Health-related laws play a crucial role in shaping public health policies and ensuring the safety and well-being of communities. These regulations govern areas such as disease control, medical practice standards, and patient rights, effectively guiding healthcare delivery and prevention measures. Understanding these laws helps individuals and professionals navigate the complex legal landscape affecting health outcomes.
Key Health Laws Shaping Our Lives
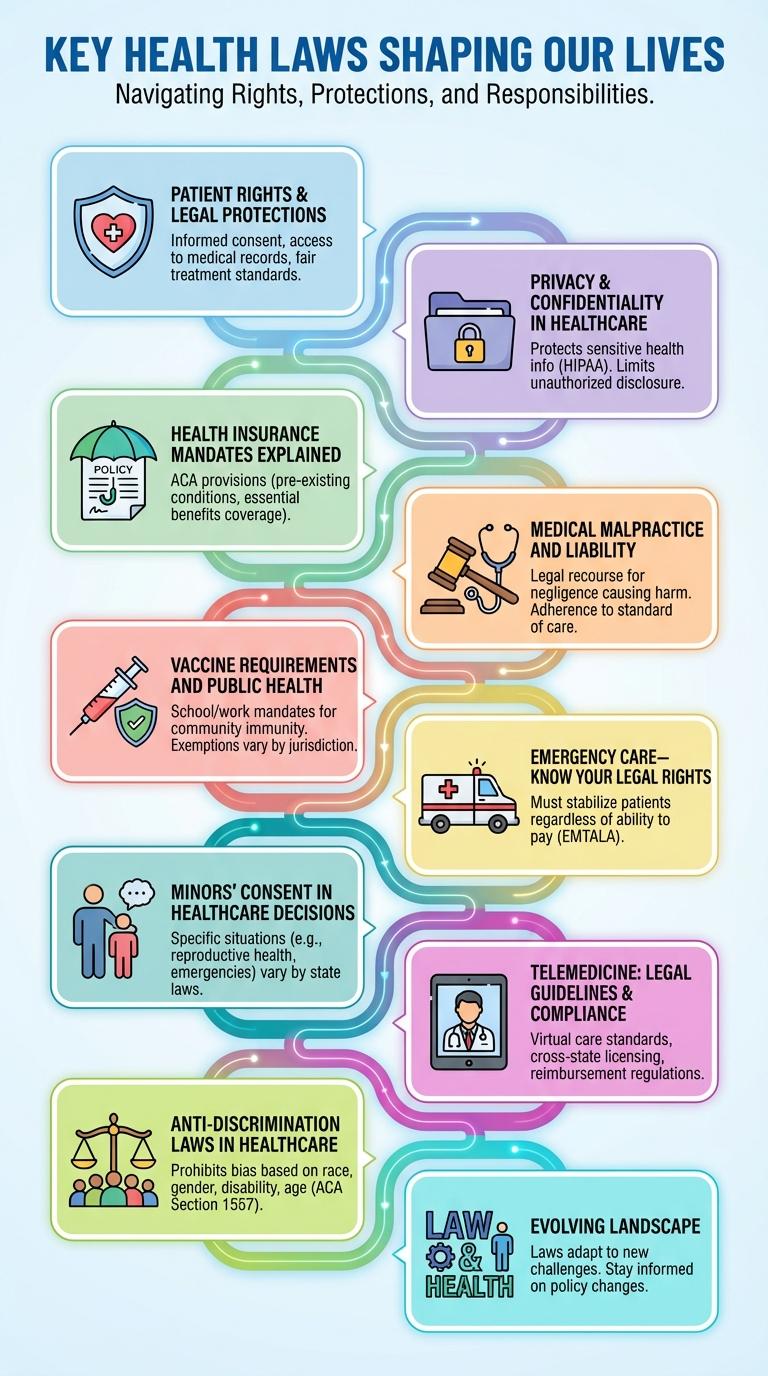
Key health laws shape the accessibility, quality, and safety of healthcare services worldwide. Examples include the Affordable Care Act, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations. These laws protect patient rights, regulate medical practices, and ensure public health standards.
Patient Rights & Legal Protections
Health-related laws safeguard patient rights and ensure legal protections within healthcare systems. These regulations promote fair treatment, privacy, and informed consent for all patients.
