Overpopulation strains resources, intensifying challenges in housing, healthcare, and food supply. Rapid population growth accelerates environmental degradation, contributing to pollution and habitat loss. Understanding these impacts through clear infographics can highlight urgent solutions for sustainable living.
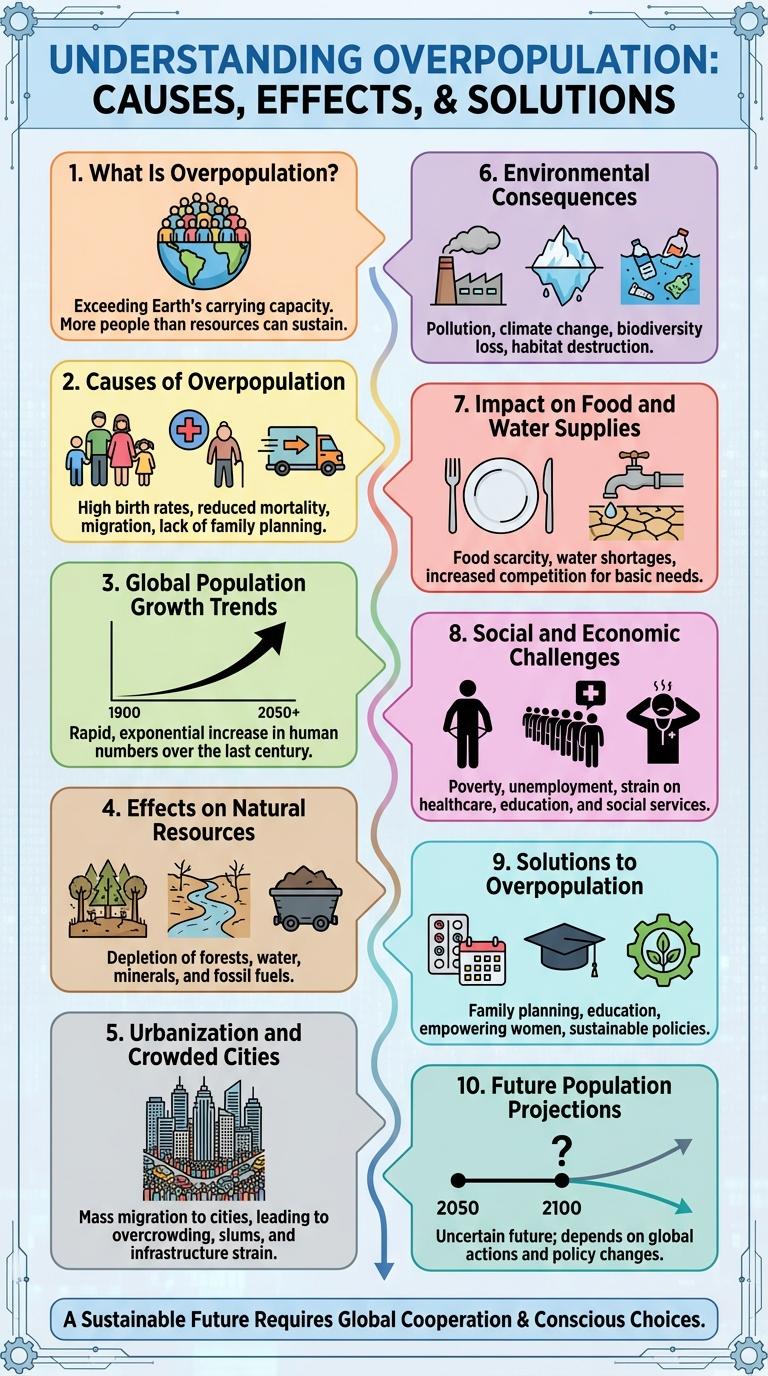
What Is Overpopulation?
Overpopulation occurs when the number of people exceeds the capacity of the environment to sustain them. It leads to strained resources such as water, food, and housing. Rapid population growth intensifies challenges in health, employment, and infrastructure.
Causes of Overpopulation
Overpopulation results from a combination of factors including high birth rates, improved healthcare, and lack of family planning. Advances in medical technology have decreased mortality rates, causing population growth. Economic and cultural influences also contribute to larger family sizes in many regions.
Global Population Growth Trends
Global population growth has accelerated significantly since the mid-20th century, reaching over 8 billion people worldwide as of 2024. This rapid increase is driven by higher birth rates in developing regions combined with declining mortality rates globally.
Asia remains the most populous continent, housing nearly 60% of the world's population, while Africa is experiencing the fastest growth rate. Urban areas are expanding rapidly, leading to increased demand for resources and infrastructure development.
Effects on Natural Resources
Overpopulation significantly strains natural resources, leading to accelerated depletion and environmental degradation. The increased demand for water, energy, and raw materials threatens ecosystem stability and sustainability.
- Water Scarcity - Excessive population growth causes high water consumption, reducing freshwater availability for agriculture and households.
- Deforestation - Expanding human settlements and agriculture result in widespread loss of forests, impacting biodiversity and carbon storage.
- Energy Demand - Growing populations increase energy consumption, leading to higher fossil fuel use and elevated greenhouse gas emissions.
Urbanization and Crowded Cities
Rapid urbanization drives the surge of population density in major cities worldwide. Crowded cities face significant challenges in infrastructure, housing, and public services.
- Urban Growth - Over half of the global population now resides in urban areas, intensifying city crowding.
- Infrastructure Strain - Urban infrastructure struggles to keep pace with the increasing demands of dense populations.
- Housing Shortages - Rising populations in cities lead to housing deficits and the growth of informal settlements.
Environmental Consequences
Overpopulation significantly accelerates environmental degradation by increasing resource consumption and waste production. This surge leads to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and depletion of natural resources.
Higher population density intensifies air and water pollution, contributing to climate change and health problems. Urban areas expand rapidly, disrupting ecosystems and increasing carbon emissions globally.
Impact on Food and Water Supplies
| Aspect | Impact of Overpopulation |
|---|---|
| Food Demand | Exponential rise in global food requirements increases pressure on agricultural systems |
| Water Consumption | Higher population leads to amplified freshwater usage, accelerating depletion of water resources |
| Agricultural Land | Expansion of farms reduces natural habitats, causing soil degradation and lower crop yields |
| Food Security | Unequal food distribution results in malnutrition and hunger crises in densely populated regions |
| Water Quality | Increased waste and pollutants degraded freshwater quality, impacting human health and ecosystems |
Social and Economic Challenges
Overpopulation presents significant social and economic challenges that affect global stability. Rising population densities strain resources and infrastructure worldwide.
- Increased Unemployment - High population growth leads to a labor market surplus, causing higher unemployment rates and underemployment.
- Resource Scarcity - Growing populations intensify demand for essential resources like water, food, and energy, resulting in shortages and increased prices.
- Infrastructure Overload - Urban areas face excessive pressure on housing, transportation, and healthcare systems, reducing quality of life and economic productivity.
Addressing overpopulation requires strategic planning to balance social needs and economic development for sustainable futures.
Solutions to Overpopulation
Overpopulation presents significant challenges to resources, environment, and quality of life. Addressing these issues requires effective and sustainable solutions.
Promoting family planning and education helps control birth rates and empowers individuals to make informed decisions. Investments in women's health and rights contribute significantly to reducing population growth. Urban planning and sustainable resource management ensure better adaptation to growing populations.
