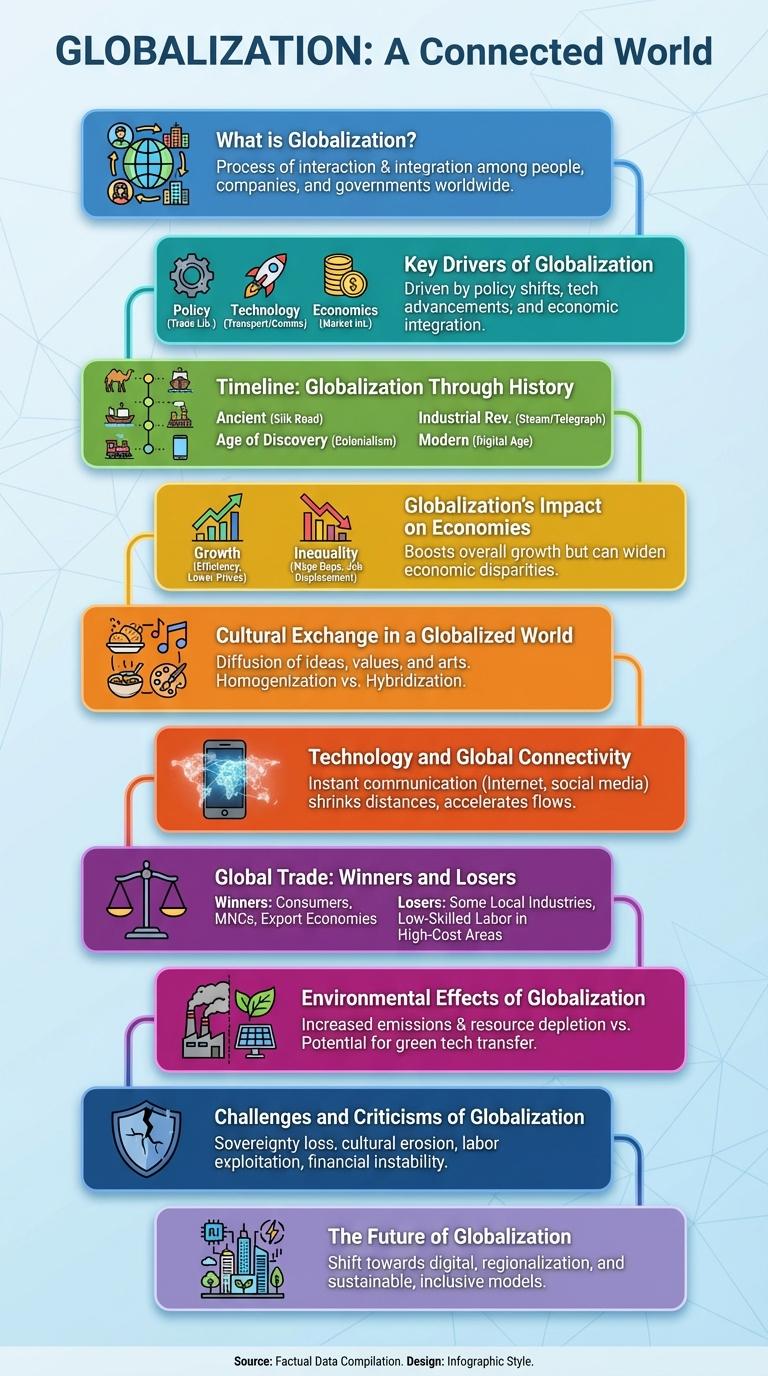
Globalization connects economies, cultures, and people across the world through trade, technology, and communication. This infographic illustrates key trends, benefits, and challenges of globalization in a clear and concise format. Visualizing these elements helps to understand its impact on society and the global market.
What is Globalization?
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness and integration of economies, cultures, and populations worldwide. It involves the exchange of goods, services, information, and ideas across international borders.
Globalization drives economic growth by expanding markets and facilitating trade. It promotes cultural exchange and collaboration between countries. Advances in technology and communication have accelerated the globalization process, making the world more accessible.
