Erosion shapes landscapes by wearing away soil and rock through natural forces like wind, water, and ice. This process influences ecosystem health, agricultural productivity, and infrastructure stability. Understanding erosion helps in developing effective prevention and mitigation strategies.
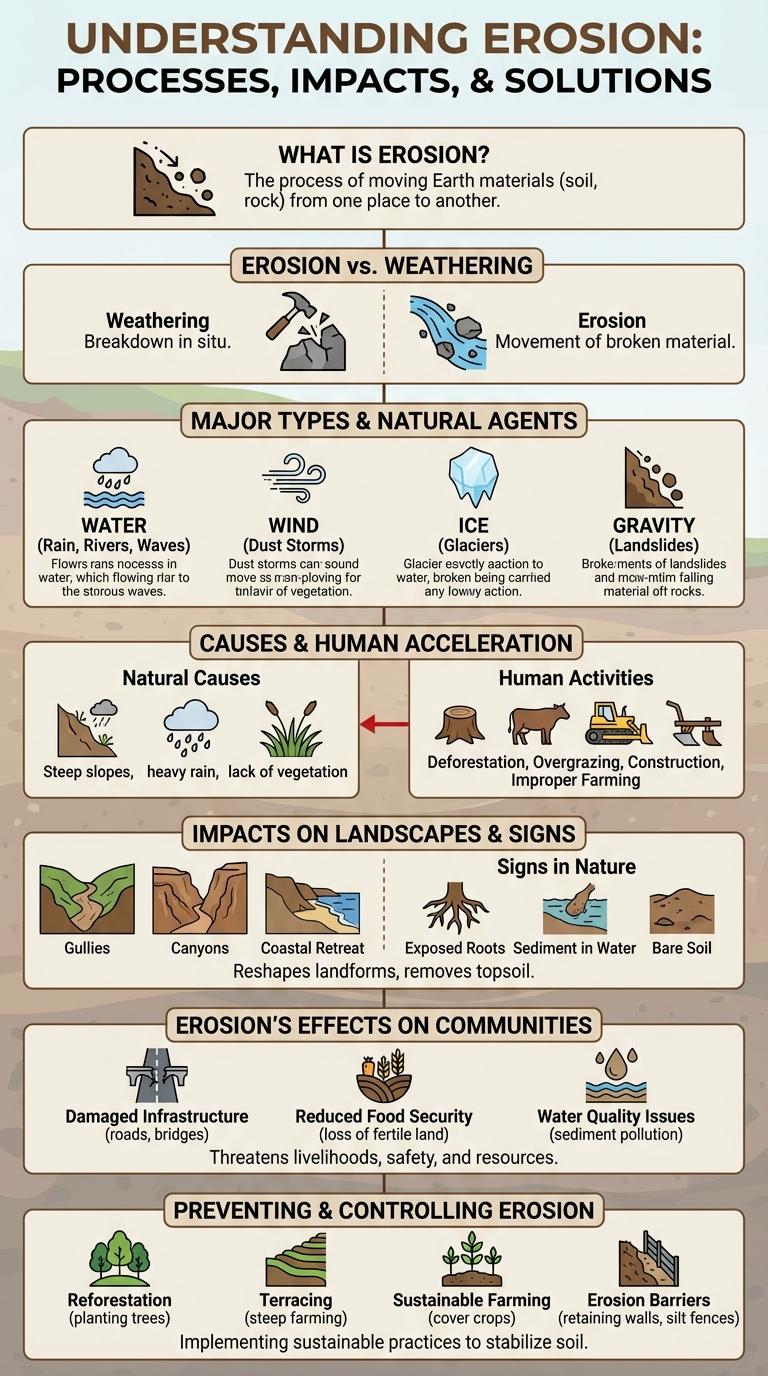
What is Erosion?
Erosion is the natural process of wearing away soil, rock, or land by wind, water, or ice. It shapes landscapes and can lead to significant environmental changes over time.
- Cause - Erosion occurs due to forces like rain, river flow, wind, glaciers, and ocean waves that move materials from one place to another.
