Islam, one of the world's major religions, encompasses a rich history, diverse cultures, and profound spiritual teachings. Its core beliefs center on the oneness of God (Allah), the prophethood of Muhammad, and the importance of the Quran as a guiding scripture. This infographic visually explores key aspects of Islam, highlighting its pillars, practices, and global presence.
What Is Islam?
Islam is a monotheistic Abrahamic religion founded in the 7th century CE by the Prophet Muhammad in Mecca. It is based on the belief in one God, Allah, and the teachings revealed in the Quran.
Followers of Islam, known as Muslims, practice the Five Pillars which guide their faith and daily actions. Islam emphasizes compassion, justice, and submission to the will of Allah as paths to spiritual fulfillment.
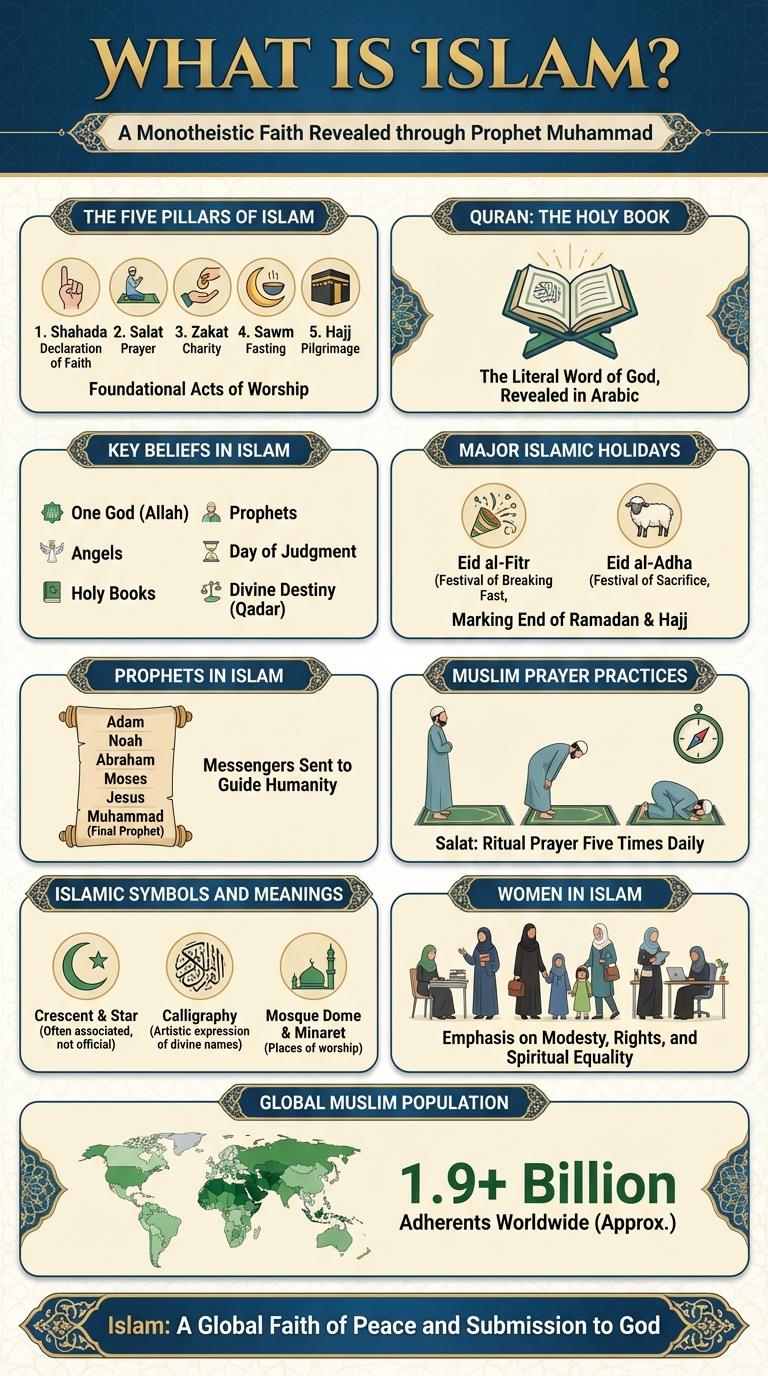
The Five Pillars of Islam
Islam is a monotheistic religion founded in the 7th century by Prophet Muhammad. The Five Pillars of Islam represent the core acts of worship and practice for Muslims worldwide.
