Education inequality highlights disparities in access, resources, and opportunities among students from different socioeconomic backgrounds. Visualizing these gaps through an infographic reveals critical data on funding, graduation rates, and achievement levels across various demographics. Understanding these disparities is essential for developing targeted policies to foster equitable learning environments.
The Global Divide in Education
Education inequality remains a critical global issue, with significant disparities between high-income and low-income countries. Access to quality education varies drastically, impacting future economic and social opportunities worldwide.
- Access to Schooling - Over 258 million children and youth are out of school globally, mostly in low-income regions.
- Quality of Education - Students in developing countries often receive lower-quality education due to inadequate resources and poorly trained teachers.
- Gender Disparities - Girls in many parts of the world face higher barriers to education, resulting in lower enrollment rates compared to boys.
Key Factors Driving Educational Inequality
| Key Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Socioeconomic Status | Students from low-income families face limited access to quality schools, resources, and extracurricular opportunities. |
| Geographic Location | Rural and underserved urban areas often have fewer educational facilities and less experienced teachers compared to affluent regions. |
| Funding Disparities | Unequal distribution of school funding results in disparities in infrastructure, technology, and learning materials. |
| Language Barriers | Non-native speakers or students from diverse linguistic backgrounds face challenges in comprehension and instruction. |
| Discrimination & Bias | Racial, ethnic, and gender biases affect student treatment, expectations, and access to advanced courses or programs. |
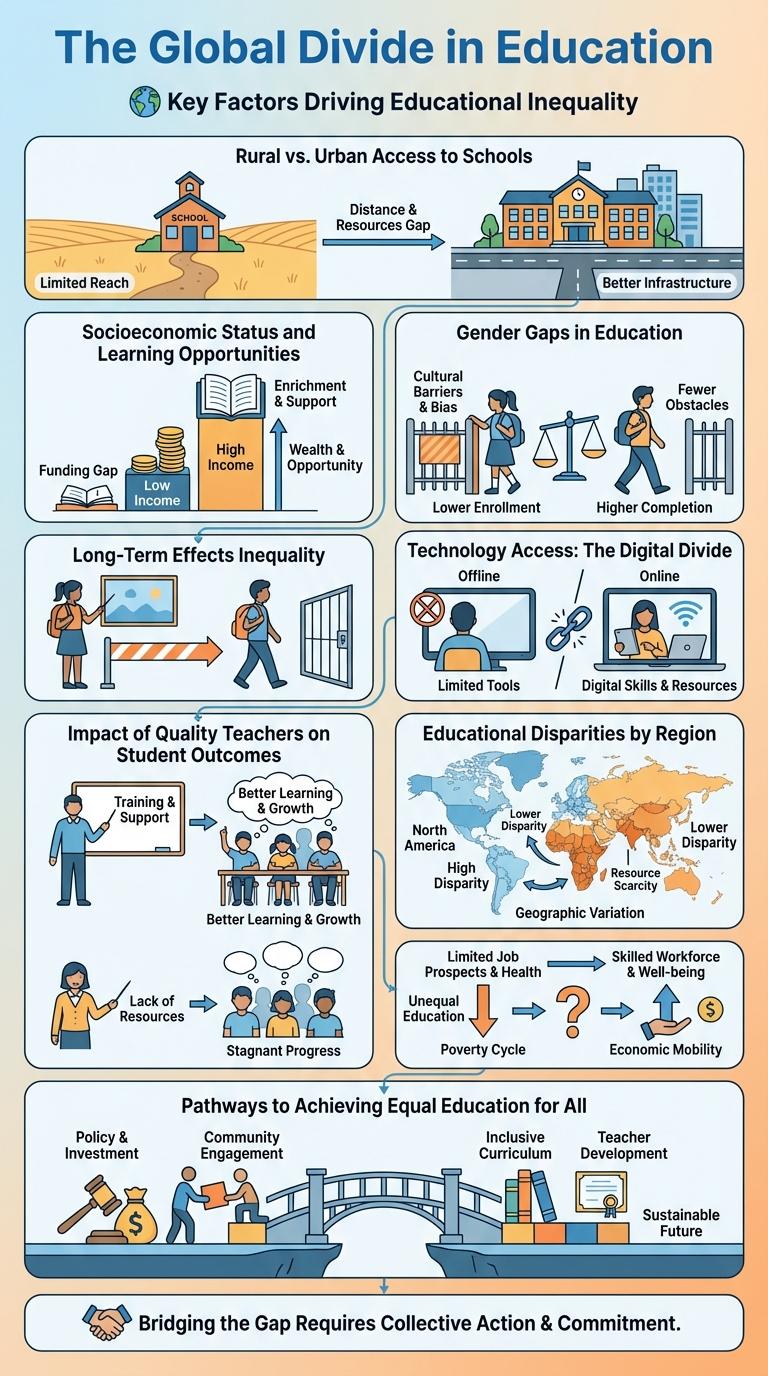
Rural vs. Urban Access to Schools
Education inequality significantly affects rural and urban areas, creating gaps in access to quality schools. Rural regions often face challenges such as limited school infrastructure and fewer qualified teachers compared to urban centers. Urban students generally have better access to resources, technology, and extracurricular opportunities, further widening the disparity.