- Effects - It results in the loss of fertile topsoil, alters habitats, and can create features like valleys, cliffs, and sand dunes.
- Types - Common types of erosion include water erosion, wind erosion, glacial erosion, and coastal erosion.
Major Types of Erosion
What are the major types of erosion that shape our landscape? Erosion is the natural process where soil and rock are worn away by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Understanding the main types helps in managing and preventing land degradation effectively.
| Type of Erosion | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Erosion | Occurs when rainfall or flowing water removes soil, often causing gullies and riverbank damage. |
| Wind Erosion | Involves the movement of soil particles by strong winds, common in dry, arid environments. |
| Glacial Erosion | Happens as glaciers move, scraping and grinding rocks beneath, shaping valleys and landscapes. |
| Gravity Erosion (Mass Wasting) | Soil and rock move downhill due to gravity, leading to landslides and rockfalls. |
Causes of Erosion
Erosion is the natural process of soil and rock being worn away by environmental factors. Understanding the primary causes of erosion helps in developing effective prevention strategies.
- Water Erosion - Rainfall and surface runoff transport soil particles, gradually wearing down the land.
- Wind Erosion - Strong winds lift and carry loose soil, especially in dry and arid regions.
- Human Activities - Deforestation, agriculture, and construction disturb the soil, increasing vulnerability to erosion.
Identifying these causes is essential for soil conservation and protecting ecosystems from degradation.
Natural Agents of Erosion
Erosion is the process by which natural forces wear away soil, rock, and other surface materials. It shapes landscapes by transporting sediments from one location to another.
Natural agents of erosion include water, wind, ice, and gravity. Water erosion occurs through rainfall, rivers, and ocean waves, carving valleys and coastlines. Wind erosion moves fine particles across dry, arid regions, reshaping dunes and deserts.
Erosion vs. Weathering
| Erosion | Weathering |
|---|---|
| Process of removing and transporting soil or rock particles by natural forces like water, wind, ice, or gravity. | Process of breaking down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces or chemical alteration at the original site. |
| Involves movement of materials from one location to another. | Involves no movement; materials remain in place during breakdown. |
| Examples include river cutting, coastal cliff retreat, and glacial transport. | Examples include freeze-thaw cycles, oxidation, and acid rain effects. |
| Contributes to landscape shaping by transporting sediments. | Prepares materials for erosion by weakening rock structures. |
Impacts on Landscapes
Erosion significantly shapes landscapes by wearing away soil and rock, leading to altered landforms. This natural process can create valleys, cliffs, and other geological features over time.
Human activities accelerate erosion, causing loss of fertile topsoil and increased sediment in waterways. These changes affect ecosystems, agriculture, and infrastructure stability.
Human Activities Accelerating Erosion
Erosion is a natural process where soil, rock, and other surface materials are worn away and transported by natural forces. Human activities significantly accelerate erosion, leading to loss of fertile land and increased sediment in waterways.
Human activities such as deforestation, agriculture, and construction disturb the land's surface and increase erosion rates.
- Deforestation - Removal of trees reduces root systems that stabilize soil, making it more vulnerable to erosion by wind and water.
- Agriculture - Plowing and overgrazing expose soil to erosion by disrupting the protective vegetation cover.
- Construction and Urban Development - Land clearing and soil disturbance increase runoff and sediment transport into nearby water bodies.
Signs of Erosion in Nature
Erosion is the gradual wearing away of soil, rocks, and land caused by natural forces such as water, wind, and ice. Common signs of erosion include exposed tree roots, which indicate the soil around them has been washed away. Other indicators are rills and gullies forming on slopes and sediment accumulation in nearby rivers or streams.
Preventing and Controlling Erosion
Erosion control is essential to protect soil health, prevent property damage, and maintain water quality. Effective methods include planting vegetation, using erosion control blankets, and implementing terracing on slopes. Regular maintenance and monitoring of these measures help ensure long-term stability and prevent soil loss.
