The circulatory system plays a crucial role in transporting blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body, ensuring cellular functions and overall health. This infographic visually breaks down the heart, blood vessels, and blood flow pathways to enhance understanding of cardiovascular processes. Clear illustrations and concise facts help demystify how the circulatory system sustains life and supports bodily functions.
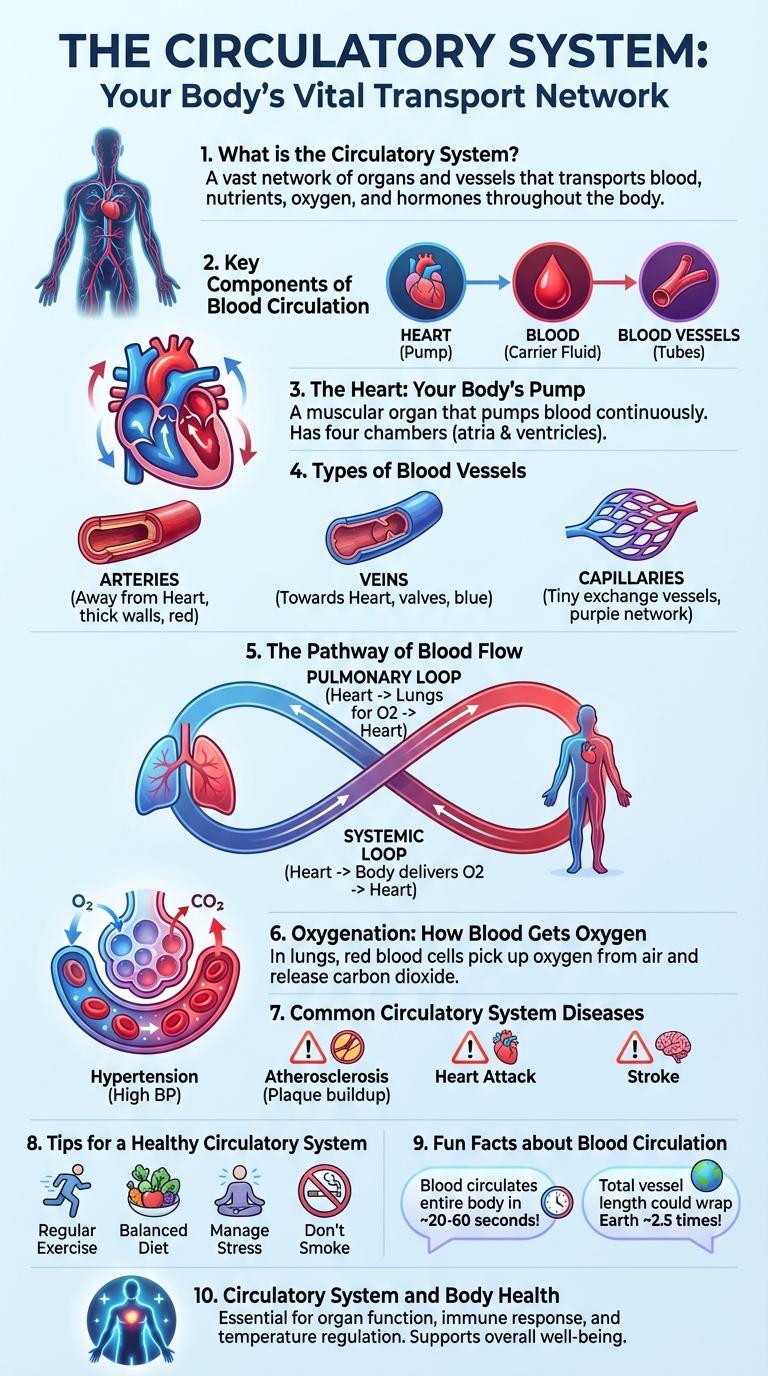
What is the Circulatory System?
The circulatory system is responsible for transporting blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and supporting cellular function.
- Heart - The muscular organ that pumps blood through the body's network of blood vessels.
- Blood Vessels - Arteries, veins, and capillaries that carry blood to and from the heart and tissues.
- Blood - The fluid containing oxygen, nutrients, and waste products that circulates in the vessels.
The circulatory system ensures efficient delivery of essential substances to every cell and removes waste products for excretion.
Key Components of Blood Circulation
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart | Pumps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the body |
| Arteries | Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to tissues |
| Veins | Return oxygen-poor blood back to the heart |
| Capillaries | Tiny vessels where oxygen and nutrients exchange with tissues |
| Blood | Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and removes waste |
The Heart: Your Body's Pump
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It ensures oxygen and nutrients reach every cell efficiently.
Located in the chest cavity, the heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. This structure supports its role as the body's powerful and continuous pump.
Types of Blood Vessels
What are the main types of blood vessels in the circulatory system?
The circulatory system consists of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Each type plays a vital role in transporting blood throughout the body.
| Type of Blood Vessel | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Arteries | Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body. |
| Veins | Return oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. |
| Capillaries | Enable exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between blood and tissues. |
The Pathway of Blood Flow
The circulatory system is essential for transporting blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients. Understanding the pathway of blood flow highlights the heart's critical role in maintaining circulation.
- Blood enters the right atrium - Deoxygenated blood returns from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava into the right atrium.
- Blood moves to the right ventricle - From the right atrium, blood flows into the right ventricle which pumps it to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium - Blood receives oxygen in the lungs and travels back to the heart's left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
- Blood is pumped into the left ventricle - The left atrium pushes blood into the left ventricle, the heart's strongest chamber.
- Oxygen-rich blood circulates the body - The left ventricle pumps blood through the aorta, distributing oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
Oxygenation: How Blood Gets Oxygen
The circulatory system plays a vital role in oxygenation by transporting oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. Blood gains oxygen primarily in the lungs where it exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen.
Oxygen enters the bloodstream through tiny air sacs called alveoli in the lungs. Hemoglobin in red blood cells binds to oxygen molecules, forming oxyhemoglobin. This oxygenated blood is then pumped by the heart to tissues and organs, supplying vital oxygen for cellular functions.
Common Circulatory System Diseases
The circulatory system is essential for transporting blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body. Common circulatory system diseases include hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, and heart failure. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes can significantly improve outcomes and reduce complications.
Tips for a Healthy Circulatory System
The circulatory system is essential for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. Maintaining its health supports overall well-being and reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Regular Exercise - Engaging in physical activities improves heart strength and promotes efficient blood flow.
- Balanced Diet - Consuming foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants supports healthy blood vessels.
- Hydration - Drinking enough water helps maintain proper blood volume and circulation.
Fun Facts about Blood Circulation
Blood circulation is a continuous loop that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. The heart pumps approximately 2,000 gallons of blood daily to sustain vital organs and tissues.
Red blood cells complete a full circuit around the body in about 20 seconds, ensuring rapid delivery of oxygen. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, are so tiny that blood cells pass through them in single file.
