A circle is a fundamental geometric shape characterized by a set of points equidistant from a central point, known as the radius. Key properties include diameter, circumference, and area, which can be calculated using specific mathematical formulas. Understanding these elements is essential for applications in design, architecture, and various scientific fields.
Understanding the Circle: A Basic Overview
The circle is a fundamental shape in geometry defined as the set of all points equidistant from a central point called the center. Key properties include the radius, diameter, circumference, and area, each essential for calculations and applications. Understanding these elements provides a foundation for exploring more complex mathematical concepts involving circles.
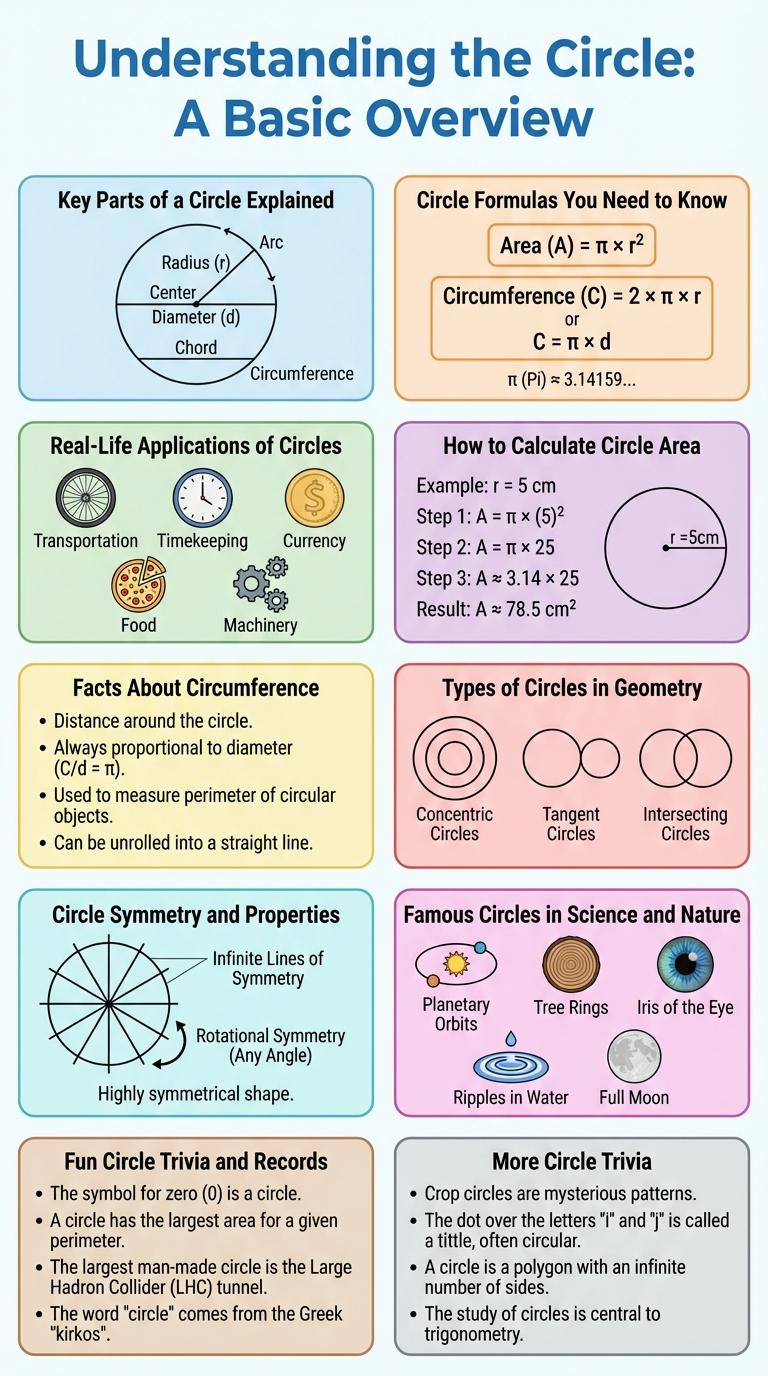
Key Parts of a Circle Explained
A circle is a fundamental geometric shape consisting of all points equidistant from a central point. Understanding its key parts helps in grasping circle-related concepts and calculations.
- Center - The fixed point equidistant from all points on the circle's edge.
- Radius - The line segment from the center to any point on the circle's circumference.
- Diameter - The longest chord passing through the center, equal to twice the radius.
- Circumference - The total distance around the circle's edge.
- Chord - A line segment connecting any two points on the circle's circumference without passing through the center.
Knowing these key parts allows for accurate measurement and application in geometry, engineering, and design.
Circle Formulas You Need to Know
Circles are fundamental geometric shapes defined by all points equidistant from a center point. Key formulas help calculate important properties like circumference, area, and radius.
The circumference of a circle is found using the formula C = 2pr, where r is the radius. The area inside the circle is calculated by A = pr2. The diameter, which spans through the center, is twice the radius, expressed as d = 2r.
Real-Life Applications of Circles
Circles play a crucial role in numerous real-life applications, ranging from engineering to everyday objects. Their unique geometric properties enable efficient design and functionality across various fields.
In transportation, wheels and gears rely on circular shapes for smooth motion and durability. Architecture incorporates circles in elements like domes and arches to distribute weight evenly and enhance structural stability.
How to Calculate Circle Area
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify Radius (r) | Measure the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary. |
| Use Formula | Apply the formula Area = p x r2, where p (Pi) is approximately 3.1416. |
| Calculate Square of Radius | Multiply the radius by itself (r x r). |
| Multiply by Pi | Multiply the squared radius by p to find the area. |
| Result Interpretation | The result is the area of the circle in square units (e.g., cm2, m2). |
Facts About Circumference
The circumference of a circle is the distance around its edge, calculated by the formula C = 2pr, where r is the radius. The value of p (pi) is approximately 3.14159, an irrational number with infinite decimals. Understanding circumference is essential in fields such as engineering, architecture, and astronomy for precise measurements.
Types of Circles in Geometry
Circles in geometry are defined by their unique properties and classifications based on radius, diameter, and points relative to the circumference. Understanding different types of circles helps in solving complex geometric problems and real-world applications.
Concentric circles share the same center but have different radii, creating multiple rings with no intersections. Tangent circles touch each other at exactly one point, either externally or internally, without overlapping.
Circle Symmetry and Properties
The circle is a perfectly symmetrical shape with unique geometric properties. Understanding these properties helps in various mathematical and engineering applications.
Circle symmetry is defined by its infinite lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of 360 degrees.
- Infinite Lines of Symmetry - Every diameter divides the circle into two identical halves, representing infinite lines of symmetry.
- Rotational Symmetry - A circle looks the same after any degree of rotation around its center point.
- Constant Radius - Every point on the circle is equidistant from the center, known as the radius.
- Circumference - The total distance around the circle is calculated as 2p times the radius.
- Area - The space enclosed by the circle is determined by p times the radius squared (pr2).
Famous Circles in Science and Nature
Circles play a crucial role in both science and nature, symbolizing perfection and infinity. Their unique properties appear in various natural phenomena and scientific concepts.
- Pi (p) - An irrational number representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, fundamental in mathematics and physics.
- Atomic Orbitals - Electrons often occupy spherical or circular orbits around a nucleus, essential to atomic structure.
- Planetary Orbits - Many planets follow nearly circular paths around stars due to gravitational forces.
- Tree Rings - Circular growth rings in trees reveal age and climatic conditions throughout history.
- Cell Membranes - The circular shape of many cells optimizes surface area for nutrient absorption and communication.
