Mathematics shapes the modern world by driving innovations in technology, science, and finance. Its principles underpin everything from computing algorithms to data encryption and economic modeling. Visualizing these applications through infographics reveals the integral role of math in everyday life and global progress.
The Role of Mathematics in Everyday Life
Mathematics is essential in modern life, influencing everything from technology to finance. It helps us solve problems, make decisions, and understand the world around us.
In daily activities, math is used for budgeting, cooking, and time management. Its principles support innovations in medicine, engineering, and communication.
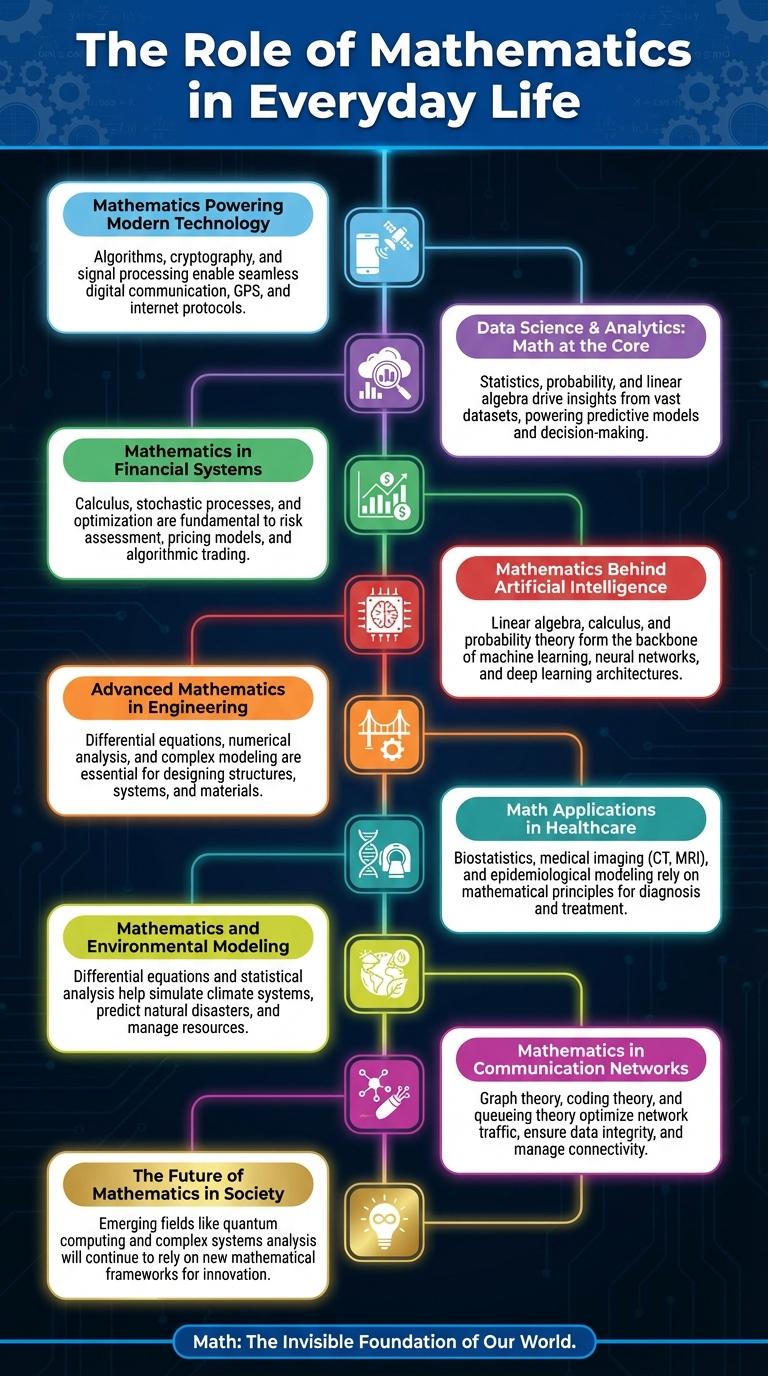
Mathematics Powering Modern Technology
Mathematics forms the foundation of modern technology, enabling advancements in computing, data encryption, and artificial intelligence. Complex algorithms and mathematical models drive innovations in software development, cybersecurity, and machine learning. The integration of mathematics in technology accelerates problem-solving and enhances digital communication worldwide.
Data Science & Analytics: Math at the Core
Mathematics serves as the foundation of Data Science and Analytics, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights from complex data. Mathematical models and algorithms drive decision-making across industries, making math indispensable in the modern analytical landscape.
- Linear Algebra - Provides tools for manipulating large datasets through matrix operations and vector spaces.
- Probability & Statistics - Supports data interpretation by quantifying uncertainty and modeling random processes.
- Optimization - Powers algorithms to find the best solutions in resource allocation and predictive modeling.
Mastering mathematical concepts is essential for innovation and precision in data-driven fields today.
Mathematics in Financial Systems
Mathematics plays a crucial role in modern financial systems, enabling precise risk assessment and efficient market analysis. Complex algorithms and quantitative models guide investment strategies and regulatory compliance.
Financial mathematics underpins derivative pricing, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection, ensuring stability and growth in global markets. Advanced statistical methods and computational tools drive innovations in banking and trading sectors.
Mathematics Behind Artificial Intelligence
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Mathematical Fields | Linear Algebra, Calculus, Probability, Statistics, Optimization |
| Linear Algebra | Transforms and manipulates data using vectors and matrices; essential for neural networks |
| Calculus | Enables the adjustment of model parameters through differentiation; backpropagation relies on it |
| Probability & Statistics | Used for modeling uncertainty, making decisions under risk, and training algorithms on data |
| Optimization | Mathematical methods used to minimize loss functions and improve AI model accuracy |
Advanced Mathematics in Engineering
Advanced mathematics serves as the foundation for innovative engineering solutions in the modern world. It enables precise modeling, simulation, and optimization across various engineering disciplines.
- Mathematical Modeling - Engineers use differential equations and linear algebra to simulate real-world systems accurately.
- Optimization Techniques - Advanced calculus and numerical methods help optimize design and performance in engineering projects.
- Computational Methods - Algorithms and discrete mathematics power computer-aided engineering tools and simulations.
Math Applications in Healthcare
How does mathematics impact healthcare in the modern world?
Mathematics plays a crucial role in healthcare by enabling accurate medical imaging and data analysis. Techniques such as statistical modeling and algorithm development improve disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
Mathematics and Environmental Modeling
Mathematics plays a critical role in understanding and predicting environmental changes. It enables precise modeling of complex natural systems to support sustainable decision-making.
- Climate Modeling - Mathematical equations simulate atmospheric and oceanic processes to forecast climate patterns and assess global warming impacts.
- Pollution Tracking - Differential equations model the dispersion of pollutants in air and water to help design effective mitigation strategies.
- Resource Management - Optimization algorithms assist in managing natural resources such as water and forests to balance human needs and ecological health.
Mathematics in Communication Networks
Mathematics is the backbone of modern communication networks, enabling efficient data transmission and error correction. Advanced algorithms and mathematical models optimize network performance and security.
Graph theory structures the layout of networks, ensuring robust connectivity between devices. Probability and statistics manage data traffic and minimize packet loss. Cryptography applies number theory to secure communication and protect sensitive information.
