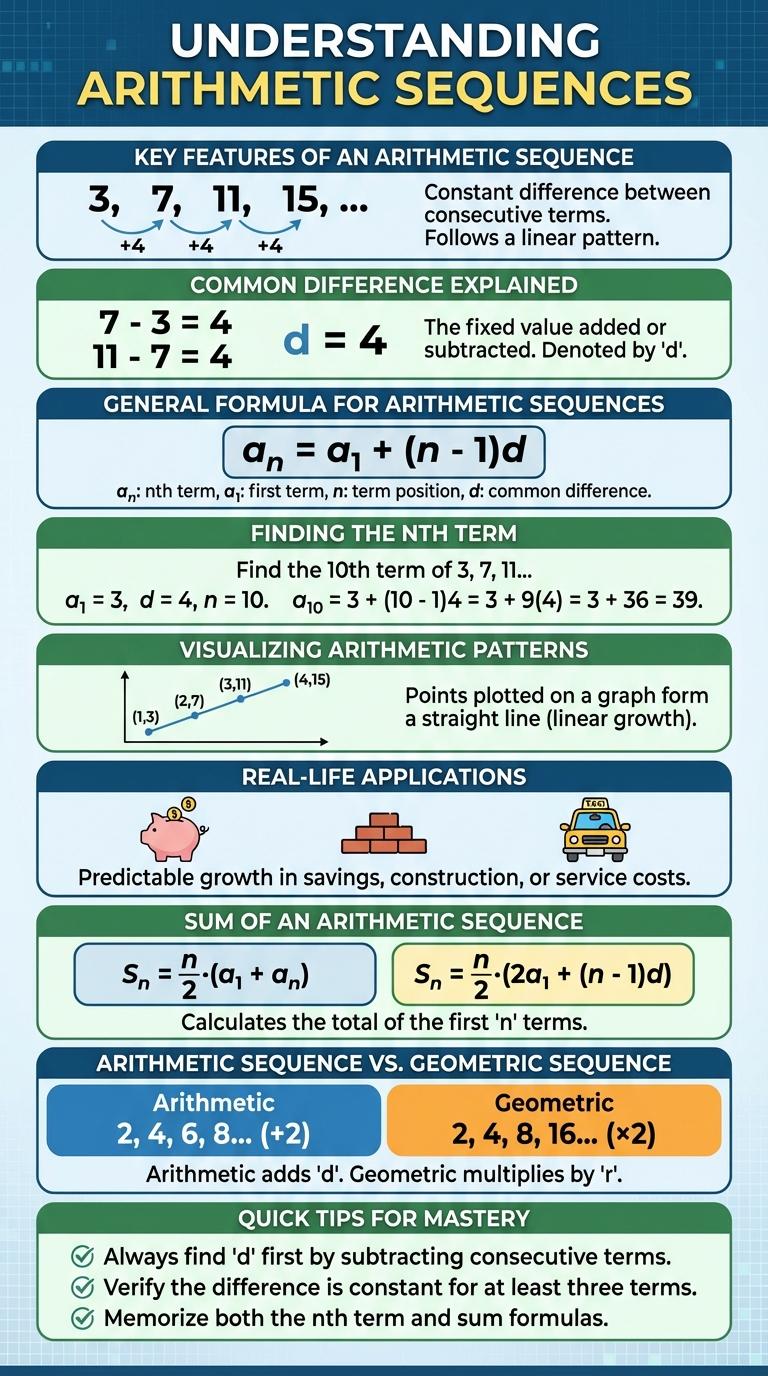
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers where each term increases by a constant difference. Understanding this pattern helps in solving various mathematical problems and real-life applications. This infographic visually breaks down the key concepts and formulas related to arithmetic sequences for easy comprehension.
Understanding Arithmetic Sequences
What is an arithmetic sequence and how is it defined?
An arithmetic sequence is a series of numbers where each term after the first is obtained by adding a constant difference. This constant, known as the common difference, remains the same throughout the sequence.
How do you identify the common difference in an arithmetic sequence?
Subtract any term from the subsequent term to find the common difference. Consistency of this difference confirms the sequence is arithmetic.
