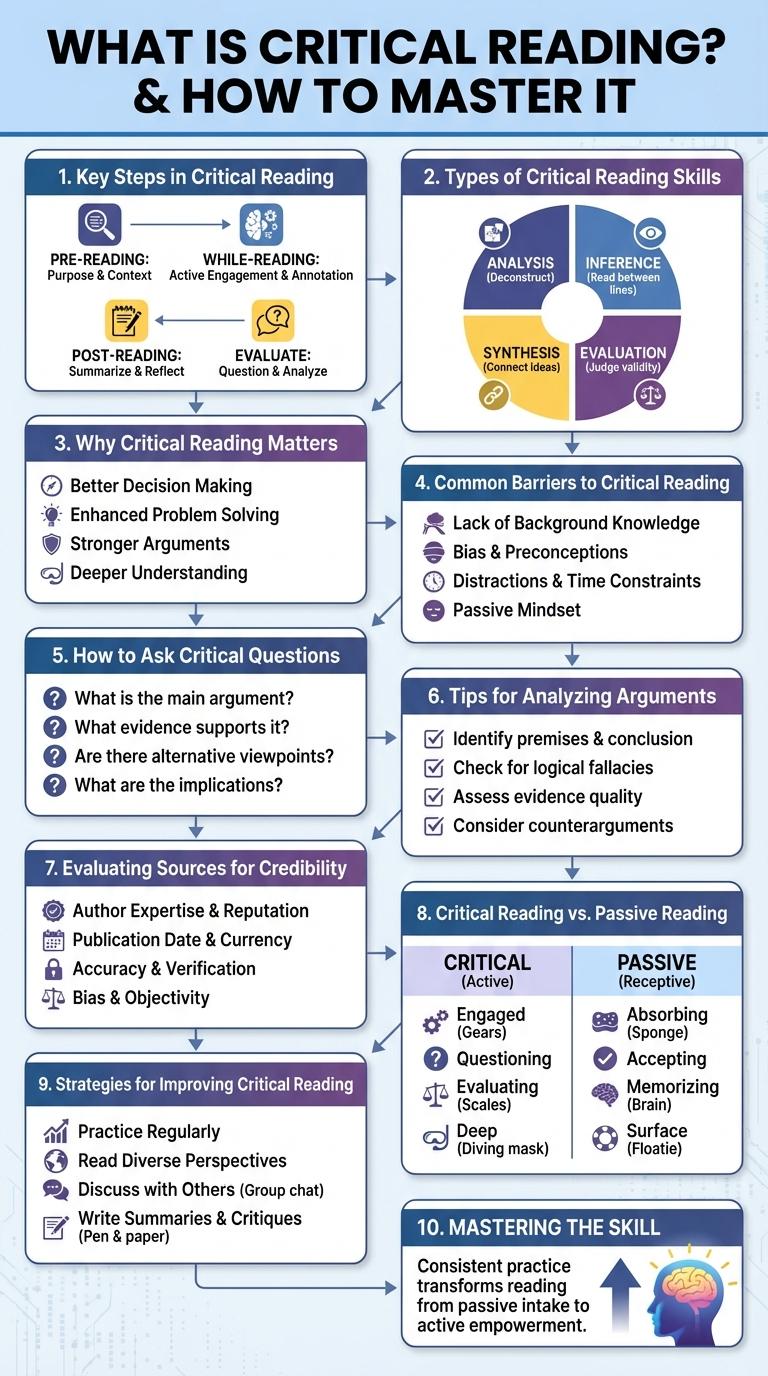
Critical reading involves analyzing and evaluating text to understand its deeper meaning and assess its validity. This infographic breaks down key strategies such as identifying main ideas, recognizing bias, and questioning assumptions. Mastering these skills enhances comprehension and sharpens decision-making in both academic and everyday contexts.
What Is Critical Reading?
