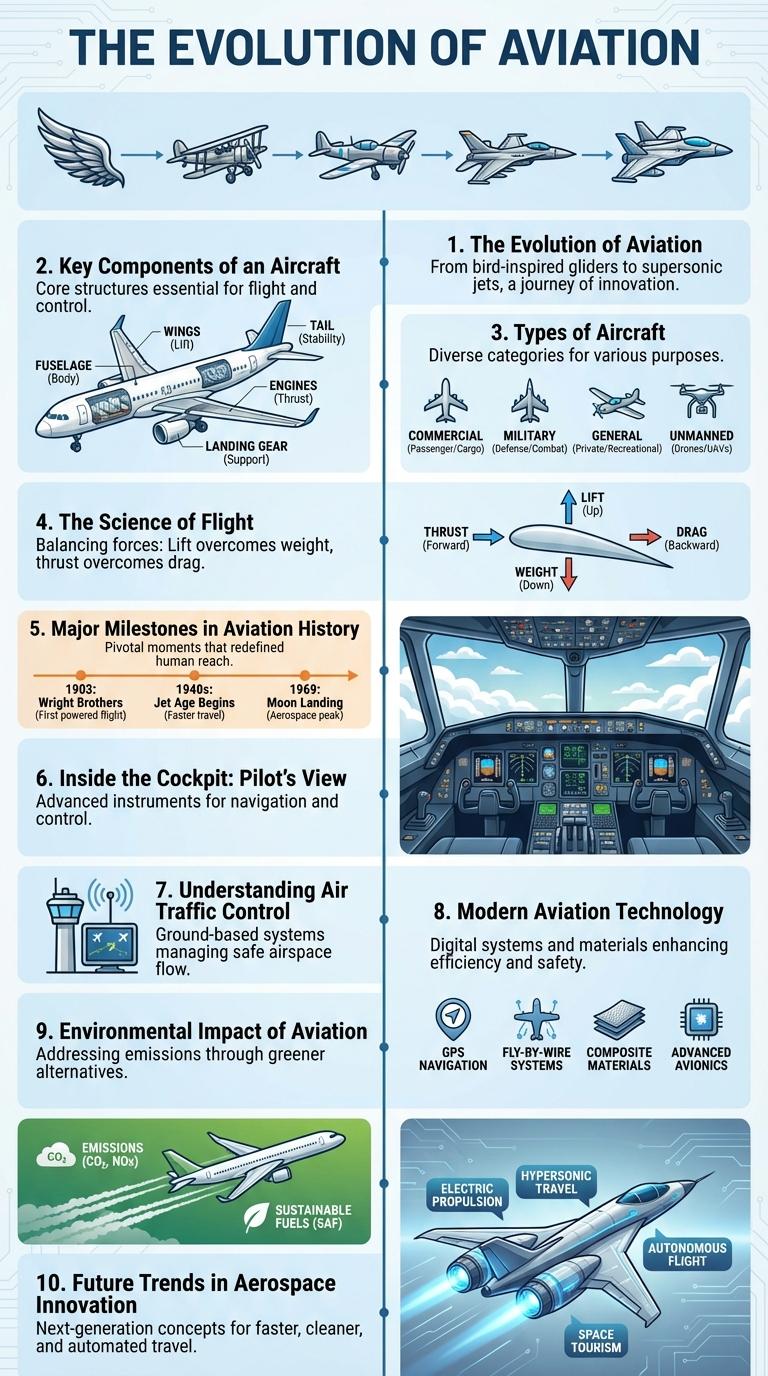
Aviation infographic visually captures key data and trends within the industry, highlighting aspects such as passenger growth, technological advancements, and safety statistics. It presents complex information clearly, enabling both experts and enthusiasts to understand the evolving dynamics of air travel. This visual tool emphasizes the global impact of aviation on commerce, connectivity, and innovation.
The Evolution of Aviation
The evolution of aviation showcases humanity's progress from early gliders to modern supersonic jets. Innovations in aircraft design, materials, and propulsion systems have drastically transformed air travel.
