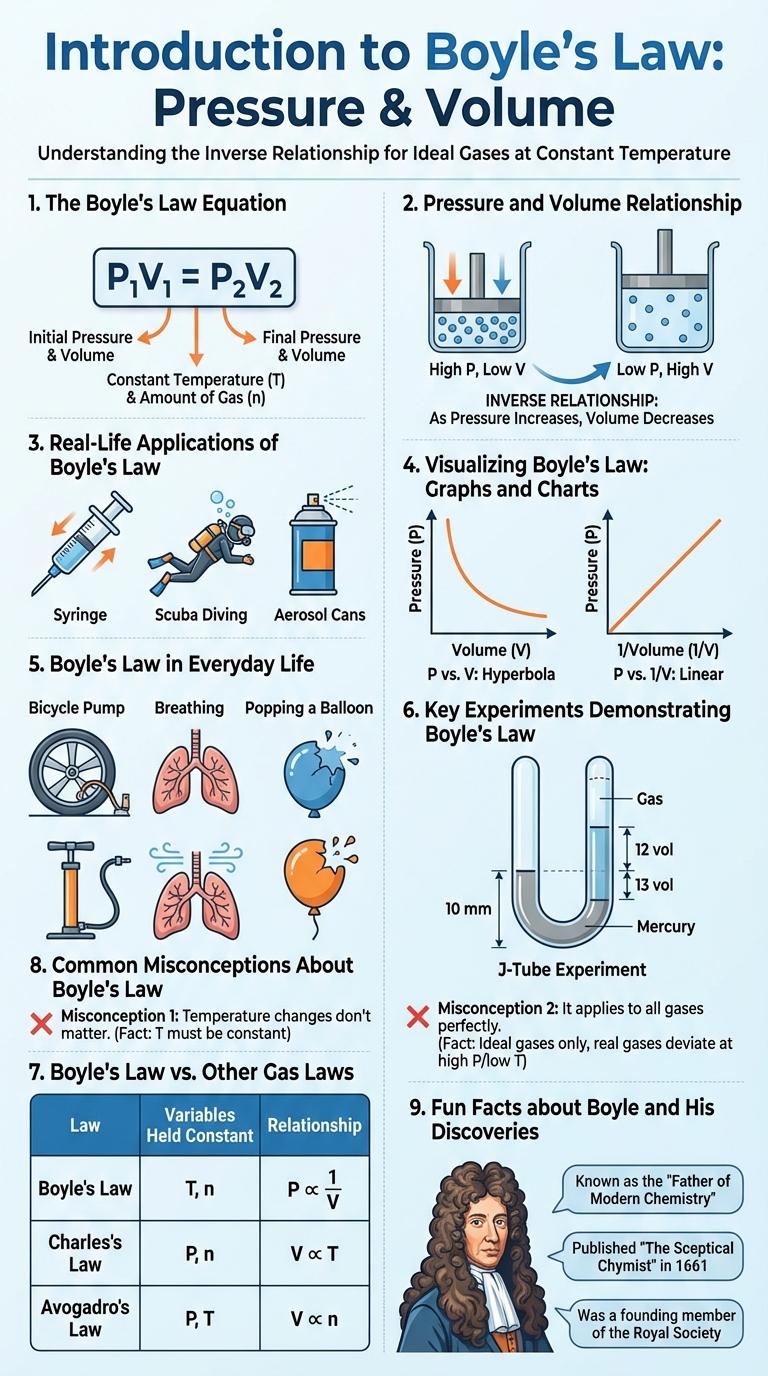
Boyle's Law explains the inverse relationship between pressure and volume of a gas at a constant temperature. When the volume decreases, the pressure increases, and vice versa, illustrating fundamental gas behavior. This infographic visually represents these concepts with clear examples and data to enhance understanding.
Introduction to Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It is a fundamental principle in gas behavior and thermodynamics.
- Pressure and Volume Relationship - As pressure increases, the volume of a given gas decreases proportionally.
- Constant Temperature - Boyle's Law applies only when the temperature remains constant during the process.
- Mathematical Expression - The law is represented as P x V = k, where P is pressure, V is volume, and k is a constant.
This principle helps explain various natural phenomena and is essential in fields like chemistry, physics, and engineering.
