Bias and prejudice shape perceptions and influence decisions in ways that are often unconscious yet deeply impactful. Understanding these concepts helps reveal how stereotypes and unfair judgments develop, affecting individuals and society. Visualizing this information through an infographic clarifies the roots, types, and consequences of bias and prejudice for more effective awareness and change.
Understanding Bias and Prejudice
What are bias and prejudice, and how do they affect our perceptions?
Bias is an unconscious tendency to favor or oppose certain groups, while prejudice involves preconceived opinions based on stereotypes. Both shape our judgments and interactions, often leading to unfair treatment.
How do bias and prejudice develop in individuals?
They develop through socialization, cultural influences, and personal experiences. Exposure to stereotypes in media and community reinforces these attitudes over time.
What is the difference between implicit and explicit bias?
Implicit bias operates unconsciously and influences behavior without awareness. Explicit bias is a conscious belief or attitude openly recognized by the individual.
Why is it important to recognize and address our biases?
Recognizing biases helps reduce discrimination and promotes fairness in decision-making. It fosters inclusive environments and improves interpersonal relationships.
What strategies can help reduce bias and prejudice?
Education on diversity, perspective-taking, and critical self-reflection are effective strategies. Engaging with diverse groups also challenges stereotypes and broadens understanding.
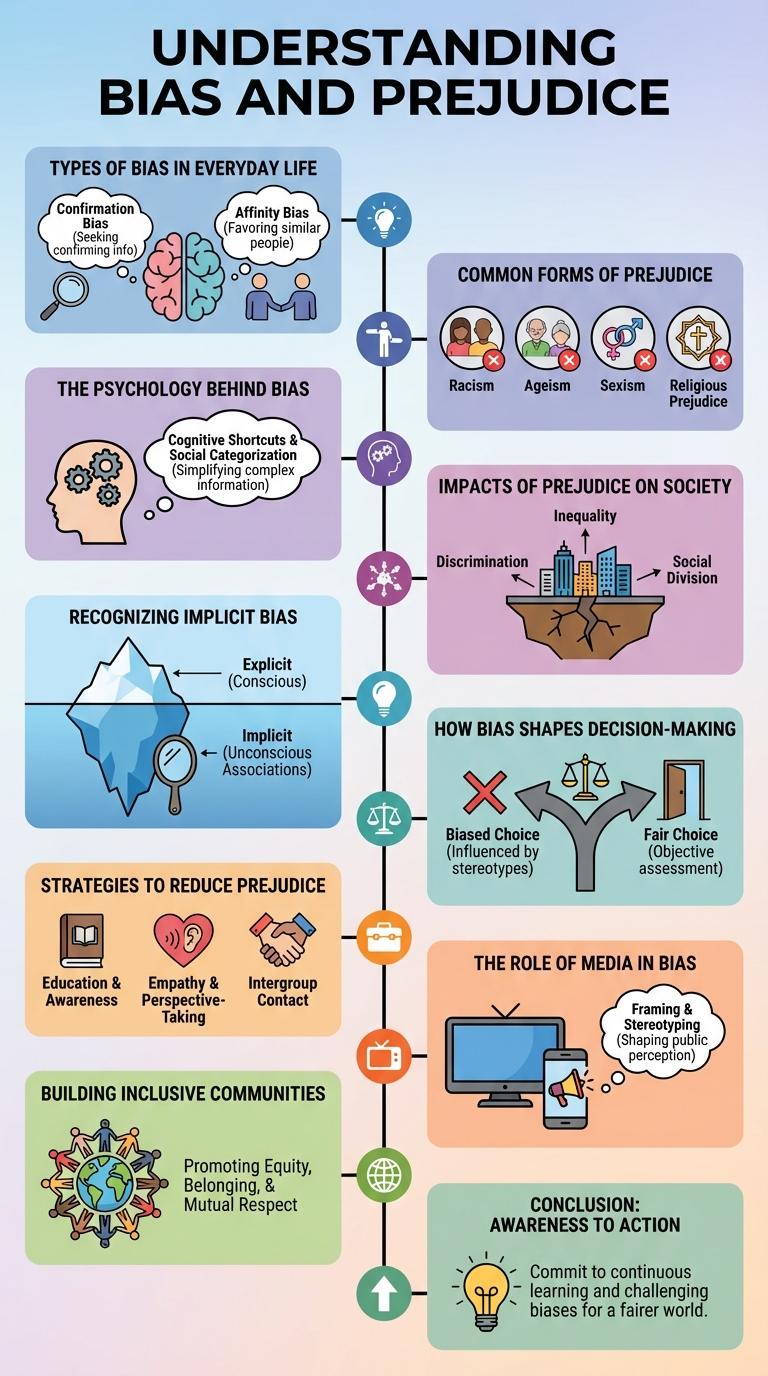
Types of Bias in Everyday Life
Bias and prejudice shape perceptions and behaviors in everyday life, influencing decisions and interactions unconsciously. Recognizing different types of bias helps in fostering awareness and promoting inclusivity.
