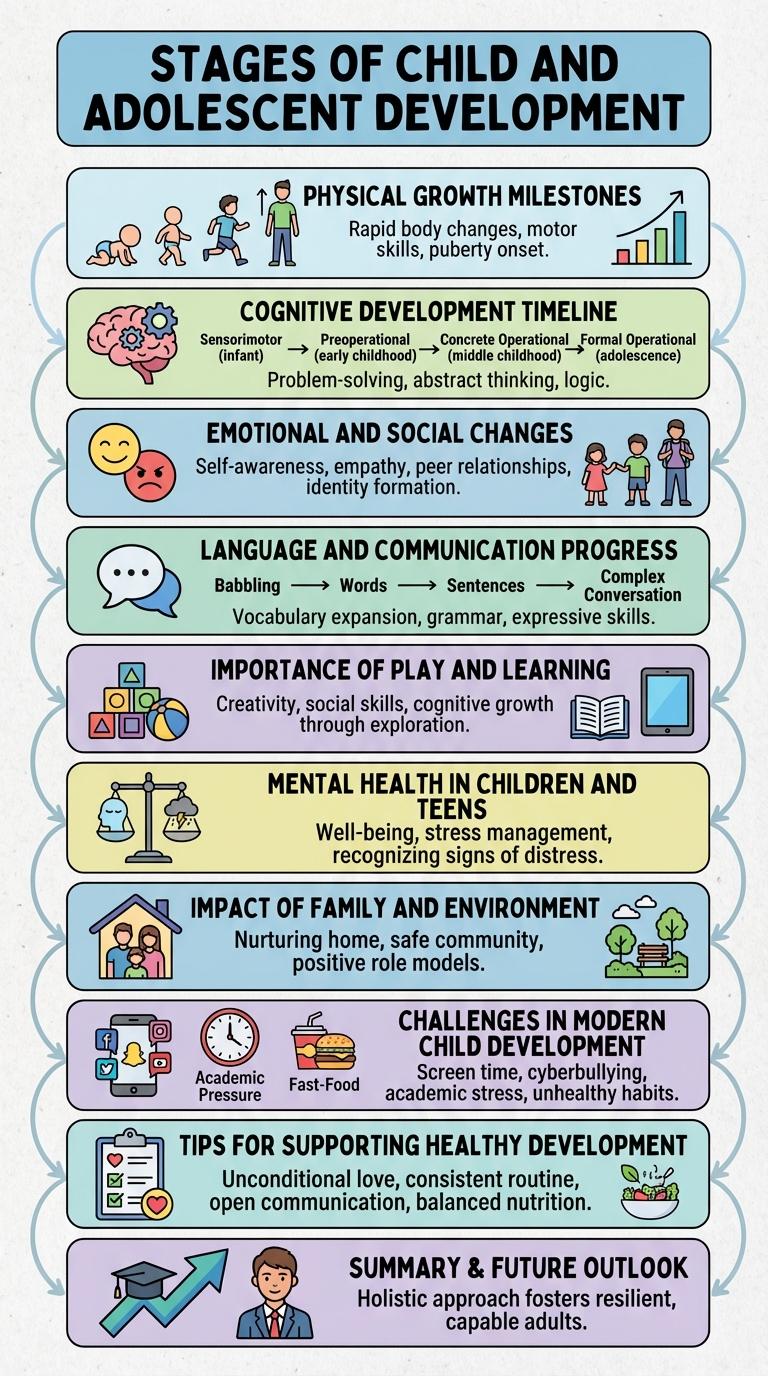
Understanding key milestones in child and adolescent development reveals critical patterns in physical growth, cognitive abilities, and emotional well-being. Tracking these stages provides valuable insights into behavior changes and learning capacities at various ages. Visualizing this information in an infographic makes it accessible and engaging for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals alike.
Stages of Child and Adolescent Development
Child and adolescent development occurs through distinct stages that reflect physical, cognitive, and emotional growth. Understanding these stages helps caregivers support healthy development effectively.
- Infancy (0-2 years) - Rapid brain growth occurs, with major milestones in motor skills and attachment formation.
- Early Childhood (3-6 years) - Language development accelerates, and children begin to explore independence and social interactions.
- Middle Childhood (7-11 years) - Cognitive skills expand, allowing for logical thinking, academic learning, and self-awareness.
