Infographics about ekonomiks present complex economic concepts in a visually engaging and easily digestible format. They simplify data through charts, graphs, and icons that highlight key trends and relationships within the economy. This approach enhances understanding of financial principles, market dynamics, and economic policies for diverse audiences.
Understanding the Basics of Economics
Economics is the study of how individuals and societies allocate scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants. It explores production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Understanding basic economic concepts like supply and demand helps explain market behavior and price formation. Economics also examines how governments influence markets through policies and regulations. Learning these fundamentals provides a foundation for analyzing financial decisions and economic trends globally.
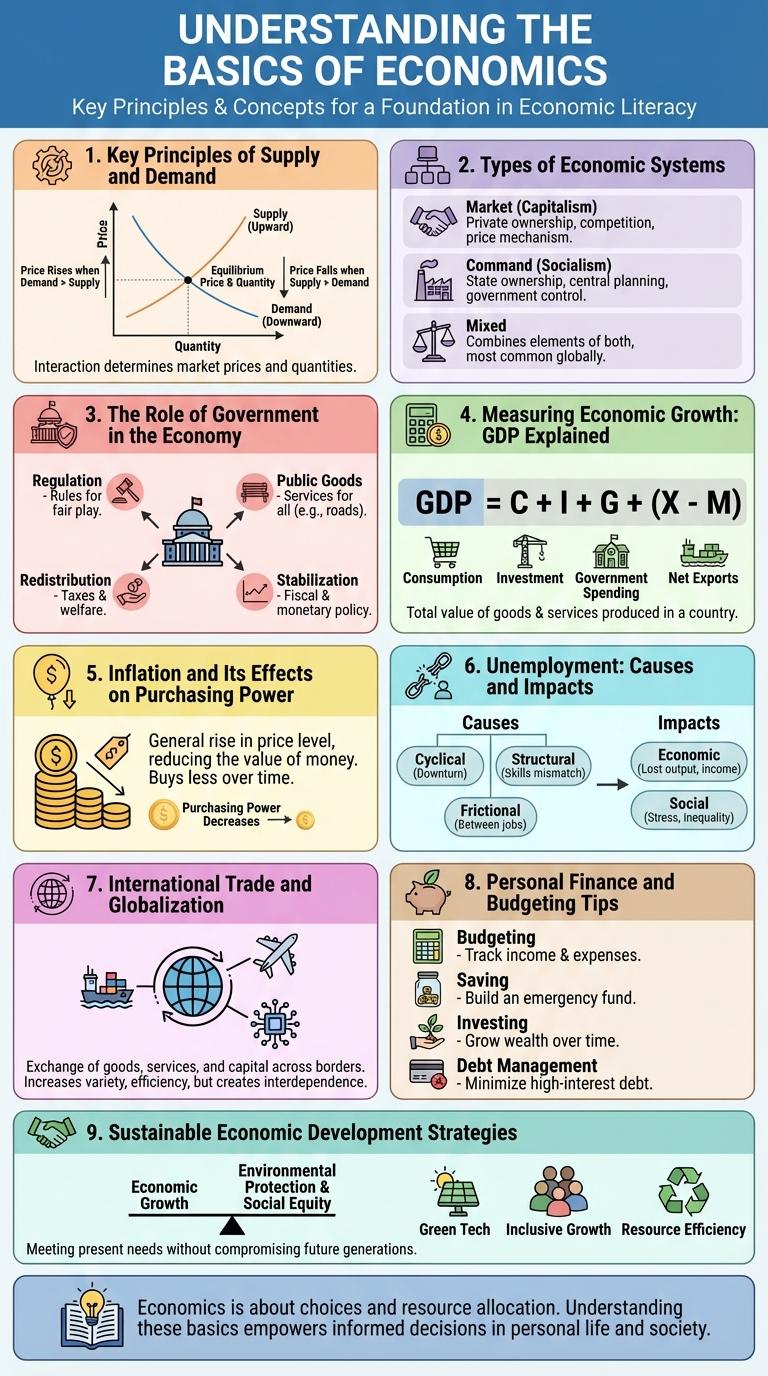
Key Principles of Supply and Demand
The principles of supply and demand form the foundation of economic theory, explaining price formation in markets. Understanding these concepts helps interpret how goods and services are allocated efficiently.
Supply refers to the quantity of a product that producers are willing to sell at various prices, while demand indicates how much consumers are willing to buy.
- Law of Demand - When the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded generally decreases, reflecting consumer behavior.
- Law of Supply - Producers tend to supply more of a good as its price increases, responding to profit incentives.
- Market Equilibrium - The point where supply equals demand sets the market price and quantity for the product.
Types of Economic Systems
What are the main types of economic systems? Economic systems determine how resources are allocated and how goods and services are produced in a society. These systems impact government control, market freedom, and economic goals.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Traditional Economy | Relies on customs and traditions to make economic decisions. Typically found in rural or indigenous communities. |
| Command Economy | Government controls all production and distribution. Central planning dictates economic activity. |
| Market Economy | Decisions driven by supply and demand with minimal government intervention. Promotes competition and innovation. |
| Mixed Economy | Combines elements of market and command systems. Balances private enterprise with government regulation. |
The Role of Government in the Economy
The government plays a crucial role in regulating economic activities to ensure stability and growth. It implements fiscal and monetary policies to manage inflation, unemployment, and economic development. Public services and infrastructure investments are also key government functions that support overall economic health.
Measuring Economic Growth: GDP Explained
Measuring economic growth is essential to understand the health of a country's economy. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) serves as the primary indicator for this purpose.
- GDP Definition - GDP represents the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period.
- Types of GDP - GDP can be measured as nominal, real, or per capita, each offering different insights into economic performance.
- Importance of GDP - GDP data helps policymakers, investors, and businesses make informed decisions by reflecting economic trends and growth rates.
Understanding GDP components and measurements provides a clearer picture of economic growth and development.
Inflation and Its Effects on Purchasing Power
Inflation measures the rate at which general prices for goods and services rise, reducing the purchasing power of money. As inflation increases, each unit of currency buys fewer goods, eroding consumer spending ability. Understanding inflation's impact is crucial for maintaining economic stability and informed financial planning.
Unemployment: Causes and Impacts
| Causes of Unemployment | Impacts of Unemployment |
|---|---|
| Technological advancement reducing labor demand | Decreased household income leading to lower living standards |
| Economic recessions causing business closures | Increased poverty rates and social inequality |
| Skills mismatch between workers and job market requirements | Higher government spending on social welfare programs |
| Seasonal fluctuations in industries like agriculture and tourism | Rising mental health issues such as anxiety and depression |
| Population growth exceeding job creation rates | Reduced economic growth due to lower consumer spending |
International Trade and Globalization
International trade drives economic growth by enabling countries to specialize and exchange goods. Globalization integrates markets, creating interconnected economies worldwide.
- Comparative Advantage - Countries export products they produce efficiently, boosting global economic efficiency.
- Trade Liberalization - Reducing tariffs and barriers fosters increased cross-border trade and investment.
- Global Supply Chains - Multinational production networks optimize resource use and lower costs internationally.
Personal Finance and Budgeting Tips
Personal finance is the management of individual or household monetary resources, including income, expenses, savings, and investments. Effective budgeting helps individuals allocate funds efficiently to meet both short-term needs and long-term financial goals.
Creating a monthly budget involves tracking income and categorizing expenses to avoid overspending. Setting aside at least 20% of income for savings or emergency funds ensures financial stability during unexpected events.