Cognitive bias includes errors in thinking, such as confirmation bias, where people favor information that supports their existing beliefs. Social bias involves attitudes toward groups based on characteristics like race, gender, or age.
Common Forms of Prejudice
Bias and prejudice manifest in various common forms, including racial, gender, age, religious, and socioeconomic prejudices. Racial prejudice involves negative attitudes or discrimination against individuals based on their race or ethnicity. Gender prejudice refers to unfair treatment or assumptions made due to a person's gender identity or expression.
Age prejudice, often called ageism, targets individuals based on their age, affecting both young and elderly populations. Religious prejudice includes negative stereotypes or hostility toward people because of their religious beliefs or practices. Socioeconomic prejudice involves discrimination based on a person's economic status or class, impacting access to opportunities and resources.
The Psychology Behind Bias
Bias and prejudice stem from deep-rooted psychological processes that influence human perception and behavior. These mental shortcuts help individuals quickly categorize information but often lead to unfair judgments.
Social identity theory explains how people favor their own groups while discriminating against others to enhance self-esteem. Cognitive biases like confirmation bias reinforce existing stereotypes by filtering information that aligns with prior beliefs. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for addressing and reducing biased attitudes in society.
Impacts of Prejudice on Society
Prejudice shapes social interactions and influences community dynamics in profound ways. Understanding its impacts helps foster more inclusive environments.
- Social Division - Prejudice creates barriers between groups, leading to segregation and mistrust within communities.
- Economic Disparities - Bias in hiring and education limits opportunities for marginalized groups, perpetuating poverty cycles.
- Psychological Harm - Experiencing prejudice causes stress, lowers self-esteem, and contributes to mental health issues.
- Reduced Social Cohesion - Widespread bias weakens the sense of unity and cooperation in society.
- Violence and Conflict - Prejudice can escalate into discrimination and hate crimes, undermining social stability.
Recognizing Implicit Bias
Implicit bias refers to the unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that affect our understanding, actions, and decisions. Recognizing these biases is essential to reduce prejudice and promote fairness in everyday interactions.
- Self-awareness - Identifying personal biases requires honest self-reflection and acknowledging unconscious preferences.
- Implicit Association Tests (IAT) - These tools measure unconscious biases by analyzing reaction times to different social categories.
- Feedback and Dialogue - Engaging in conversations and receiving feedback helps uncover hidden prejudices and challenges assumptions.
Recognizing implicit bias is the first step toward fostering inclusive and equitable environments.
How Bias Shapes Decision-Making
| Aspect of Bias | Impact on Decision-Making |
|---|---|
| Implicit Bias | Influences unconscious judgments and affects choices without awareness |
| Stereotyping | Leads to generalized assumptions, limiting objective evaluation of individuals |
| Confirmation Bias | Promotes preference for information that supports existing beliefs, skewing decisions |
| In-group Favoritism | Encourages preferential treatment of people perceived as part of one's group |
| Prejudice | Creates negative attitudes that obstruct fair and equitable decision outcomes |
Strategies to Reduce Prejudice
Bias and prejudice are deeply ingrained attitudes that affect social interactions and decision-making. Addressing these requires conscious efforts to promote understanding and empathy among diverse groups.
Strategies to reduce prejudice include education that challenges stereotypes and encourages critical thinking. Intergroup contact promotes positive relationships and reduces fear of the unknown.
The Role of Media in Bias
The media plays a crucial role in shaping public perceptions and can influence bias through selective reporting and representation. Coverage choices often reinforce stereotypes and contribute to the persistence of prejudice in society.
- Framing of Stories - Media frames events in ways that highlight negative traits of certain groups, which can amplify bias among audiences.
- Underrepresentation - Marginalized communities are often underrepresented or misrepresented in media, leading to skewed public understanding.
- Sensationalism - Sensational headlines and visuals focus on dramatic incidents, reinforcing fear and prejudice against specific groups.