Critical reading is an active process of analyzing and evaluating a text to fully understand its meaning and implications. It involves questioning the content, context, and purpose of the material being read.
- Understanding Context - Identifying the background, author's perspective, and intended audience of the text.
- Analyzing Arguments - Examining the logic, evidence, and reasoning used to support claims within the reading.
- Evaluating Credibility - Assessing the reliability and validity of the information and sources presented.
Key Steps in Critical Reading
Critical reading is an essential skill for understanding and evaluating texts effectively. It involves actively engaging with the content to interpret meaning and assess its validity.
- Preview the Text - Scan headings, subheadings, and summaries to grasp the main idea before a detailed read.
- Analyze Arguments - Identify claims, evidence, and assumptions to evaluate the strength of the author's reasoning.
- Reflect and Question - Consider the purpose, context, and potential biases, asking critical questions to deepen understanding.
Types of Critical Reading Skills
Critical reading involves analyzing and evaluating texts to understand deeper meanings beyond the surface. It requires active engagement with the material to assess the author's purpose, arguments, and evidence.
Types of critical reading skills include comprehension, analysis, inference, evaluation, and synthesis. Comprehension ensures understanding of the text's content, while analysis breaks down the structure and main ideas. Inference allows readers to draw conclusions, evaluation judges the credibility and relevance of information, and synthesis integrates new knowledge with existing understanding.
Why Critical Reading Matters
Critical reading enhances comprehension by enabling readers to evaluate and interpret information effectively. It fosters analytical thinking, helping individuals discern biases and underlying meanings in texts. Developing critical reading skills empowers informed decision-making and promotes lifelong learning.
Common Barriers to Critical Reading
| Common Barrier | Description |
|---|---|
| Preconceived Notions | Biases and prior beliefs that hinder objective evaluation of the text. |
| Emotional Interference | Strong emotions that cloud judgment and reduce analytical thinking. |
| Lack of Background Knowledge | Insufficient context or understanding of the topic that impedes comprehension. |
| Distractions | External or internal factors that disrupt focus and reduce reading efficiency. |
| Overreliance on Literal Meaning | Ignoring implied messages, nuances, and deeper interpretations in the text. |
How to Ask Critical Questions
Critical reading involves analyzing a text beyond its surface meaning to understand the author's intent and the validity of the arguments. Asking the right questions helps uncover biases, assumptions, and hidden messages.
Start by questioning the purpose: Why was this text written and who is the intended audience? Next, evaluate the evidence: Are the facts accurate, relevant, and supported by credible sources?
Tips for Analyzing Arguments
Critical reading requires evaluating the strength and validity of arguments within a text. Understanding how to analyze arguments helps in distinguishing fact from opinion and identifying logical fallacies.
- Identify the Claim - Determine the main point or thesis the author is trying to prove.
- Examine Evidence - Assess the quality, relevance, and sufficiency of supporting facts or data.
- Evaluate Reasoning - Check for logical consistency and the presence of any fallacies in the argument.
Mastering these tips enhances comprehension and fosters critical thinking skills when engaging with complex texts.
Evaluating Sources for Credibility
Evaluating sources for credibility involves assessing the author's qualifications, the publication's reputation, and the evidence provided. Reliable sources often include peer-reviewed journals, official reports, and expert-authored content. Critical readers verify facts by cross-referencing multiple trustworthy sources to ensure accuracy and bias reduction.
Critical Reading vs. Passive Reading
What distinguishes critical reading from passive reading?
Critical reading involves actively analyzing and questioning the text, while passive reading means simply absorbing information without engagement. Engaging critically improves comprehension and retention.
| Critical Reading | Passive Reading |
|---|---|
| Questioning arguments and evidence | Accepting text at face value |
| Identifying biases and assumptions | Ignoring underlying messages |
| Analyzing structure and style | Skimming through content |
| Making connections with prior knowledge | Limited interaction with ideas |
| Evaluating credibility and relevance | Reading without reflection |
