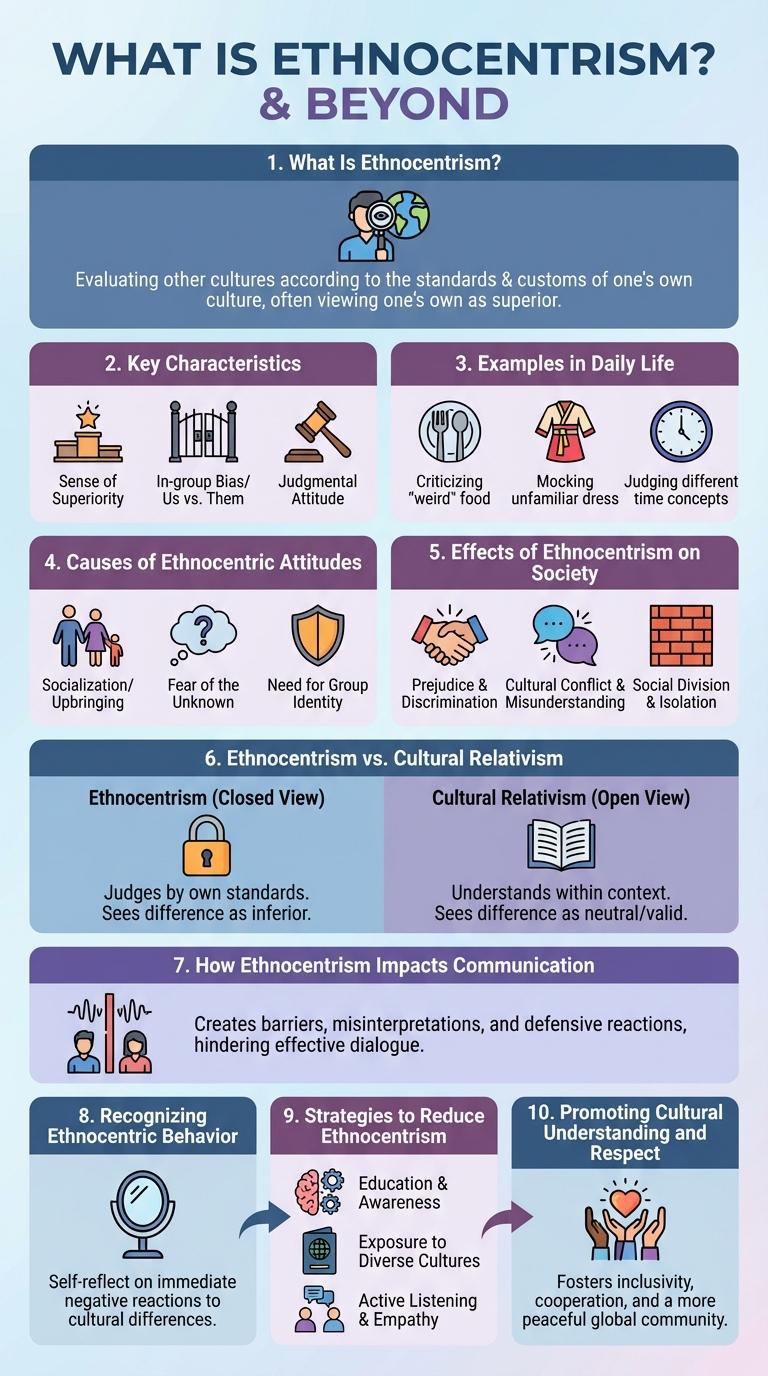
Ethnocentrism is the tendency to view one's own culture as superior to others, often leading to misunderstandings and prejudice. This infographic visually explains the key concepts, causes, and effects of ethnocentrism, highlighting how it influences social interactions and cultural perceptions. Understanding ethnocentrism fosters greater cultural awareness and promotes more inclusive communities.
What Is Ethnocentrism?
Ethnocentrism is the belief that one's own culture or ethnic group is superior to others. It influences how individuals perceive and judge other cultures based on their own cultural standards.
