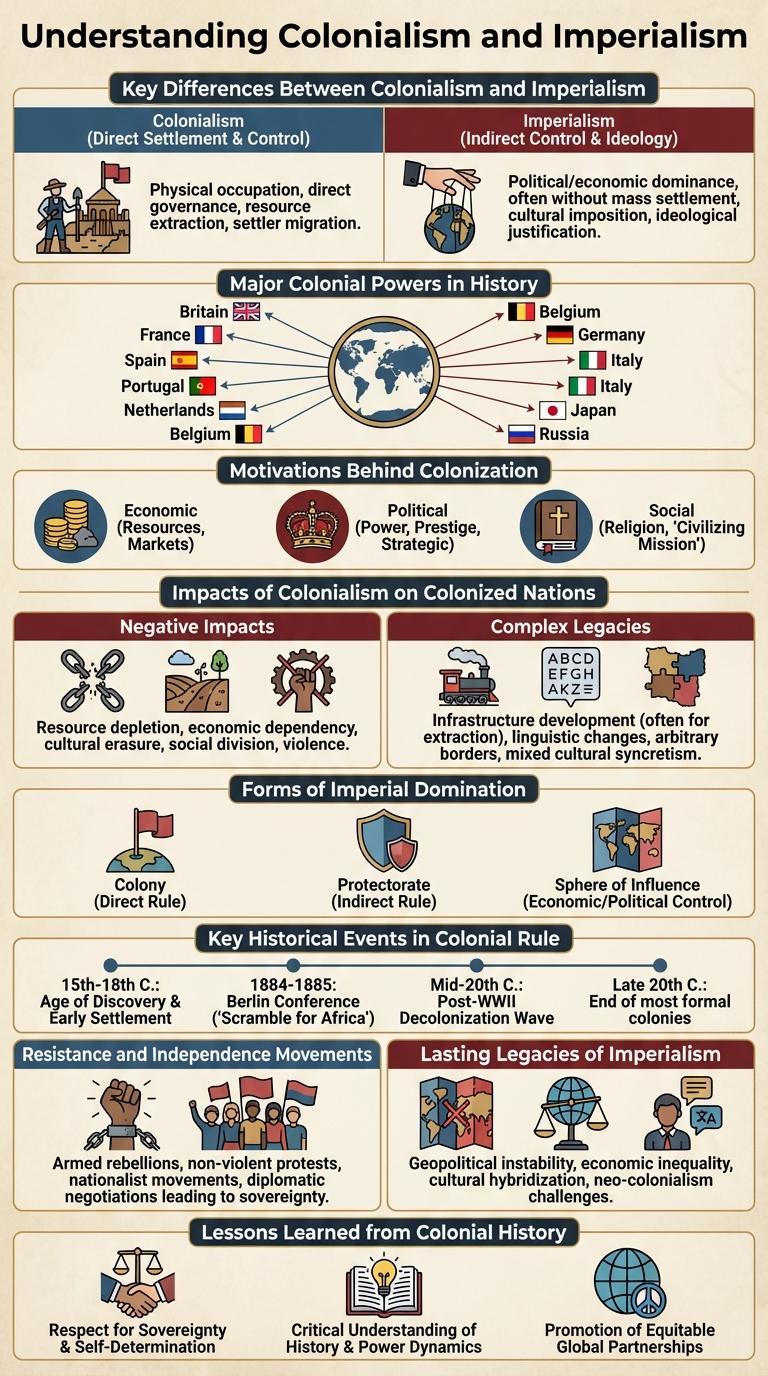
Kolonyalismo at imperyalismo ay mga makasaysayang proseso kung saan sinuportahan ng mga makapangyarihang bansa ang pagkuha at pagsakop sa mga teritoryo sa ibang bahagi ng mundo. Ang infographic ay naglalaman ng mga pangunahing impormasyon, epekto, at mga halimbawa ng dalawang konsepto upang maunawaan ang kanilang impluwensya sa kasaysayan at kultura ng mga nasabing rehiyon. Makikita dito ang ugnayan ng kapangyarihan, ekonomiya, at pulitika sa likod ng kolonyalismo at imperyalismo.
Understanding Colonialism and Imperialism
What defines colonialism and imperialism in history?
Colonialism involves the control and exploitation of one territory by another, often through settlement and resource extraction. Imperialism extends this dominance, including political and economic influence over foreign lands without direct settlement.