- Early Adolescence (12-14 years) - Puberty begins, causing physical changes and heightened emotional intensity.
- Late Adolescence (15-18 years) - Identity formation continues as abstract thinking develops and social relationships deepen.
Physical Growth Milestones
Physical growth milestones mark significant stages in a child's and adolescent's development. These milestones track progress in height, weight, motor skills, and overall body composition.
Infants typically double their birth weight by six months and triple it by their first birthday. During adolescence, rapid growth spurts lead to an average height increase of 8 to 12 inches over 2 to 3 years.
Cognitive Development Timeline
How does cognitive development progress in children and adolescents? Cognitive development involves the growth of perception, memory, language, and problem-solving skills. This development occurs in predictable stages from infancy through adolescence.
| Age Range | Cognitive Milestones |
|---|---|
| 0-2 years | Sensorimotor stage: Learning through sensory experiences and motor actions |
| 2-7 years | Preoperational stage: Development of language and symbolic thinking, limited logical reasoning |
| 7-11 years | Concrete operational stage: Logical thinking about concrete events, understanding conservation |
| 12+ years | Formal operational stage: Abstract reasoning, hypothesis testing, and advanced problem-solving |
What factors influence cognitive development during these stages? Genetics, environment, education, and social interactions all play significant roles. Supportive learning environments enhance cognitive skills and promote healthy mental growth.
Emotional and Social Changes
Emotional and social changes during childhood and adolescence shape identity and interpersonal skills. Peer relationships become increasingly important, influencing self-esteem and emotional regulation. Developing empathy and communication skills supports healthy social interactions and emotional well-being.
Language and Communication Progress
Language and communication skills rapidly develop during childhood and adolescence, forming the foundation for social interaction and academic success. Early childhood sees significant progress in vocabulary explosion, sentence formation, and understanding of grammar. Adolescents refine these abilities, mastering complex language structures and enhancing pragmatic communication to navigate social and educational environments effectively.
Importance of Play and Learning
Play is a fundamental component of child and adolescent development, fostering creativity, social skills, and emotional resilience. Engaging in play supports cognitive growth and helps children understand the world around them.
Learning through play enhances problem-solving abilities and language development. It encourages collaboration and negotiation among peers, building essential interpersonal skills. Structured and unstructured play experiences are equally vital for holistic growth during childhood and adolescence.
Mental Health in Children and Teens
Mental health in children and adolescents is a critical aspect of overall development, influencing emotional well-being and social functioning. Early identification and support can prevent long-term psychological issues and promote healthy growth.
- Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders - Approximately 1 in 5 children and teens experience a diagnosable mental health disorder each year.
- Impact of Anxiety and Depression - Anxiety and depression are the most common mental health issues affecting youth, often leading to academic and social challenges.
- Importance of Early Intervention - Timely mental health support significantly improves outcomes and reduces the risk of chronic mental illness during adulthood.
Promoting awareness and access to mental health resources is essential for fostering resilience in children and adolescents.
Impact of Family and Environment
| Factor | Impact on Child and Adolescent Development |
|---|---|
| Parental Involvement | Enhances cognitive skills, emotional security, and academic performance. |
| Home Environment | Stable and nurturing homes promote social competence and self-esteem. |
| Socioeconomic Status | Higher status correlates with better access to education, healthcare, and nutrition. |
| Peer Influence | Shapes social behaviors, identity formation, and risk-taking tendencies. |
| Community Safety | Safe neighborhoods reduce stress and encourage positive developmental outcomes. |
Challenges in Modern Child Development
Modern child and adolescent development faces complex challenges shaped by rapid technological, social, and environmental changes. These factors impact physical health, emotional well-being, and social skills during critical growth periods.
- Screen Time and Digital Addiction - Excessive exposure to screens disrupts attention spans and interferes with healthy sleep patterns in children and teens.
- Mental Health Concerns - Increasing rates of anxiety and depression affect emotional development and academic performance.
- Social Isolation - Reduced face-to-face interaction impairs the development of communication and interpersonal skills.
- Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle - Limited physical activity contributes to rising childhood obesity rates and related health issues.
- Environmental Stressors - Exposure to pollution and socio-economic instability hinders cognitive and emotional growth.