The Boyle's Law Equation
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. The Boyle's Law equation mathematically expresses this relationship.
The equation is written as P1V1 = P2V2, where P represents pressure and V represents volume.
- Pressure and Volume Inverse Proportionality - As pressure increases, volume decreases proportionally, keeping the product constant.
- Ideal Gas Behavior - The equation assumes constant temperature and is applicable to ideal gases under these conditions.
- Practical Applications - Boyle's Law equation is used in fields such as scuba diving and respiratory therapy to understand gas behavior under pressure changes.
Pressure and Volume Relationship
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. When volume decreases, pressure increases proportionally, and vice versa. This principle is fundamental in understanding gas behaviors in sealed containers and various physical processes.
Real-Life Applications of Boyle's Law
How does Boyle's Law apply in everyday life? Boyle's Law explains the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. Many real-life technologies and natural phenomena rely on this principle to function efficiently.
In what ways is Boyle's Law used in scuba diving? Scuba divers monitor air pressure and volume in their tanks carefully to avoid lung over-expansion injuries. The changing pressure underwater affects the air volume, which Boyle's Law helps predict and manage.
Why is Boyle's Law important in breathing? Human lungs operate based on the principles of Boyle's Law, where the diaphragm contracts to increase lung volume and decrease pressure, allowing air to flow in. When the diaphragm relaxes, lung volume decreases, increasing pressure and pushing air out.
How does Boyle's Law influence syringes? Syringes use the law to draw in and expel fluids; pulling the plunger increases volume inside the barrel, decreasing pressure and drawing fluid in. Pushing the plunger reverses the process, increasing pressure and forcing fluid out.
Where else is Boyle's Law evident in daily devices? In automotive engines, Boyle's Law helps understand how air-fuel mixtures compress and expand in cylinders. This relationship optimizes combustion efficiency, contributing to better engine performance.
Visualizing Boyle's Law: Graphs and Charts
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Boyle's Law Definition | Describes the inverse relationship between pressure and volume of a gas, when temperature is constant. Mathematically expressed as P x V = k. |
| Graph Type | Pressure vs. Volume Curve (Hyperbola) |
| Graph Characteristics | The curve shows pressure decreasing as volume increases, illustrating an inverse proportionality between the two variables. |
| Chart Example | A plot with Pressure (P) on the Y-axis and Volume (V) on the X-axis; the curve approaches both axes but never touches them, confirming that P x V remains constant. |
| Practical Applications | Used in medical fields (breathing mechanisms), engineering (gas compression), and physics education to demonstrate fundamental gas behavior. |
Boyle's Law in Everyday Life
Boyle's Law explains the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas, stating that pressure increases as volume decreases when temperature is constant. In everyday life, this principle is seen in breathing, where lung volume changes cause air pressure variations to draw air in and out. Another example is a syringe, where pulling the plunger increases volume and decreases pressure, allowing fluid to be drawn into the tube.
Key Experiments Demonstrating Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It states that when the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases proportionally, and vice versa.
Robert Boyle conducted several experiments using a J-shaped tube partially filled with mercury to demonstrate this relationship. By adding mercury, he varied the pressure on the trapped air and observed changes in its volume. These key experiments provided clear quantitative evidence supporting the law that pressure and volume are inversely proportional.
Boyle's Law vs. Other Gas Laws
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature, stating that as pressure increases, volume decreases proportionally. This fundamental principle applies primarily to ideal gases under isothermal conditions.
Other gas laws, such as Charles's Law and Gay-Lussac's Law, focus on how volume or pressure changes with temperature, rather than pressure-volume interactions. Combining these individual laws forms the Ideal Gas Law, which integrates temperature, pressure, and volume into one equation for general gas behavior.
Common Misconceptions About Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law illustrates the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. Misunderstandings about this principle often lead to incorrect applications in scientific contexts.
Common misconceptions about Boyle's Law include errors about gas properties and system conditions.
- Pressure Always Increases with Decreasing Volume - This ignores the requirement that temperature remains constant for Boyle's Law to apply.
- Boyle's Law Applies to All Gases Equally - Real gases deviate from ideal behavior under high pressure or low temperature, affecting accuracy.
- Volume Changes Cause Pressure Changes Instantly - Time lag can occur in practical systems, so changes are not always immediate.
