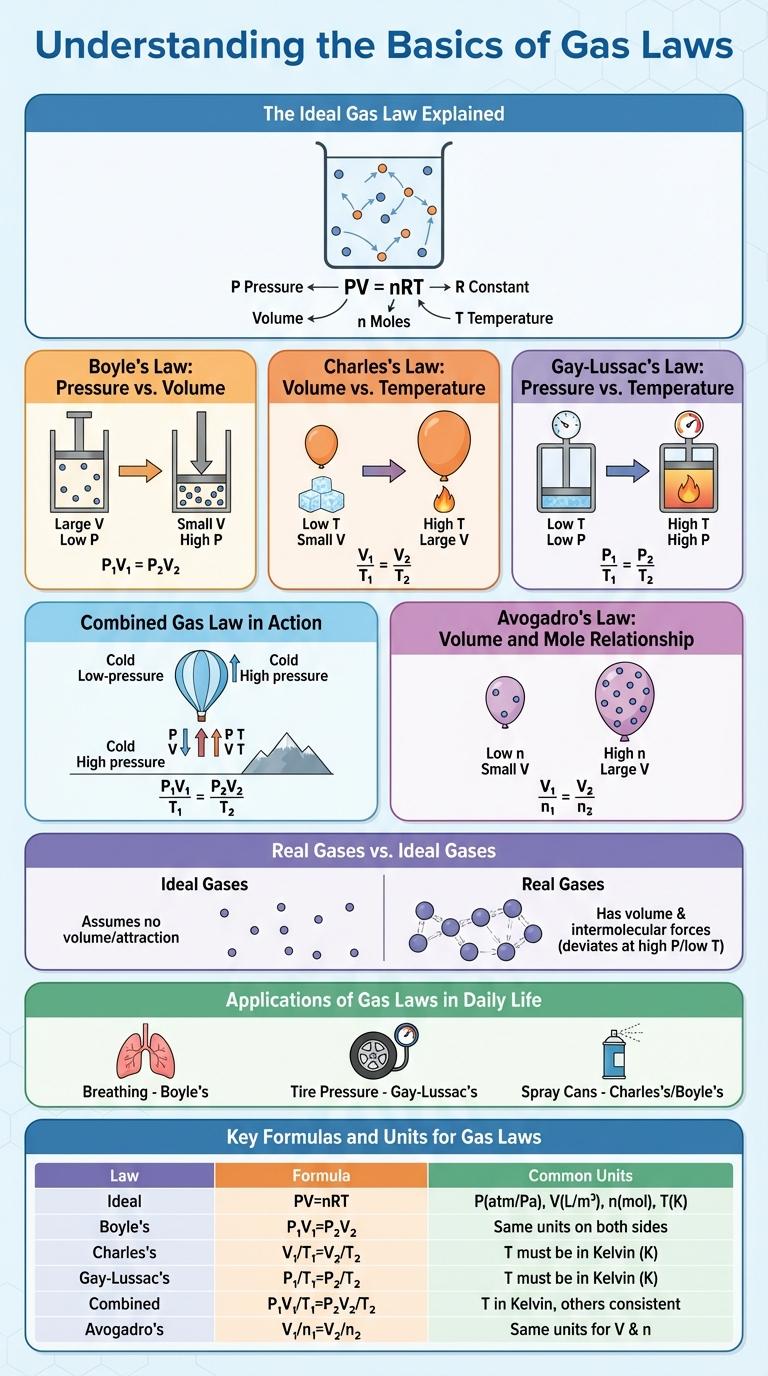
Gas laws describe the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature of gases, revealing how gases behave under varying conditions. Understanding these principles is essential for applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering. This infographic visually simplifies complex gas law concepts, making them easier to grasp and apply.
Understanding the Basics of Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases in relation to temperature, pressure, and volume. Understanding these principles is essential for fields like chemistry, physics, and engineering.
- Boyle's Law - Pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional at constant temperature.
- Charles's Law - Volume of a gas increases linearly with temperature at constant pressure.
