Python's versatile programming language enables developers to create everything from simple scripts to complex applications. Its clear syntax and extensive libraries make it ideal for data analysis, web development, artificial intelligence, and automation. Visualizing Python's key features and use cases through an infographic highlights its widespread adoption and powerful capabilities.
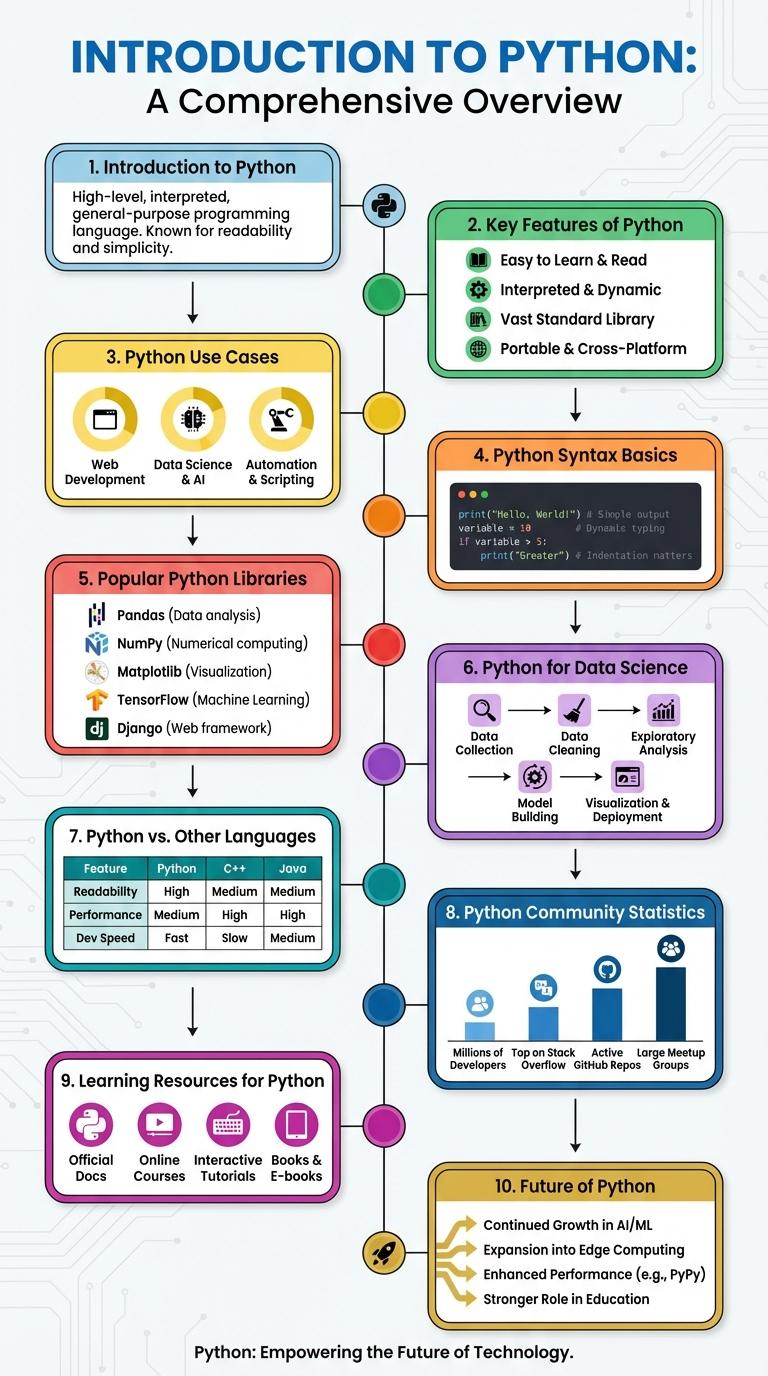
Introduction to Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its readability and versatility. It is widely used in web development, data science, automation, and artificial intelligence.
- Easy to Learn - Python's simple syntax makes it accessible for beginners and efficient for experts.
- Open Source - Python is freely available, with a large community contributing to its development and libraries.
- Extensive Libraries - Python offers a vast selection of libraries for scientific computing, machine learning, and web frameworks.
Python's adaptability and powerful features make it a top choice for developers across various industries.
Key Features of Python
Python is a high-level programming language known for its clear syntax and readability. It supports multiple programming paradigms, making it versatile for various applications.
- Easy to Learn - Python's simple syntax allows beginners to quickly grasp programming concepts.
- Extensive Libraries - It features a rich ecosystem of libraries for data analysis, web development, and more.
- Cross-Platform - Python runs smoothly on Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
- Interactive Shell - The interactive interpreter helps developers test code snippets efficiently.
- Strong Community - Python benefits from a large, active community contributing to its continuous improvement.
Python Use Cases
What are the main use cases of Python? Python is a versatile programming language used in various domains. It supports rapid development and has a rich ecosystem of libraries.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Web Development | Python frameworks like Django and Flask enable scalable and secure web applications. |
| Data Science | Libraries such as Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib facilitate data analysis and visualization. |
| Machine Learning | TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn provide tools for developing predictive models. |
| Automation | Python scripts automate repetitive tasks, improving productivity and efficiency. |
| Software Development | Python supports backend development and integrates well with other programming languages. |
Python Syntax Basics
| Python Syntax Basics | Description |
|---|---|
| Indentation | Python uses indentation to define code blocks instead of braces or keywords. |
| Variables | Variables are assigned without explicit type declaration, e.g., x = 5. |
| Comments | Single-line comments start with #; multi-line with triple quotes. |
| Statements | Statements end with a newline; no semicolons needed. |
| Functions | Defined using def keyword followed by function name and parentheses. |
Popular Python Libraries
Python offers a diverse range of popular libraries that simplify coding and accelerate development. Libraries such as NumPy and Pandas are essential for data analysis and manipulation, while Matplotlib and Seaborn provide powerful data visualization tools. Flask and Django are widely used frameworks for web development, making Python a versatile choice across multiple domains.
Python for Data Science
Python is a leading programming language in data science due to its simplicity and powerful libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib. These tools streamline data manipulation, analysis, and visualization, making Python essential for data scientists.
Machine learning frameworks such as Scikit-learn and TensorFlow enhance Python's capabilities, supporting predictive analytics and artificial intelligence projects. Its extensive community and open-source resources provide continuous innovation and support for data science applications.
Python vs. Other Languages
Python consistently ranks among the top programming languages due to its simplicity and versatility. Its performance and ease of use make it a favorite for both beginners and experienced developers.
- Readability and Syntax - Python's clean and readable syntax reduces development time compared to languages like C++ or Java.
- Library Ecosystem - Python boasts an extensive standard library and third-party packages supporting various fields like data science, web development, and automation.
- Execution Speed - While Python is generally slower than compiled languages such as C or C++, its speed is adequate for most applications and can be improved with tools like Cython or PyPy.
Python Community Statistics
Python ranks among the most popular programming languages worldwide, with over 10 million active users as of 2024. Its community spans various industries, including web development, data science, and artificial intelligence.
The Python Package Index (PyPI) hosts more than 400,000 libraries, reflecting rapid growth and extensive collaboration. Approximately 75% of developers report using Python for machine learning projects. Frequent contributions and open-source involvement highlight Python's dynamic and supportive ecosystem.
Learning Resources for Python
Python offers a wealth of learning resources suitable for beginners and advanced developers alike. Popular platforms include Codecademy, Coursera, and freeCodeCamp, providing interactive tutorials and comprehensive courses. Official documentation and community forums like Stack Overflow enhance learning through practical examples and peer support.
