JavaScript is a versatile programming language used to create dynamic and interactive web experiences. This infographic breaks down core concepts, key features, and popular frameworks that power modern web development. Understanding these essentials can help both beginners and experts enhance their coding skills effectively.
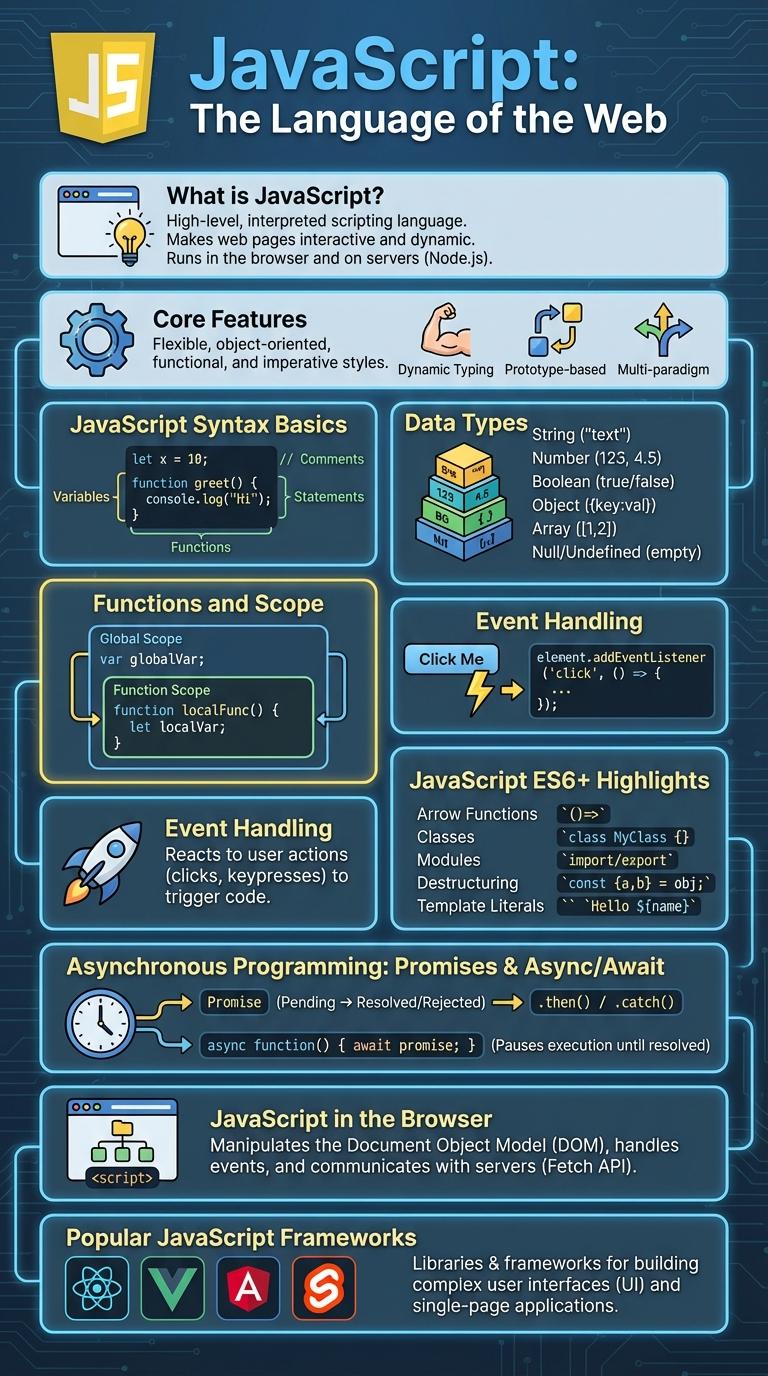
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a versatile programming language primarily used to create interactive effects within web browsers. It enables dynamic content such as animations, form validations, and interactive maps.
Initially developed in 1995, JavaScript has evolved into a powerful tool for both client-side and server-side development. It works seamlessly with HTML and CSS to enhance user experience on websites and applications.
Core Features of JavaScript
JavaScript is a versatile programming language primarily used for web development to create interactive and dynamic user experiences. It operates seamlessly on both client and server sides, making it essential for modern web applications.
- Event-Driven Programming - JavaScript allows developers to respond to user actions like clicks, form submissions, and key presses in real-time.
- First-Class Functions - Functions in JavaScript can be assigned to variables, passed as arguments, and returned from other functions.
- Asynchronous Processing - JavaScript supports asynchronous code execution through callbacks, promises, and async/await, enhancing performance and responsiveness.
JavaScript Syntax Basics
JavaScript syntax consists of variables, functions, and control structures that define how the code operates. Variables are declared using var, let, or const to store data values. Functions encapsulate reusable code blocks, while control structures like if statements and loops manage the flow of execution.
Data Types in JavaScript
What are the primary data types in JavaScript? JavaScript features seven fundamental data types that enable efficient programming and data manipulation. These types include primitive and complex categories, each serving unique purposes.
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Number | Represents both integer and floating-point values for mathematical operations. |
| String | Sequence of characters used to represent text. |
| Boolean | A logical entity with two values: true or false. |
| Null | Denotes the intentional absence of any object value. |
| Undefined | Indicates a variable that has been declared but not assigned a value. |
What complex data types does JavaScript support? Objects and Symbols extend JavaScript's capability by enabling structured and unique value storage. These data types facilitate advanced programming patterns and metaprogramming.
Functions and Scope
JavaScript functions are reusable blocks of code designed to perform specific tasks. They allow developers to write modular and maintainable programs by encapsulating logic within named or anonymous functions.
Scope in JavaScript determines the accessibility of variables and functions in different parts of the code. Functions create their own local scope, meaning variables declared inside a function are not accessible outside of it. Understanding the difference between global scope, function scope, and block scope is essential for managing variable lifetimes and avoiding conflicts.
Event Handling in JavaScript
JavaScript's event handling enables interaction and dynamic behavior on web pages by responding to user actions. It uses event listeners to capture and process events such as clicks, key presses, and mouse movements.
- Event Listeners - Attach functions to DOM elements that execute when specified events occur.
- Event Types - Include common events like click, load, input, and mouseover for diverse interactivity options.
- Event Propagation - Controls event flow through capturing, target, and bubbling phases for precise event management.
JavaScript ES6+ Highlights
JavaScript ES6+ introduced powerful features that revolutionized modern web development. These enhancements improve code readability, maintainability, and performance.
Key features include arrow functions, template literals, and destructuring assignments. ES6+ also brought promises, modules, and enhanced object properties for better asynchronous and modular coding.
Asynchronous Programming: Promises & Async/Await
JavaScript's asynchronous programming allows for non-blocking code execution, improving performance and user experience. Promises and async/await syntax provide clear and manageable ways to handle asynchronous operations.
- Promises - Objects representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation.
- .then() and .catch() - Methods to handle resolved and rejected promise outcomes, respectively.
- Async/Await - Syntactic sugar over promises that enables writing asynchronous code in a synchronous style.
Using Promises and async/await simplifies error handling and enhances code readability in complex asynchronous workflows.