- Shahada (Faith) - Declaration of belief in the oneness of Allah and Muhammad as His prophet.
- Salah (Prayer) - Performing five daily prayers facing the Kaaba in Mecca.
- Zakat (Charity) - Giving a fixed portion of wealth to those in need to purify one's income.
- Sawm (Fasting) - Abstaining from food, drink, and other physical needs during daylight hours in Ramadan.
- Hajj (Pilgrimage) - Performing the pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in a lifetime if physically and financially able.
These pillars form the foundation of a Muslim's faith and practice, guiding their spiritual and social life.
Quran: The Holy Book
What is the Quran in Islam?
The Quran is the holy book of Islam, believed to be the word of God as revealed to Prophet Muhammad. It serves as the primary source of guidance for Muslims worldwide.
How is the Quran structured?
The Quran consists of 114 chapters called Surahs, each varying in length and theme. Its original text is written in classical Arabic, preserving its linguistic and spiritual integrity.
Why is the Quran important for Muslims?
The Quran provides moral, legal, and spiritual guidance that shapes Muslim beliefs and practices. It is recited during prayers and memorized by millions as an act of devotion.
How was the Quran revealed to Muhammad?
The Quran was revealed over 23 years through the angel Gabriel to Prophet Muhammad. This gradual revelation ensured clear understanding and preservation of the message.
In what ways is the Quran preserved today?
The Quran is preserved through memorization, known as Tajweed, and written manuscripts. Modern digital copies and translations make it accessible to a global audience while maintaining its original text.
Key Beliefs in Islam
Islam is a monotheistic Abrahamic faith centered on the belief in one God, Allah. It is based on the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad as conveyed in the Quran.
Key beliefs in Islam include the Five Pillars: Shahada (faith), Salah (prayer), Zakat (charity), Sawm (fasting during Ramadan), and Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca). Muslims believe in angels, divine scriptures, and the Day of Judgment. These core principles guide the spiritual and ethical conduct of Muslims worldwide.
Major Islamic Holidays
| Holiday | Description |
|---|---|
| Eid al-Fitr | Celebrates the end of Ramadan, the Islamic holy month of fasting. It includes communal prayers, feasting, and giving of charity (Zakat al-Fitr). |
| Eid al-Adha | Commemorates the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God. Marked by prayer, sacrifice of animals, and distribution to the needy. |
| Ramadan | A month of fasting from dawn to sunset, spiritual reflection, increased prayer, and devotion to worship. |
| Islamic New Year (Hijri New Year) | Marks the beginning of the Islamic lunar calendar year. It commemorates the Hijra, Prophet Muhammad's migration from Mecca to Medina. |
| Mawlid al-Nabi | Celebrates the birth of Prophet Muhammad. Observances include religious gatherings, recitations of the Quran, and storytelling about the Prophet's life. |
Prophets in Islam
Islam honors numerous prophets who conveyed God's guidance to humanity. These prophets are respected as exemplary figures in faith and morality.
Muslims recognize 25 prophets explicitly mentioned in the Quran, with Prophet Muhammad being the final messenger.
- Prophet Adam - Regarded as the first human and the first prophet in Islam, who introduced monotheism.
- Prophet Noah - Known for his perseverance in preaching and leading the Ark during the great flood.
- Prophet Abraham - Called the "friend of Allah," he is a central figure in Islamic tradition and ancestor of many prophets.
Muslim Prayer Practices
Muslim prayer, known as Salah, is performed five times daily at specific times: Fajr, Dhuhr, Asr, Maghrib, and Isha. Each prayer involves a series of physical postures and Quranic recitations, fostering spiritual discipline and connection to Allah. The mosque serves as a communal prayer space, emphasizing unity and equality among worshippers.
Islamic Symbols and Meanings
Islamic symbols carry deep spiritual and cultural meanings within the Muslim world. The crescent moon and star represent guidance and light in darkness, often seen atop mosques. The calligraphic representation of "Allah" and the Kaaba outline symbolize faith and the unity of Muslims during prayer and pilgrimage.
Women in Islam
Women in Islam hold a significant and respected position within the faith, with numerous rights and responsibilities outlined in the Qur'an and Hadith. Their roles encompass spiritual, social, and familial dimensions, emphasizing dignity, equality, and empowerment.
Islamic teachings grant women the right to education, property ownership, and participation in social and economic activities. Historical and contemporary examples illustrate the impact and contributions of Muslim women across diverse cultures and societies.