Key Differences Between Colonialism and Imperialism
Colonialism involves the direct control and settlement of foreign territories by a country, often exploiting resources and indigenous populations. Imperialism extends beyond colonization, encompassing economic, political, and cultural dominance without necessarily involving direct governance. Both practices shaped global history but differ in methods and scale of influence.
Major Colonial Powers in History
Colonialism and imperialism shaped global history through the expansion of powerful nations across continents. Major colonial powers established vast empires, influencing politics, culture, and economies worldwide.
- British Empire - Controlled territories on every inhabited continent, with India as its "jewel in the crown."
- Spanish Empire - Established extensive colonies throughout the Americas, spreading its language and culture.
- French Empire - Held significant territories in Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Caribbean.
- Portuguese Empire - Early global maritime power with colonies in South America, Africa, and Asia.
- Dutch Empire - Dominated trade routes and controlled key ports in Asia and the Americas.
Motivations Behind Colonization
| Kolonyalismo | Imperyalismo |
|---|---|
| Economic gain through resource extraction and new markets | Expansion of political power and global influence |
| Strategic military positioning and naval bases | Control over trade routes and securing strategic territories |
| Spread of religion and cultural beliefs | Imposition of cultural dominance and social hierarchy |
| Desire to civilize and modernize indigenous populations | National prestige and competition among world powers |
| Population pressure relief through migration | Exploitation of local labor and resources for industrial development |
Impacts of Colonialism on Colonized Nations
Colonialism drastically transformed colonized nations by exploiting their natural resources and labor, leading to economic dependency and underdevelopment. The imposition of foreign governance systems disrupted traditional social and political structures, often causing long-term instability. Cultural erosion and loss of indigenous identities occurred as colonial powers promoted their own languages, religions, and customs.
Forms of Imperial Domination
Kolonyalismo at imperyalismo ay mga anyo ng kontrol kung saan isang bansa ay nagpapalawak ng kapangyarihan sa iba pang mga teritoryo. Ito ay naglalayong gawin ang mga nasasakupang lupa bilang bahagi ng ekonomiya at pulitika ng mananakop.
Mga anyo ng Imperyal na Dominasyon ay kinabibilangan ng direktang pamamahala, kung saan ang mananakop ay may direktang kontrol sa lokal na gobyerno. Mayroon ding hindi direktang pamamahala kung saan ang mga lokal na pinuno ay ginagamit upang ipatupad ang kapangyarihan ng imperyo.
Key Historical Events in Colonial Rule
Colonial rule and imperialism shaped the modern geopolitical landscape through several pivotal historical events. Understanding these key moments reveals the impact of foreign domination on colonized societies.
- Scramble for Africa (1881-1914) - European powers aggressively divided Africa, establishing colonies and exploiting resources.
- British Raj in India (1858-1947) - Britain formalized control over India, influencing its political, economic, and social systems.
- Spanish-American War (1898) - Resulted in U.S. acquisition of former Spanish colonies, marking a new phase of American imperialism.
Resistance and Independence Movements
Colonialism and imperialism spurred numerous resistance and independence movements worldwide. These movements sought to reclaim sovereignty and cultural identity from foreign rule.
- Indian Independence Movement - Led by figures like Mahatma Gandhi, it employed nonviolent resistance to end British colonial rule.
- Algerian War of Independence - A brutal conflict between Algerian nationalists and French forces that resulted in Algeria's liberation in 1962.
- Philippine Revolution - Filipino revolutionaries fought against Spanish colonizers in the late 19th century to establish an independent republic.
Resistance and independence movements significantly reshaped global political boundaries and inspired decolonization efforts throughout the 20th century.
Lasting Legacies of Imperialism
Imperyalismo at kolonyalismo ay nag-iwan ng malalim na bakas sa kasaysayan ng mga bansa, lalo na sa ekonomiya, kultura, at politika. Ang mga dating kolonya ay patuloy na nakararanas ng epekto ng mga estrukturang itinayo ng mga mananakop.
Ang mga sistemang pang-ekonomiya ay madalas na nakaangkla sa mga pangangailangan ng mga bansang mananakop, nagdudulot ng hindi pantay na paglago at kahirapan. Sa kultural na aspeto, maraming mga tradisyon at wika ang naapektuhan, habang sa politika, ilang bansa ay nakakaranas pa rin ng mga hamon sa soberanya at pamamahala.
