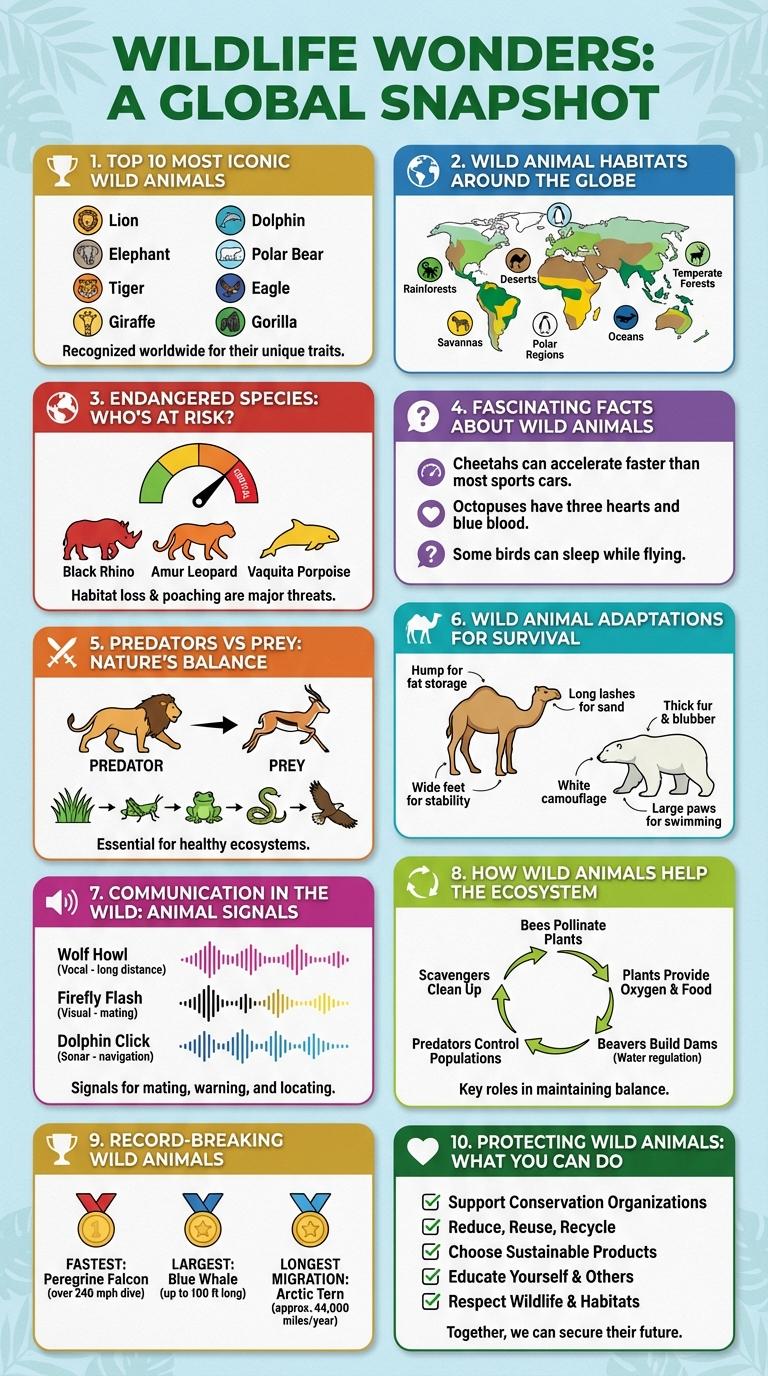
Wild animals play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance and biodiversity. Understanding their behaviors, habitats, and threats enhances conservation efforts worldwide. Infographics provide a clear and engaging way to visualize key facts about these fascinating creatures.