- Cultural Bias - Ethnocentrism leads to evaluating other cultures through the lens of one's own cultural norms and values.
- Social Identity - It reinforces group identity by emphasizing differences and promoting in-group favoritism.
- Potential Consequences - Ethnocentrism can result in misunderstandings, prejudice, and conflicts between diverse cultural groups.
Key Characteristics of Ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism involves judging other cultures based on the standards and values of one's own culture. This mindset often leads to misunderstandings and biased evaluations of different cultural practices.
Key Characteristics of Ethnocentrism:
- Cultural Superiority - A belief that one's own culture is superior to others, often resulting in prejudice.
- In-group Favoritism - Preference for members of one's own cultural group over outsiders.
- Resistance to Cultural Differences - Difficulty accepting or respecting cultural practices that differ from one's own.
Examples of Ethnocentrism in Daily Life
| Example of Ethnocentrism | Description |
|---|---|
| Language Judgments | Believing one's native language is superior and viewing other languages as inferior or incorrect. |
| Food Preferences | Rejecting or mocking cuisines from other cultures based on unfamiliar ingredients or preparation methods. |
| Cultural Dress | Criticizing traditional clothing from other cultures for not aligning with one's own fashion standards. |
| Social Norms | Assuming one's cultural customs are the "right" or "normal" way to behave in social settings. |
| Education Systems | Devaluing teaching methods or curricula rooted in different cultural perspectives. |
Causes of Ethnocentric Attitudes
Ethnocentrism arises from the natural human tendency to view one's own culture as superior to others. This perspective often leads to biased judgments and misunderstandings between different cultural groups.
Causes of ethnocentric attitudes include socialization processes where individuals learn cultural norms and values from family and community. Limited exposure to diverse cultures reinforces stereotypes and resistance to alternative viewpoints. Economic or political conflicts can also exacerbate feelings of in-group superiority and out-group hostility.
Effects of Ethnocentrism on Society
Ethnocentrism leads to social division by promoting the belief that one's own culture is superior to others. This attitude fosters prejudice, discrimination, and conflict within multicultural societies.
Communities influenced by ethnocentrism often experience reduced cooperation and increased misunderstandings. Over time, these effects undermine social cohesion and hinder the development of inclusive policies.
Ethnocentrism vs. Cultural Relativism
What distinguishes ethnocentrism from cultural relativism? Ethnocentrism involves judging other cultures based on one's own cultural standards, often leading to biased perceptions. Cultural relativism promotes understanding cultures on their own terms, fostering respect and reducing prejudice.
How Ethnocentrism Impacts Communication
Ethnocentrism is the belief in the superiority of one's own culture or ethnic group, often leading to misunderstandings in communication. It creates barriers that hinder open and effective interaction between people from different backgrounds.
- Misinterpretation - Ethnocentrism causes individuals to misinterpret behaviors and messages from other cultures based on their own cultural norms.
- Bias and Stereotyping - It fosters biased judgments and stereotypes that distort how messages are received and understood across cultural lines.
- Reduced Empathy - Ethnocentrism limits the ability to empathize with others, decreasing willingness to engage in meaningful dialogue.
Recognizing and addressing ethnocentrism is crucial for improving cross-cultural communication and building mutual understanding.
Recognizing Ethnocentric Behavior
Ethnocentrism involves evaluating other cultures based on the standards of one's own culture. Recognizing ethnocentric behavior is essential for fostering cultural sensitivity and understanding.
Common signs include judging other customs as inferior or assuming one's culture is superior. Awareness of these behaviors helps promote inclusivity and respect in diverse social settings.
Strategies to Reduce Ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism, the tendency to view one's own culture as superior, often leads to misunderstanding and prejudice. Strategies to reduce ethnocentrism include promoting cultural awareness, encouraging open-mindedness, and fostering intercultural communication. Educational programs and diverse social interactions help individuals appreciate cultural differences and build empathy.
