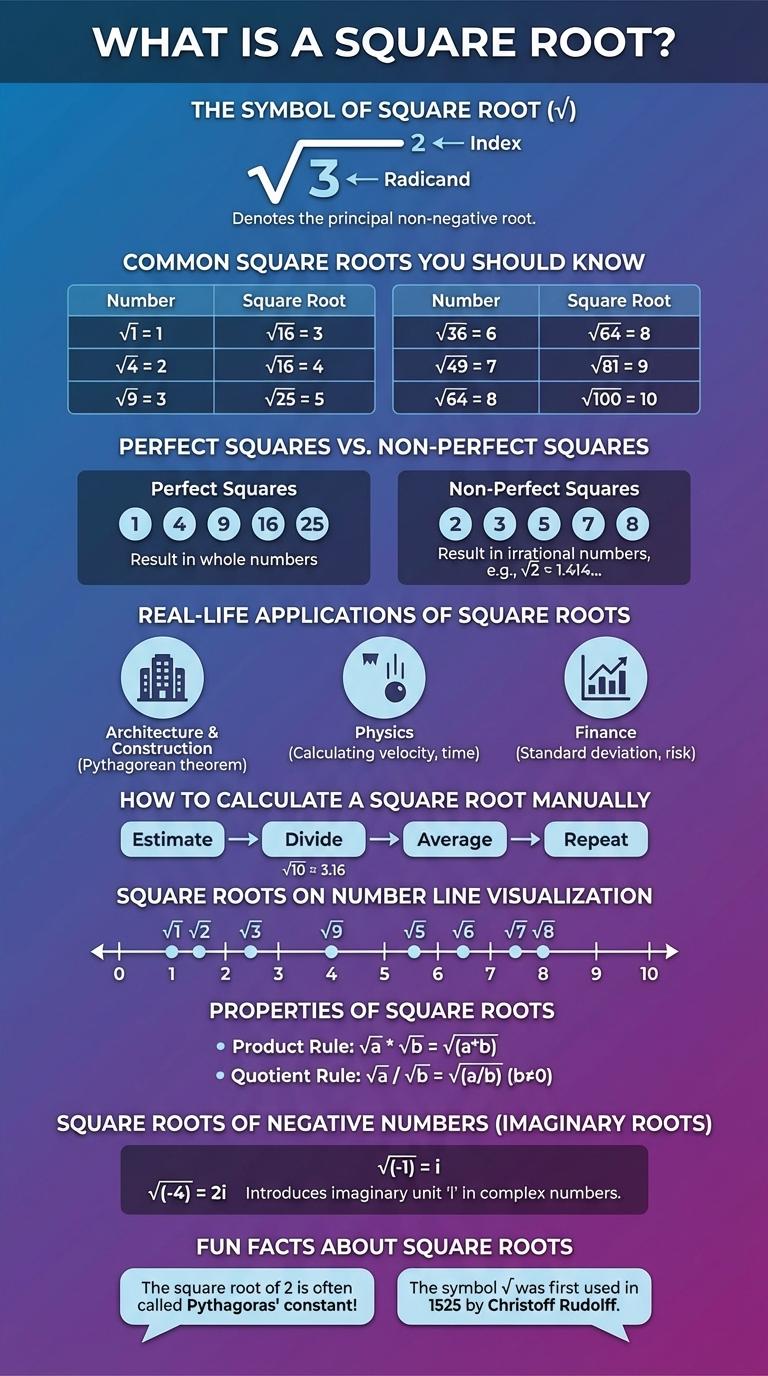
Understanding square roots is essential for mastering fundamental math concepts and solving equations involving exponents. This infographic visually breaks down the process of finding square roots, highlights their properties, and demonstrates real-life applications. Exploring these elements enhances numerical literacy and deepens comprehension of mathematical relationships.
What is a Square Root?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Square roots are fundamental in mathematics and appear in various fields like geometry and algebra.
- Definition - The square root of a number x is a number y such that y2 = x.
- Positive and Negative Roots - Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- Notation - The square root is denoted by the radical symbol followed by the number.
The Symbol of Square Root (√)
The square root symbol () is a mathematical notation used to represent the principal square root of a number. It is one of the fundamental symbols in arithmetic and algebra.
- Origin - The square root symbol originates from the Latin letter "r," representing "radix," meaning root.
- Usage - The symbol is placed before a number or expression to indicate the square root operation.
- Appearance - The symbol consists of a radical sign with a horizontal bar called a vinculum, which groups the number under the root.
The square root symbol is essential for simplifying expressions and solving quadratic equations in mathematics.
Common Square Roots You Should Know
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, representing a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Understanding common square roots facilitates quicker calculations and deeper insight into number properties.
Square root of 1 is 1, as 1 x 1 = 1. The square root of 4 is 2, since 2 x 2 = 4.
Square root of 9 equals 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. Square root of 16 results in 4, with 4 x 4 = 16.
The square root of 25 is 5, following 5 x 5 = 25. Knowing these common roots helps in solving algebraic equations efficiently.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
Perfect Squares vs. Non-Perfect Squares
Real-Life Applications of Square Roots
How are square roots used in real life? Square roots play a crucial role in fields like engineering, architecture, and computer graphics. They help calculate distances, areas, and optimize designs efficiently.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Engineering | Calculating structural stress and material strength using square root formulas. |
| Architecture | Determining accurate measurements for blueprints and building layouts. |
| Physics | Analyzing wave functions and motion equations involving square root values. |
| Computer Graphics | Calculating pixel distances for rendering 3D environments. |
| Finance | Estimating volatility in stock market analysis using square root formulas. |
How to Calculate a Square Root Manually
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Calculating square roots manually involves estimation and refining through division or averaging methods.
One common manual method is the long division technique, dividing the number into pairs of digits from right to left. Another approach is the iterative averaging method, where you average a guess with the quotient of the original number divided by that guess to improve accuracy.
Square Roots on Number Line Visualization
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Visualizing square roots on a number line helps to better understand their magnitude and position relative to whole numbers.
Start by locating perfect squares on the number line, such as 1, 4, 9, and 16. The square root of these numbers corresponds to the points 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. For non-perfect squares, estimate the square root by identifying between which two perfect squares the number lies, providing an approximate decimal value on the number line.
Properties of Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Square roots are always non-negative in the set of real numbers, denoted by the radical symbol . Key properties include: the square root of a product equals the product of square roots, the square root of a quotient equals the quotient of square roots, and the square root of a square returns the absolute value of the original number.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| (a x b) | = a x b |
| (a / b) | = a / b, b 0 |
| (a2) | = |a| |
| 0 | = 0 |
| 1 | = 1 |
Square Roots of Negative Numbers (Imaginary Roots)
The square root of a negative number is not defined within the set of real numbers. Imaginary roots involve the unit "i," which represents the square root of -1.
Imaginary numbers extend the concept of square roots to negative values, broadening number system applications in mathematics.
- Imaginary Unit (i) - Defined as -1, it forms the basis for all imaginary numbers.
- Complex Numbers - Combine real and imaginary parts, expressed as a + bi.
- Properties of Imaginary Roots - The square root of a negative number x equals i times the square root of the absolute value of x.