The Wright brothers' first powered flight in 1903 marked the beginning of controlled aviation. Today, advancements in technology enable efficient, safe, and sustainable flights worldwide.
Key Components of an Aircraft
The key components of an aircraft work together to ensure safe and efficient flight. Understanding these elements highlights how complex and precise aviation technology truly is.
- Fuselage - The main body of the aircraft holds passengers, cargo, and flight crew.
- Wings - Generate lift to keep the aircraft airborne during flight.
- Engines - Provide thrust to propel the airplane forward through the air.
- Landing Gear - Supports the aircraft during takeoff, landing, and while on the ground.
- Empennage - Includes the tail assembly, which stabilizes and controls the airplane's direction.
Types of Aircraft
Aviation encompasses diverse types of aircraft designed for specific purposes. Common categories include commercial airliners, military jets, and general aviation planes. Each type serves unique roles from passenger transport to defense and recreational flying.
The Science of Flight
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lift | Generated by air pressure differences on the wing surfaces, allowing the aircraft to rise. Wing shapes are designed to accelerate air over the top surface, lowering pressure. |
| Thrust | Produced by engines to propel the aircraft forward, overcoming drag. Common engines include turbofans and propellers. |
| Drag | Air resistance opposing motion, influenced by aircraft shape and surface smoothness. Minimizing drag improves fuel efficiency. |
| Weight | Force due to gravity pulling the aircraft downward. Balancing weight with lift is crucial for stable flight. |
| Bernoulli's Principle | Fundamental theory explaining lift: faster airflow on wing's upper surface causes lower pressure compared to the bottom. |
Major Milestones in Aviation History
Aviation has transformed global connectivity and commerce through groundbreaking innovations. Key milestones highlight humanity's progress from early flight attempts to modern aerospace technology.
- Wright Brothers' First Powered Flight (1903) - Achieved the first controlled, sustained flight of a powered aircraft in Kitty Hawk, North Carolina.
- Introduction of Commercial Air Travel (1914) - The St. Petersburg-Tampa Airboat Line began scheduled passenger service, marking the birth of commercial aviation.
- Development of Jet Engines (1939) - Frank Whittle and Hans von Ohain independently invented the jet engine, revolutionizing aircraft speed and efficiency.
- The First Supersonic Flight (1947) - Chuck Yeager broke the sound barrier in the Bell X-1, demonstrating supersonic flight capability.
- Moon Landing and Spaceflight (1969) - Apollo 11's lunar mission expanded aviation into space exploration, symbolizing the pinnacle of aerospace achievement.
Inside the Cockpit: Pilot's View
What does a pilot see inside the cockpit during flight? The cockpit offers a panoramic view filled with an array of critical flight instruments, navigation displays, and communication panels. Pilots rely on this high-tech environment to monitor aircraft performance and ensure safe operation throughout the journey.
Understanding Air Traffic Control
Air Traffic Control (ATC) is a vital service that ensures the safe and efficient movement of aircraft in the sky and on the ground. Controllers use radar, radio communication, and advanced technology to manage aircraft during takeoff, flight, and landing.
ATC divides airspace into sectors, each monitored by specialized controllers responsible for guiding pilots and preventing collisions. The system supports thousands of flights daily, maintaining orderly traffic flow and enhancing aviation safety worldwide.
Modern Aviation Technology
Modern aviation technology has revolutionized air travel by enhancing safety, efficiency, and passenger comfort. Advanced navigation systems and innovative aircraft designs contribute to faster and more reliable flights.
State-of-the-art avionics integrate GPS, radar, and real-time data communication to optimize flight routes and reduce fuel consumption. Composite materials and aerodynamic improvements decrease aircraft weight and increase durability. Automation in cockpit systems assists pilots with critical decision-making, improving overall flight safety standards.
Environmental Impact of Aviation
Aviation contributes approximately 2-3% of global carbon dioxide emissions, significantly impacting climate change. Aircraft engines emit nitrogen oxides, water vapor, and particulate matter, which intensify atmospheric warming. Sustainable aviation fuels and advancements in electric aircraft technology aim to reduce the environmental footprint of air travel.
