development.
Affordable green housing combines cost-effective construction with eco-friendly materials and technologies to minimize carbon footprints and utility costs.
- Energy-efficient design - Utilizes insulation, solar panels, and smart home systems to decrease energy consumption and costs.
- Use of sustainable materials - Incorporates recycled, locally sourced, and non-toxic construction materials to reduce environmental harm.
- Affordable housing programs - Provides financial incentives, subsidies, and community partnerships to lower barriers to green housing access.
Water Conservation in Urban Areas
How can urban areas effectively conserve water to promote sustainability? Sustainable cities implement advanced water-saving technologies and promote community awareness to reduce water waste. Efficient management of urban water resources ensures long-term availability and supports ecosystem health.
Building Resilient Infrastructure
Building resilient infrastructure is essential for creating sustainable cities and communities able to withstand environmental, social, and economic challenges. Such infrastructure reduces vulnerability to natural disasters and supports long-term urban growth.
Investing in durable materials, smart technologies, and adaptive design enhances infrastructure longevity and efficiency. This approach promotes resource conservation, reduces maintenance costs, and improves public safety in urban environments.
Inclusive Communities for All
Sustainable cities and communities prioritize inclusivity, ensuring that all residents have access to essential services, affordable housing, and safe public spaces. Diverse populations, including people with disabilities, elderly individuals, and marginalized groups, benefit from urban designs that promote accessibility and social cohesion. Inclusive policies foster strong community engagement, economic opportunities, and environmental sustainability for everyone.
Sustainable Food Systems in Cities
Sustainable food systems in cities promote environmental health and social equity by integrating local agriculture and waste reduction. These systems support resilient urban communities through access to nutritious food and reduction of carbon footprints.
Urban agriculture and food policies are key in transforming food systems towards sustainability.
- Local Food Production - Urban farms and community gardens increase fresh food availability while reducing transportation emissions.
- Food Waste Reduction - Composting and food recovery programs minimize landfill waste and improve resource efficiency.
- Access to Nutritious Food - Equitable distribution initiatives ensure all city residents can obtain healthy and affordable food options.