Key Drivers of Globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interconnectedness and integration among countries, economies, and cultures worldwide. It is driven by multiple factors that facilitate cross-border exchange and cooperation.
- Technological Advancements - Innovations in communication and transportation technologies have reduced barriers to global interaction and commerce.
- Trade Liberalization - The reduction of tariffs and trade barriers has expanded international markets and encouraged foreign investment.
- Economic Policies - National governments adopt policies promoting open markets and international business to stimulate economic growth.
Timeline: Globalization Through History
Globalization is a dynamic process shaped by centuries of cultural exchange, trade, and technological advancements. Its development reflects key historical milestones that have interconnected world economies and societies.
- Silk Road Establishment (circa 130 BCE) - The Silk Road facilitated early trade and cultural exchanges between Asia, Europe, and Africa, laying foundational global connections.
- Age of Exploration (15th-17th centuries) - European maritime expeditions expanded global trade networks, leading to increased cultural and economic interactions worldwide.
- Industrial Revolution (18th-19th centuries) - Technological innovations accelerated mass production and international commerce, intensifying global interdependence.
- Post-World War II World Order (mid-20th century) - Institutions like the United Nations and IMF were formed to foster international cooperation and economic integration.
- Digital Revolution (late 20th century to present) - The rise of the internet and digital communication transformed global connectivity, enabling instantaneous information exchange and global markets.
Globalization's Impact on Economies
Globalization has transformed economies by increasing international trade and investment flows, fostering economic growth worldwide. It facilitates access to larger markets, enabling businesses to expand and innovate more rapidly.
Economic integration through globalization has led to job creation in emerging markets while intensifying competition for industries in developed countries. The interconnected economies result in shared risks and opportunities, influencing global economic stability and development.
Cultural Exchange in a Globalized World
How does globalization enhance cultural exchange worldwide?
Globalization facilitates the sharing of traditions, languages, and arts across national borders. This exchange enriches societies by promoting diversity and mutual understanding.
What role do technology and media play in cultural exchange?
Digital platforms and social media connect people from different cultures instantly. These tools enable the rapid spread of cultural content and ideas globally.
How do international events contribute to cultural exchange?
Events like global sports competitions and world expos bring diverse cultures together. They create opportunities for direct interaction and appreciation of different cultures.
What impact does cultural exchange have on local traditions?
It can lead to the adaptation and evolution of local customs while preserving core cultural identities. This dynamic process helps cultures remain vibrant and relevant.
How does cultural exchange influence global cooperation?
Understanding cultural differences fosters respect and collaboration among nations. This foundation strengthens diplomatic relationships and global partnerships.
Technology and Global Connectivity
Globalization accelerates through technology, enabling instant communication and data exchange worldwide. Advances in digital platforms, satellite networks, and cloud computing connect businesses, governments, and individuals across continents. This global connectivity fosters economic integration, cultural exchange, and collaborative innovation on an unprecedented scale.
Global Trade: Winners and Losers
Global trade, a key driver of globalization, has expanded markets and created economic opportunities worldwide. Countries with competitive industries and resources often emerge as winners in this dynamic landscape.
However, some nations and workers face challenges due to job displacement and unequal wealth distribution. Addressing these disparities remains crucial for achieving more inclusive global trade benefits.
Environmental Effects of Globalization
Globalization accelerates economic growth and cultural exchange worldwide. However, it also imposes significant environmental challenges affecting ecosystems and climate patterns.
- Increased Carbon Emissions - Global trade and transportation activities result in higher greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change.
- Deforestation - Expansion of agriculture and industry to meet global demand leads to widespread loss of forests and biodiversity.
- Pollution Spread - Industrial activities in less regulated countries cause water, air, and soil pollution affecting local and global health.
Sustainable globalization strategies are essential to reduce environmental damage and promote ecological balance.
Challenges and Criticisms of Globalization
Globalization has led to increased economic interdependence but has also intensified income inequality, with wealth concentrated in developed nations while many developing countries face poverty. Critics argue that globalization threatens cultural diversity, promoting homogenization of cultures and loss of local traditions. Environmental degradation is another major concern, as global trade can drive resource exploitation and increased carbon emissions.