What is the formula to find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence?
The nth term can be calculated using the formula: a_n = a_1 + (n - 1)d, where a_1 is the first term, d is the common difference, and n is the term number.
How do arithmetic sequences apply in real life?
Arithmetic sequences model situations with constant incremental change, such as saving money over time or arranging sports seating. Their predictable pattern aids in forecasting and planning.
| Example Sequence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 2, 5, 8, 11, 14 | Common difference is 3; each number increases by 3 |
| 10, 7, 4, 1, -2 | Common difference is -3; each number decreases by 3 |
| 5, 5, 5, 5, 5 | Common difference is 0; all terms are equal |
Key Features of an Arithmetic Sequence
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers with a constant difference between consecutive terms, known as the common difference. Each term after the first is found by adding this common difference to the previous term. The general formula for the nth term is \(a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d\), where \(a_1\) is the first term and \(d\) is the common difference.
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Common Difference | Constant value added to each term |
| First Term (\(a_1\)) | Starting point of the sequence |
| General Term Formula | \(a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d\) |
| Linear Growth | Sequence increases or decreases by the common difference |
| Sum Formula | \(S_n = \frac{n}{2}(a_1 + a_n)\) |
Common Difference Explained
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers with a constant difference between consecutive terms. The common difference is the fixed amount added or subtracted to get from one term to the next.
- Definition - The common difference is the constant value that separates each term in the arithmetic sequence.
- Calculation - It is found by subtracting any term from the following term in the sequence.
- Significance - The common difference determines the linear growth or decline in the sequence.
Every arithmetic sequence can be fully described using its first term and the common difference.
General Formula for Arithmetic Sequences
An arithmetic sequence is a numerical series where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. This constant difference is known as the common difference, denoted by d.
The general formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence is an = a1 + (n - 1)d. Here, a1 is the first term, n is the term number, and d is the common difference.
Finding the nth Term
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers with a constant difference between consecutive terms. Finding the nth term allows you to determine any term in the sequence without listing all previous terms.
The nth term of an arithmetic sequence is calculated using the formula: an = a1 + (n - 1)d, where a1 is the first term, d is the common difference, and n is the term number. This formula helps in quickly identifying a specific term in sequences that increase or decrease uniformly. Understanding this concept is essential for solving problems in mathematics, finance, and computer science.
Visualizing Arithmetic Patterns
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers with a constant difference between each term. Visualizing this pattern helps in understanding how the sequence progresses step by step.
Each term in the sequence can be seen as points evenly spaced on a number line. Connecting these points reveals a linear pattern that represents the arithmetic sequence clearly.
Real-Life Applications
| Real-Life Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Planning | Modeling regular savings deposits or loan repayments using arithmetic sequences helps predict future balances. |
| Construction | Determining consistent incremental increases in material dimensions or spacing between supports follows an arithmetic sequence. |
| Scheduling | Planning events or tasks at fixed time intervals, such as weekly meetings, aligns with arithmetic sequence principles. |
| Inventory Management | Tracking stock replenishment where quantities increase or decrease by the same amount over regular periods. |
| Physical Training | Structuring workout progressions with steady increments in repetitions or duration based on arithmetic sequences. |
Sum of an Arithmetic Sequence
An arithmetic sequence is a series of numbers with a constant difference between consecutive terms. The sum of an arithmetic sequence can be calculated using the formula S = n/2 (a1 + an), where S is the sum, n is the number of terms, a1 is the first term, and an is the last term. This formula simplifies finding the total sum without adding each term individually.
Arithmetic Sequence vs. Geometric Sequence
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers with a constant difference between consecutive terms. A geometric sequence features a constant ratio between consecutive terms.
Both sequences form the foundation of many mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques.
- Arithmetic Sequence - Each term increases or decreases by a fixed amount called the common difference.
- Geometric Sequence - Each term is multiplied or divided by a fixed number called the common ratio.
- Formula Comparison - Arithmetic sequence: \( a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d \); geometric sequence: \( a_n = a_1 \times r^{(n-1)} \).