Top 10 Most Iconic Wild Animals
| Animal | Key Facts |
|---|---|
| Lion | Symbol of strength and courage; found primarily in African savannas. |
| Tiger | Largest cat species; known for its distinctive orange coat with black stripes. |
| Elephant | Largest land mammal; recognized for intelligence and strong social bonds. |
| Giraffe | World's tallest mammal; characterized by long neck and spotted coat pattern. |
| Panda | Native to China; famous for its distinctive black and white fur and bamboo diet. |
| Wolf | Known for pack behavior; apex predator in many forest ecosystems. |
| Polar Bear | Largest bear species; adapted to Arctic cold with thick fur and fat layer. |
| Kangaroo | Iconic to Australia; notable for powerful hind legs and unique hopping movement. |
| Rhinoceros | Heavyset herbivore with prominent horn(s); facing threats from poaching. |
| Eagle | Symbolic bird of prey; known for exceptional vision and soaring flight. |
Wild Animal Habitats Around the Globe
Where do wild animals primarily live around the world? Wild animal habitats span diverse ecosystems including forests, savannas, deserts, wetlands, and oceans. Each habitat supports unique species adapted to its environmental conditions.
Endangered Species: Who's at Risk?
Wild animals face numerous threats that push many species toward extinction. Understanding which animals are most at risk helps guide conservation efforts effectively.
- Tigers - Habitat loss and poaching have drastically reduced tiger populations worldwide.
- Asian Elephants - Human encroachment and illegal ivory trade endanger these majestic creatures.
- Amur Leopards - Fewer than 100 individuals remain due to habitat fragmentation and poaching.
Conserving endangered species requires global awareness and immediate action to preserve biodiversity.
Fascinating Facts About Wild Animals
Wild animals play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity. Many species possess unique adaptations, such as the cheetah's incredible speed and the elephant's complex social structures. Understanding these fascinating traits helps promote wildlife conservation efforts worldwide.
Predators vs Prey: Nature's Balance
Wild animals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Predators regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and ensuring biodiversity.
Prey species provide essential food sources for predators, supporting their survival and reproductive success. This dynamic interaction sustains natural habitats and promotes ecological stability.
Wild Animal Adaptations for Survival
Wild animals develop unique adaptations to survive in diverse environments. These adaptations enhance their ability to find food, avoid predators, and reproduce successfully.
- Camouflage - Wild animals use coloration that blends with their surroundings to evade predators and increase hunting success.
- Physical Adaptations - Features like sharp claws, strong limbs, and thick fur help animals navigate their habitats and protect themselves.
- Behavioral Changes - Migration, nocturnal activity, and hibernation are behavioral strategies animals use to optimize survival.
Communication in the Wild: Animal Signals
Wild animals use a variety of signals to communicate essential information for survival. These signals include visual, auditory, and chemical forms that convey messages like warnings, mating readiness, and territory boundaries.
Understanding animal communication helps reveal the complexity of wildlife behavior and ecosystem dynamics.
- Visual Signals - Animals use body postures, colors, and movements like the peacock's tail display to attract mates or warn predators.
- Auditory Signals - Sounds such as bird songs, wolf howls, and elephant rumbles serve to locate others and mark territory.
- Chemical Signals - Many species release pheromones to communicate reproductive status or establish dominance within a group.
How Wild Animals Help the Ecosystem
Wild animals play a crucial role in maintaining balanced ecosystems by regulating populations and promoting biodiversity. They contribute to seed dispersal, pollination, and nutrient cycling, which supports plant growth and soil health.
Predators control herbivore numbers, preventing overgrazing and preserving vegetation. Scavengers accelerate decomposition, recycling nutrients back into the environment for sustained ecosystem productivity.
Record-Breaking Wild Animals
Wild animals exhibit extraordinary traits that set records in the natural world. These record-breaking animals showcase remarkable adaptations and abilities.
The cheetah is the fastest land animal, reaching speeds up to 70 mph. The blue whale, the largest animal ever, can weigh over 200 tons and stretch 100 feet long. The harpy eagle has the most powerful talons, enabling it to hunt prey much larger than itself.
