Gas strand infographics visually represent the complex processes and components involved in detecting and managing gas leaks. By combining clear icons, concise data points, and informative visuals, these infographics enhance understanding of gas strand mechanisms and safety protocols. They serve as essential tools for industrial workers, safety engineers, and environmental professionals aiming to prevent hazardous incidents.
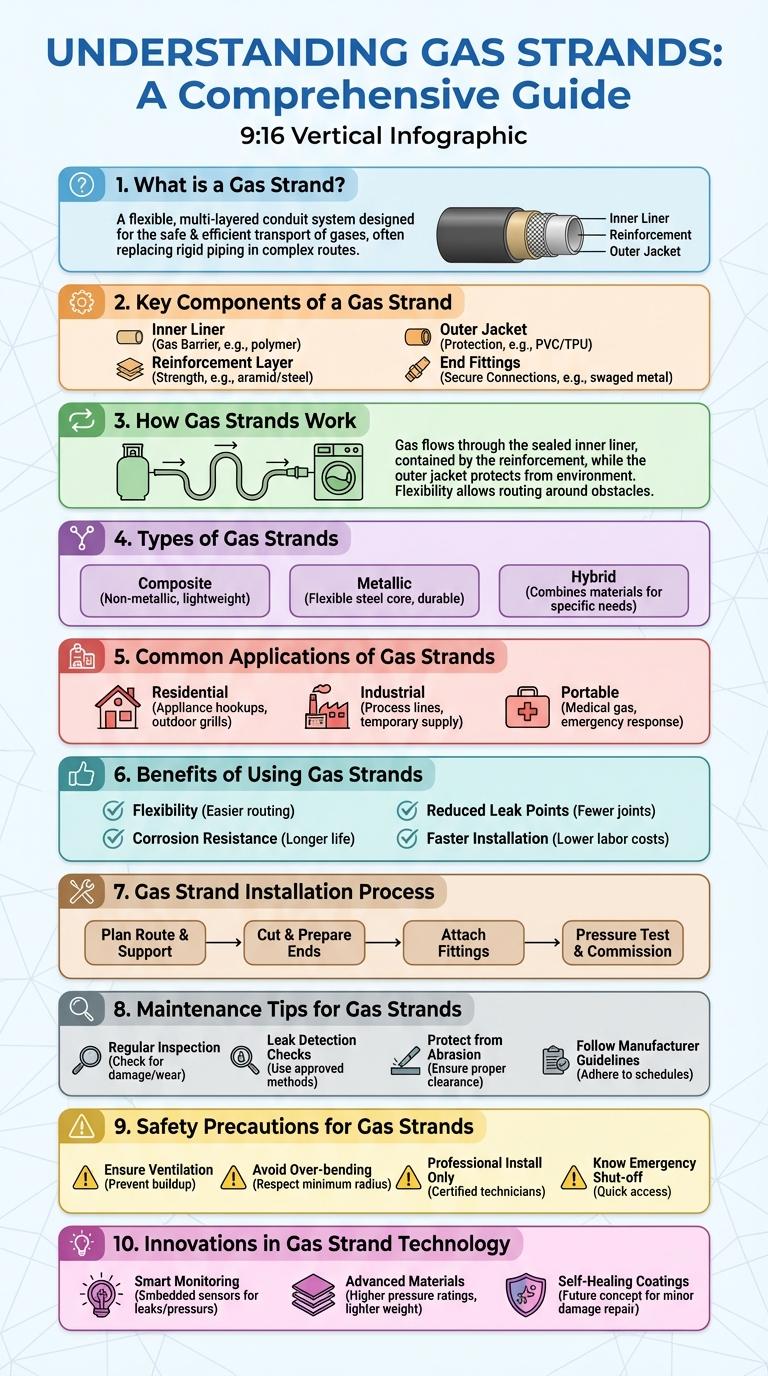
What is a Gas Strand?
A gas strand is a narrow, elongated flow of gas moving through a medium. It often occurs in natural environments or industrial processes.
Gas strands influence the distribution and behavior of gases in various applications.
- Definition - A gas strand refers to a concentrated, directional flow of gas particles within a larger volume.
- Occurrence - Gas strands frequently appear in atmospheric phenomena and engineered gas pipelines.
- Importance - Understanding gas strands helps optimize combustion efficiency and pollutant dispersion.
Key Components of a Gas Strand
An infographic about the key components of a gas strand highlights essential elements such as the gas pipeline, compressor stations, and metering devices. These components ensure efficient gas transportation, pressure regulation, and accurate measurement of gas flow. Understanding each part's function is crucial for maintaining safety and operational efficiency in gas distribution systems.
How Gas Strands Work
| Step | How Gas Strands Work |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gas strands are pipelines that transport natural gas from extraction sites to processing plants or end users. |
| 2 | Gas flows under high pressure through the pipeline, maintained by compressor stations to ensure steady movement. |
| 3 | Along the strand, pressure regulators adjust gas pressure to safe levels for distribution and consumption. |
| 4 | Gas quality is monitored continuously to detect impurities and ensure compliance with safety standards. |
| 5 | End users receive natural gas for residential heating, industrial use, or electricity generation through connected distribution lines. |
Types of Gas Strands
Gas strands are natural deposits of hydrocarbons trapped in porous rock formations. These strands can vary significantly in composition and origin, influencing their utility and extraction methods.
The main types of gas strands include conventional, shale, tight, coalbed methane, and biogenic gas. Each type differs in geological formation and extraction techniques used to access the gas.
Common Applications of Gas Strands
Gas strands play a crucial role in various industrial and residential applications. These specialized gas delivery systems ensure safe and efficient transportation of gases.
Common applications of gas strands include heating systems, where they supply natural gas to furnaces and boilers. In the medical field, gas strands provide essential gases like oxygen and nitrous oxide for patient care. Industrial sectors use gas strands for welding, cutting, and other manufacturing processes that require precise gas control.
Benefits of Using Gas Strands
What are the key benefits of using gas strands? Gas strands provide enhanced energy efficiency and cost savings for industrial and residential applications. They also offer higher safety standards and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional fuels.
Gas Strand Installation Process
The Gas Strand Installation Process ensures safe and efficient delivery of gas through specialized pipelines. Proper steps during installation prevent leaks and optimize performance.
First, the site is prepared by clearing the area and marking the route for the gas strand. Next, trenches are dug to precise depths following safety regulations.
Maintenance Tips for Gas Strands
Proper maintenance of gas strands ensures safety and optimal performance. Regular checks prevent leaks and extend the lifespan of gas equipment.
- Inspect Connections - Regularly check all gas connections for tightness and signs of wear to avoid leaks.
- Clean Components - Remove dirt and debris from valves and tubes to maintain clear gas flow.
- Test for Leaks - Use soapy water or electronic detectors to identify and fix leaks promptly.
Safety Precautions for Gas Strands
Gas strands pose significant safety risks including fire hazards and toxic exposure. Proper ventilation, use of gas detectors, and wearing protective gear are essential safety precautions. Regular maintenance and immediate leak detection can prevent accidents and ensure a safe environment.