- Gay-Lussac's Law - Pressure of a gas rises with temperature when volume remains constant.
These fundamental laws provide insight into gas dynamics and are applied in many scientific and industrial processes.
The Ideal Gas Law Explained
The Ideal Gas Law combines several fundamental gas laws into one equation: PV = nRT. It describes the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), amount of gas (n), gas constant (R), and temperature (T) in an ideal gas.
This equation helps predict how gases behave under various conditions. Pressure and volume vary inversely when temperature and moles of gas remain constant. Increasing temperature raises gas pressure if volume and moles stay unchanged.
Boyle's Law: Pressure vs. Volume
Boyle's Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when temperature is constant. This means as volume decreases, pressure increases, and vice versa.
The mathematical expression is P x V = k, where P is pressure, V is volume, and k is a constant. This law is fundamental to understanding gas behavior in closed systems.
Charles's Law: Volume vs. Temperature
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is constant. This relationship means that as temperature increases, the volume of the gas expands.
The formula for Charles's Law is V1/T1 = V2/T2, where V represents volume and T represents temperature in Kelvin. This law is essential in understanding gas behavior in various scientific and engineering applications.
Gay-Lussac's Law: Pressure vs. Temperature
Gay-Lussac's Law states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature when volume is held constant. As the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure increases, provided the volume remains unchanged. This principle is commonly represented by the formula P/T = constant, where P is pressure and T is temperature in Kelvin.
Combined Gas Law in Action
The Combined Gas Law explains the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas when the amount of gas is constant. It combines Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws to predict changes in gas behavior under varying conditions.
This law is essential for understanding real-world gas reactions involving simultaneous changes in pressure, volume, and temperature.
- Pressure and Volume Relationship - When temperature is constant, pressure and volume are inversely proportional.
- Volume and Temperature Relationship - When pressure is constant, volume is directly proportional to temperature in kelvins.
- Pressure and Temperature Relationship - When volume is constant, pressure increases with temperature.
Avogadro's Law: Volume and Mole Relationship
Avogadro's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles when temperature and pressure are constant. This means that equal volumes of gases contain the same number of molecules. The relationship is mathematically expressed as V n, where V is volume and n is moles.
Real Gases vs. Ideal Gases
| Aspect | Real Gases |
|---|---|
| Intermolecular Forces | Experience attractive and repulsive forces between molecules |
| Molecular Volume | Molecules occupy a finite volume |
| Behavior Under Pressure | Deviates from ideal gas law at high pressure |
| Temperature Impact | Deviates at low temperatures, close to condensation point |
| Equation of State | Better described by Van der Waals equation or other real gas models |
| Aspect | Ideal Gases |
|---|---|
| Intermolecular Forces | No forces; molecules neither attract nor repel |
| Molecular Volume | Assumed negligible, treated as point particles |
| Behavior Under Pressure | Obeys PV = nRT under all conditions |
| Temperature Impact | Valid across wide temperature ranges assuming ideal conditions |
| Equation of State | Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT |
Applications of Gas Laws in Daily Life
How do gas laws apply to everyday activities? Gas laws explain the behavior of gases under different conditions of temperature, pressure, and volume. These principles help us understand many daily phenomena involving air and gases.
Where is Boyle's Law used in daily life? Boyle's Law, which relates pressure and volume, is seen when pumping air into bicycle tires. Compressing the air increases pressure while decreasing volume inside the tire.
How does Charles's Law affect hot air balloons? Charles's Law states that gas volume increases with temperature at constant pressure. Heating the air inside the balloon causes it to expand, making the balloon rise.
What role does Gay-Lussac's Law play in cooking? Gay-Lussac's Law relates pressure and temperature of a gas at constant volume, important in pressure cookers. As temperature rises, pressure increases, cooking food faster.
Where do we observe the combined gas law in daily life? The combined gas law combines Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws, explaining how gases behave with changing pressure, volume, and temperature. It helps in understanding how car tires behave during temperature changes.
