Nanotechnology explores the manipulation of matter at an atomic and molecular scale to create groundbreaking innovations across various industries. This infographic visually presents key concepts, applications, and future potential of nanotechnology in medicine, electronics, and environmental solutions. Understanding these nanoscale advancements highlights their transformative impact on science and technology.
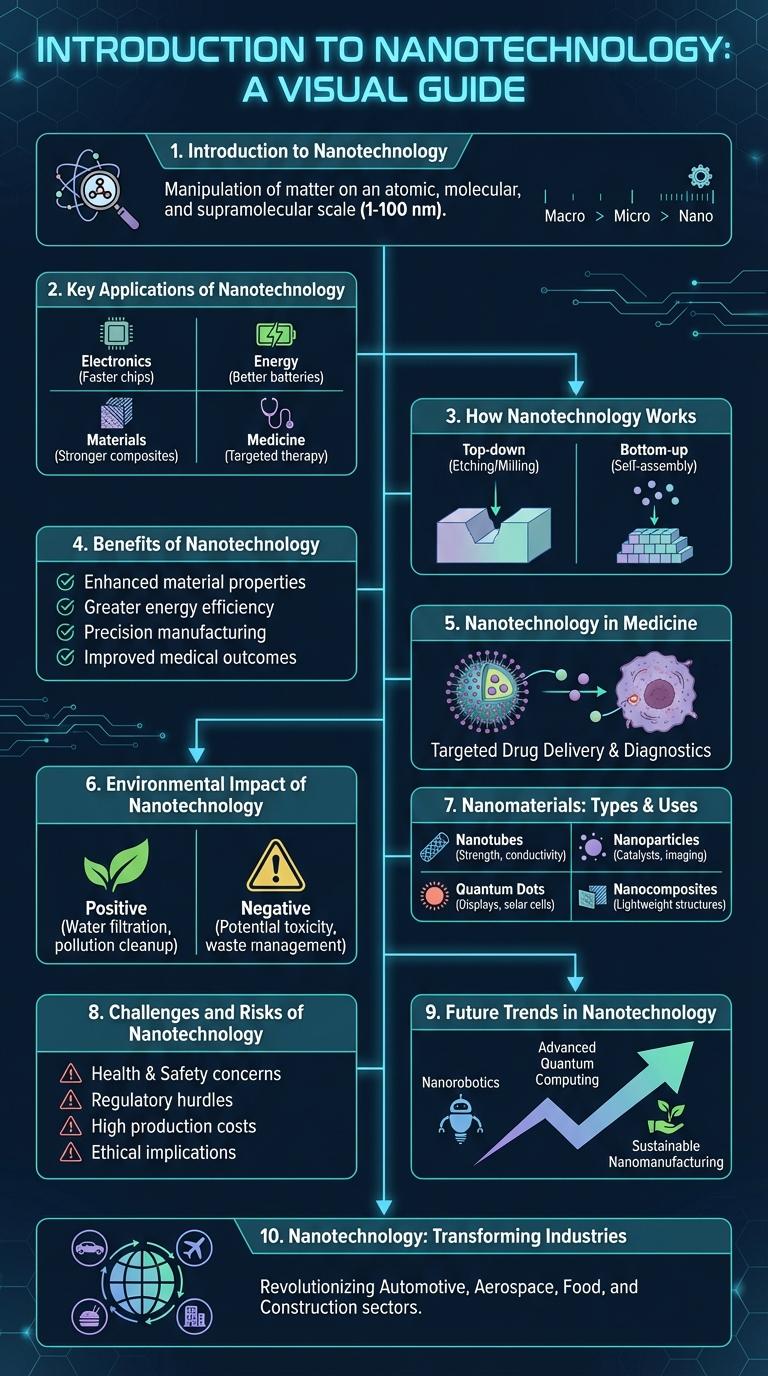
Introduction to Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale, typically below 100 nanometers. It enables the creation of materials and devices with unique properties and functions that are impossible to achieve at larger scales. This technology impacts various fields including medicine, electronics, and energy, driving innovation and advancements.
Key Applications of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale to create innovative materials and devices. Key applications include medicine, where nanoparticles improve drug delivery and diagnostic techniques. It also revolutionizes electronics by enabling smaller, faster components and enhances environmental solutions through efficient energy storage and pollution control.
How Nanotechnology Works
Nanotechnology manipulates matter at the atomic and molecular scale, typically below 100 nanometers. This science enables the design and creation of materials and devices with unique properties and functions.
- Atomic Precision - Nanotechnology controls the arrangement of atoms to build structures with extraordinary accuracy.
- Quantum Effects - Materials at the nanoscale exhibit distinct physical and chemical behaviors due to quantum mechanics.
- Nanoscale Tools - Instruments like scanning tunneling microscopes and atomic force microscopes visualize and manipulate nanoparticles.
Benefits of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale to create innovative materials and devices. It offers groundbreaking solutions across medicine, electronics, and environmental science.
Benefits include targeted drug delivery systems that improve treatment effectiveness and reduce side effects. Nanotechnology also enhances energy storage, leading to more efficient batteries and renewable energy technologies.
Nanotechnology in Medicine
Nanotechnology in medicine revolutionizes diagnosis and treatment by manipulating materials at the molecular and atomic levels. This technology enables targeted drug delivery systems, improving therapeutic outcomes and minimizing side effects.
Nanoparticles can identify and attack cancer cells precisely, reducing damage to healthy tissue. Nanodevices facilitate real-time monitoring of biological processes, enhancing disease detection and management. Innovations like nano-robots and nanocarriers are transforming personalized medicine and regenerative therapies.
Environmental Impact of Nanotechnology
How does nanotechnology affect the environment?
Nanotechnology has the potential to both benefit and challenge environmental sustainability. It enables advanced pollution control and energy-efficient solutions while raising concerns about nanoparticle toxicity and environmental accumulation.
Nanomaterials: Types & Uses
Nanomaterials exhibit unique properties due to their nanoscale dimensions, enabling innovative applications across various industries. These materials are engineered with precise control over size, shape, and surface characteristics to enhance performance and functionality.
- Carbon Nanotubes - Cylindrical carbon structures known for exceptional strength and electrical conductivity used in electronics and composite materials.
- Quantum Dots - Semiconductor nanoparticles that emit specific light wavelengths, utilized in displays, imaging, and solar cells.
- Nanoparticles - Particles less than 100nm applied in drug delivery systems, catalysis, and antimicrobial coatings.
- Nanosheets - Two-dimensional materials like graphene, offering high surface area for sensors and energy storage devices.
- Nanowires - Ultra-thin wires used in nanoscale electronics and photonic devices due to their conductive properties.
Challenges and Risks of Nanotechnology
| Challenges | Risks |
|---|---|
| Controlling nanoparticle behavior at atomic scale | Toxicity to human health from nanoparticle exposure |
| Manufacturing consistency and scalability | Environmental contamination and bioaccumulation |
| High cost of research and development | Unpredictable interactions with biological systems |
| Regulatory and ethical uncertainties | Resistance development leading to antimicrobial failure |
| Public perception and acceptance | Potential long-term ecological impacts |
Future Trends in Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is rapidly evolving, with future trends focusing on advancements in nanomedicine, energy storage, and environmental applications. Innovations in nanoscale materials are driving breakthroughs in electronics and sustainable technologies.
The integration of nanotechnology with artificial intelligence and biotechnology promises personalized healthcare and smarter devices. Researchers are exploring nanorobots and quantum dots to revolutionize diagnostics and treatment methods.
