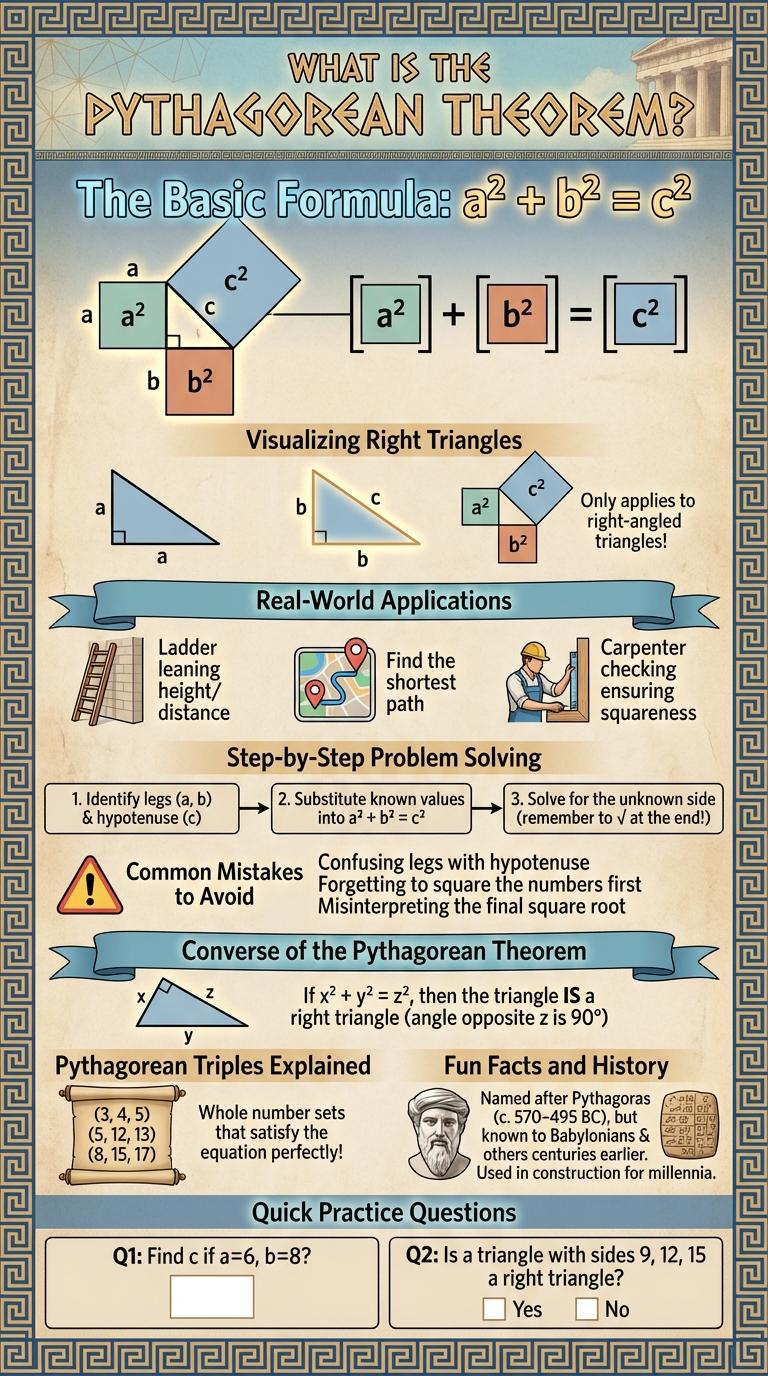
The Pythagorean theorem describes the relationship between the sides of a right triangle, stating that the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This infographic visually breaks down the theorem, offering clear illustrations and step-by-step explanations to enhance understanding. Explore practical examples and real-world applications to see how this fundamental concept is used in geometry and beyond.
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides in a right triangle. It establishes a precise relationship between the hypotenuse and the two legs of the triangle.
This theorem is essential in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science.
- Theorem Statement - The square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- Mathematical Formula - Expressed as \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), where c is the hypotenuse.
- Practical Usage - Used to calculate distances and angles in right-angled triangles across real-world applications.
The Basic Formula: a² + b² = c²
What is the Pythagorean Theorem and how is it used in geometry?
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. The basic formula, a2 + b2 = c2, states that the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides equals the square of the hypotenuse.
Visualizing Right Triangles
The Pythagorean theorem explains the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. Visualizing right triangles aids in understanding how the theorem applies to real-world problems.
- Right Triangle - A triangle with one 90-degree angle, forming the basis for the theorem.
- Hypotenuse - The longest side opposite the right angle, calculated with the theorem.
- Legs - The two sides adjacent to the right angle, used in the formula a2 + b2 = c2.
Visual diagrams help learners grasp how the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Real-World Applications
The Pythagorean Theorem is vital in various real-world applications, helping to determine distances and measurements accurately. It applies to fields such as construction, navigation, and computer graphics.
Engineers use the theorem to calculate the slope of roofs and supports in buildings. Navigators rely on it to find straight-line distances between locations on maps. In computer graphics, it helps render images by calculating pixel distances and creating realistic visual effects.
Step-by-Step Problem Solving
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. To solve problems step-by-step, first identify the right angle and label the sides as a, b, and c, where c is the hypotenuse. Next, apply the formula \(c^2 = a^2 + b^2\) to find the missing side by plugging in known values and solving for the unknown.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. A common mistake is confusing the hypotenuse with one of the legs, leading to incorrect calculations. Another frequent error is neglecting to verify that the triangle is right-angled before applying the theorem.
Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
The Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem states that if the square of one side of a triangle equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. This property helps in identifying right-angled triangles when side lengths are known.
For example, given a triangle with sides a, b, and c, if \( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \) holds true, then the angle opposite side c is a right angle. This converse is widely used in geometry, construction, and trigonometry to verify right angles.
Pythagorean Triples Explained
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Pythagorean triples are sets of three positive integers that satisfy this relationship.
Common examples include (3, 4, 5) and (5, 12, 13), where the sides form perfect right triangles. These triples are fundamental in geometry, number theory, and practical applications like construction and navigation.
Fun Facts and History
| Fun Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Ancient Origins | The Pythagorean theorem was known long before Pythagoras, used by Babylonian and Egyptian mathematicians around 1900 BC. |
| Countless Proofs | There are over 350 known proofs of the Pythagorean theorem, including geometric, algebraic, and even visual proofs. |
| Widespread Applications | Used in architecture, navigation, physics, and computer science to solve problems involving right triangles. |
| Named After Pythagoras | Pythagoras, a Greek mathematician and philosopher from around 570-495 BC, is credited with the first formal proof. |
| Symbolic Representation | The formula \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\) relates the squares of a right triangle's legs to the square of the hypotenuse. |
