Opioids are powerful pain-relieving medications that carry a high risk of addiction and overdose. This infographic highlights critical statistics, usage trends, and safety guidelines to raise awareness about the opioid crisis. Understanding these facts can help support prevention efforts and informed decision-making.
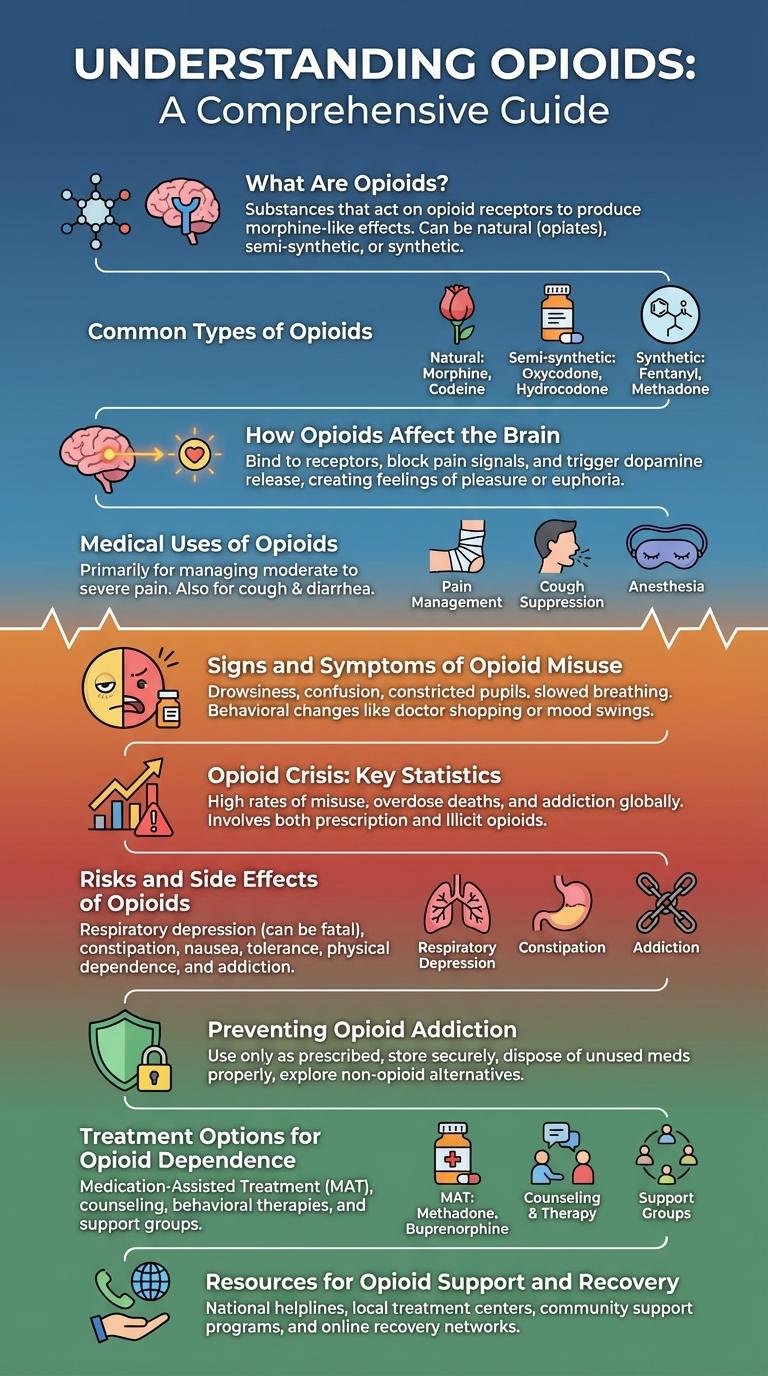
What Are Opioids?
What are opioids?
Opioids are a class of drugs used to relieve pain by acting on the nervous system. They include prescription medications like morphine and oxycodone, as well as illegal substances such as heroin.
Common Types of Opioids
Opioids are a class of drugs commonly prescribed for pain relief but can lead to dependence and overdose. Understanding the different types of opioids helps in recognizing their uses and risks.
- Morphine - A natural opioid used to manage severe pain, commonly administered in hospitals.
- Codeine - A mild opioid often found in cough syrups and pain relievers.
- Oxycodone - A semi-synthetic opioid prescribed for moderate to severe pain.
- Fentanyl - A powerful synthetic opioid used for intense pain, significantly stronger than morphine.
- Heroin - An illegal opioid derived from morphine, known for high addiction potential and health risks.
How Opioids Affect the Brain
Opioids bind to specific receptors in the brain called mu-opioid receptors, blocking pain signals and producing feelings of euphoria. This interaction alters the brain's reward system, increasing dopamine release and reinforcing drug use behavior. Long-term opioid use can change brain function, leading to dependence, tolerance, and addiction.
Medical Uses of Opioids
Opioids are powerful medications primarily used for pain relief in medical settings. They interact with specific receptors in the brain to reduce the perception of pain.
- Acute Pain Management - Opioids effectively relieve severe pain following surgeries or traumatic injuries.
- Chronic Pain Treatment - They are prescribed for long-term pain conditions like cancer-related pain, improving patient comfort.
- Cough Suppression - Certain opioids act as antitussives to reduce persistent coughing.
- Diarrhea Control - Some opioid formulations help manage severe diarrhea by slowing intestinal movement.
- Anesthesia Adjunct - Opioids are used during anesthesia to enhance pain control and sedation.
Medical use of opioids requires careful dosing and monitoring to balance pain relief with risk of side effects.
Signs and Symptoms of Opioid Misuse
Opioid misuse affects both physical and behavioral health, often leading to serious complications. Recognizing early signs and symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and support.
- Constriction of Pupils - Users often display pinpoint pupils, which is a distinct physical indicator of opioid influence.
- Altered Mental State - Confusion, drowsiness, or difficulty concentrating can signal opioid misuse.
- Respiratory Depression - Slowed or irregular breathing is a dangerous symptom associated with opioid overdose.
Opioid Crisis: Key Statistics
The opioid crisis continues to affect millions globally, with over 80,000 drug overdose deaths reported in the United States in 2023. Opioids, including prescription painkillers and illegal drugs like heroin, contribute to a majority of these fatalities.
Approximately 10.1 million people misused prescription opioids in the past year, highlighting the widespread nature of the epidemic. Emergency room visits related to opioid overdoses increased by 30% between 2020 and 2023, underscoring urgent public health challenges.
Risks and Side Effects of Opioids
Opioids are powerful pain-relieving medications often prescribed for moderate to severe pain. While effective, these drugs carry significant risks and side effects that can impact patients' health.
Common side effects include drowsiness, constipation, and nausea, which can reduce quality of life. Long-term use increases the risk of tolerance, dependence, and potentially fatal overdose. Misuse of opioids can lead to addiction, respiratory depression, and severe withdrawal symptoms.
Preventing Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction prevention involves education on safe medication usage and awareness of risks. Early intervention and proper prescribing practices reduce dependency chances.
Access to support programs and alternative pain management methods helps minimize opioid misuse. Community efforts and policy changes are crucial to stopping addiction before it starts.
Treatment Options for Opioid Dependence
Effective treatment options for opioid dependence include medication-assisted treatment (MAT), behavioral therapies, and support groups. MAT uses medications like methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Combining these medications with counseling provides a comprehensive approach to recovery.