Socioeconomic Status and Learning Opportunities
Education inequality is significantly influenced by socioeconomic status, affecting students' access to quality learning opportunities. Children from low-income families often attend underfunded schools with fewer resources, limiting their academic achievement. Bridging this gap requires targeted policies that expand access to enriched educational programs for disadvantaged communities.
Gender Gaps in Education
Gender gaps in education remain a significant barrier to equal opportunity worldwide. Disparities in access, enrollment, and completion rates affect girls disproportionately in many regions.
- Enrollment Disparity - In low-income countries, girls are 9% less likely than boys to be enrolled in primary school.
- Completion Rates - Only 66% of girls in developing countries complete lower secondary education compared to 73% of boys.
- Impact of Socioeconomic Factors - Poverty and cultural norms often prioritize boys' education over girls', limiting girls' educational advancement.
Addressing gender gaps in education is crucial for achieving global equality and economic growth.
Technology Access: The Digital Divide
How does technology access impact education inequality? Limited access to digital devices and reliable internet connection prevents many students from participating equally in online learning. This digital divide widens the achievement gap between students from low-income and high-income families.
What data highlights the extent of the digital divide in education? Approximately 15 million U.S. public school students lack adequate access to technology for remote learning. Rural and minority communities are disproportionately affected, with up to 25% of students having limited or no internet access at home.
| Group | Technology Access Gap |
|---|---|
| Low-Income Families | 35% lack broadband internet |
| Rural Students | 25% lack computer access |
| Minority Students | 20% have limited device availability |
| Urban Students | 10% lack reliable internet |
| High-Income Families | 5% lack technology access |
Impact of Quality Teachers on Student Outcomes
Education inequality significantly affects student outcomes, with quality teachers playing a critical role in bridging this gap. Schools with experienced and well-supported teachers see higher student achievement and improved graduation rates.
Access to high-quality educators helps reduce disparities in literacy, math proficiency, and college readiness among students from diverse backgrounds. Investing in teacher training and retention directly enhances overall educational equity and student success.
Educational Disparities by Region
Educational inequality remains a critical issue worldwide, with significant disparities observed across different regions. Access to quality education, resources, and infrastructure varies greatly, impacting student achievement and long-term opportunities.
Regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia face the most severe educational disparities, with lower enrollment rates and higher dropout rates compared to North America and Europe. Urban areas generally provide better educational facilities than rural regions, where poverty limits access to learning materials and trained teachers. These regional gaps highlight the urgent need for targeted policies and investments to ensure equitable education for all children.
Long-Term Effects of Education Inequality
Education inequality creates lasting disparities that affect individuals and society over time. Understanding these long-term effects is crucial for promoting equal opportunities and economic growth.
- Lower Lifetime Earnings - Individuals with limited access to quality education often experience reduced career opportunities and lower income levels.
- Health Disparities - Education inequality correlates with poorer health outcomes due to decreased access to health resources and information.
- Social Mobility Barriers - Unequal education restricts upward mobility, perpetuating cycles of poverty across generations.