Patient rights include access to medical records, confidentiality, and the right to refuse treatment. Legal protections enforce adherence to these rights, preventing discrimination and abuse. Healthcare providers must comply with laws such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe to protect patient information.
Privacy & Confidentiality in Healthcare
Health-related laws ensure strict privacy and confidentiality of patient information, safeguarding sensitive medical data from unauthorized access. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets national standards for protecting health information in the United States. Compliance with these laws promotes trust between patients and healthcare providers by maintaining the security and confidentiality of personal health records.
Health Insurance Mandates Explained
Health insurance mandates require individuals to obtain health coverage or face penalties, promoting broader access to medical care. These laws aim to reduce uninsured rates and distribute healthcare costs more evenly across populations.
Mandates often include specific coverage requirements, such as preventive services and essential health benefits. Compliance ensures access to necessary treatments and helps maintain a stable insurance market.
Medical Malpractice and Liability
Medical malpractice laws govern the legal responsibilities of healthcare professionals when providing care. These laws ensure patients receive compensation for injuries caused by negligence or substandard treatment.
Liability in medical malpractice cases requires proving duty, breach, causation, and damages. Strict regulations and statutes of limitations vary by jurisdiction, impacting the filing and outcome of claims.
Vaccine Requirements and Public Health
Vaccine requirements serve as a critical legal measure to protect public health by preventing the spread of infectious diseases. These laws ensure high immunization rates in communities, reducing outbreaks and safeguarding vulnerable populations.
- Mandatory Vaccination for School Entry - Most jurisdictions require children to receive certain vaccines before attending public or private schools to maintain herd immunity.
- Healthcare Worker Immunization Policies - Laws often mandate healthcare professionals to be vaccinated to protect patients from transmissible diseases.
- Exemptions Regulations - Legal frameworks specify allowable exemptions for vaccines, such as medical, religious, or philosophical reasons, balancing individual rights and public safety.
Public health laws on vaccine requirements are essential in managing community health risks and promoting disease prevention strategies.
Emergency Care-Know Your Legal Rights
Understanding your legal rights during emergency medical situations is crucial for protecting your health and safety. Several laws ensure you receive necessary care without discrimination or delay.
- Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act (EMTALA) - Requires hospitals to provide emergency care regardless of a patient's ability to pay or insurance status.
- American with Disabilities Act (ADA) - Guarantees access to emergency services for individuals with disabilities without discrimination.
- Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA) - Ensures patients are informed about their rights to accept or refuse emergency medical treatment.
- Good Samaritan Laws - Protect individuals who provide emergency assistance from legal liability in most cases.
- HIPAA Privacy Rule - Safeguards patient health information during emergency care situations to maintain confidentiality.
Minors' Consent in Healthcare Decisions
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | The legal right of minors to consent to their own healthcare without parental approval under specific conditions. |
| Age Threshold | Varies by jurisdiction; commonly ranges from 12 to 18 years old for certain treatments. |
| Types of Care Covered | Includes reproductive health, mental health services, substance abuse treatment, and emergency care. |
| Confidentiality | Laws often protect the privacy of minors consenting to their own healthcare to encourage seeking timely treatment. |
| Limitations | Some treatments still require parental consent; capacity and maturity assessment may apply. |
Telemedicine: Legal Guidelines & Compliance
Telemedicine is transforming healthcare delivery by enabling remote patient consultations through digital platforms. Compliance with legal guidelines is essential to protect patient privacy and ensure quality care.
Understanding the key legal requirements helps providers navigate telemedicine regulations effectively.
- Licensing Requirements - Healthcare providers must be licensed in the state where the patient is located during the telemedicine session.
- Patient Consent - Obtaining informed consent from patients before telemedicine services is mandated by law to ensure transparency.
- Data Privacy - Compliance with HIPAA ensures protection of patient health information during telemedicine interactions.
- Reimbursement Policies - Telehealth services reimbursement varies by payer and state regulations, requiring providers to stay updated on coverage rules.
- Prescribing Regulations - Controlled substances prescribed via telemedicine must comply with federal and state laws to prevent misuse.
